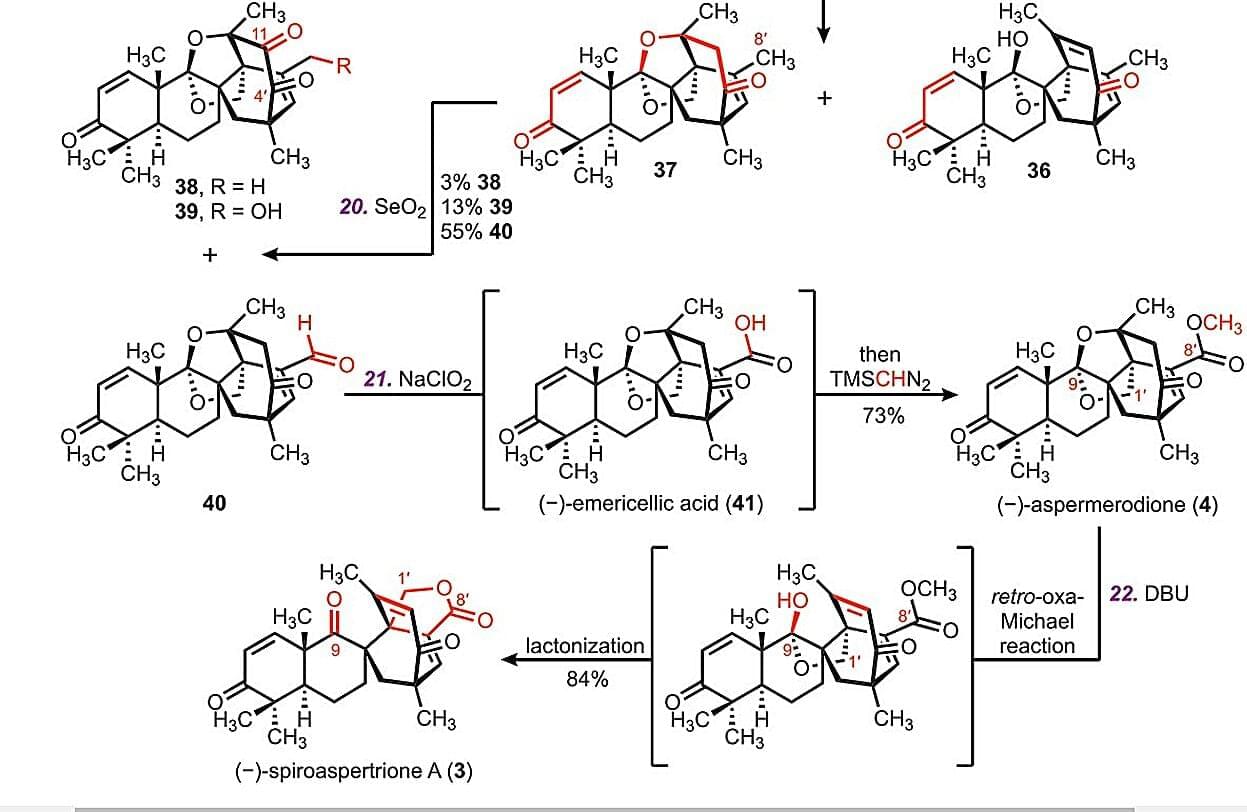
Spiroaspertrione A is a complex polycyclic compound naturally produced by the fungus Aspergillus sp. TJ23. First isolated in 2017, it quickly drew scientific attention for its promising ability to combat drug-resistant bacteria and restore their sensitivity to existing antibiotics.
Scientists have now found a way to carry out the total synthesis of the molecule in 16 steps, starting from a chiral pool building block called (+)-enoxolone that costs less than one euro per gram. The synthesis technique is presented in Science.
Staphylococcus aureus (staph) is a type of bacteria that quietly lives on our skin and in our noses. It usually does no harm, but when it turns invasive, it triggers dangerous infections like sepsis, pneumonia, and many hospital-acquired infections. What makes it truly alarming is its growing resistance to antibiotics, which can turn treatable infections into deadly threats.