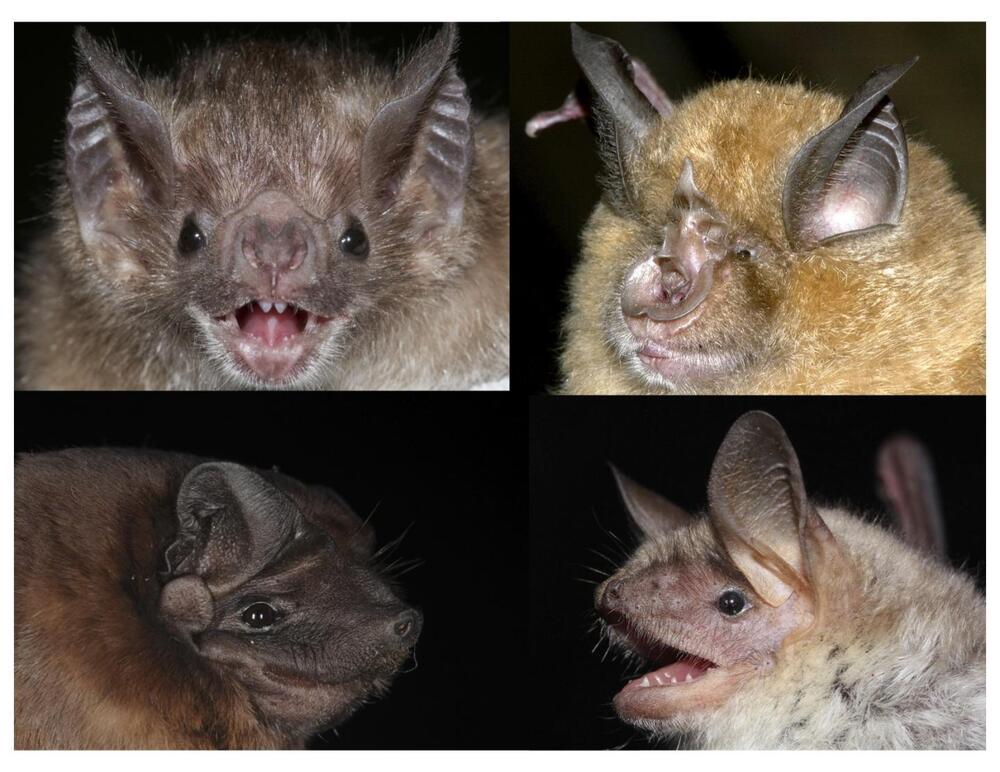
A new study led by University of Maryland and UCLA researchers found that DNA from tissue samples can be used to accurately predict the age of bats in the wild. The study also showed age-related changes to the DNA of long-lived species are different from those in short-lived species, especially in regions of the genome near genes associated with cancer and immunity. This work provides new insight into causes of age-related declines.
This is the first research paper to show that animals in the wild can be accurately aged using an epigenetic clock, which predicts age based on specific changes to DNA. This work provides a new tool for biologists studying animals in the wild. In addition, the results provide insight into possible mechanisms behind the exceptional longevity of many bat species. The study appears in the March 12, 2021, issue of the journal Nature Communications.
“We hoped that these epigenetic changes would be predictive of age,” said Gerald Wilkinson, a professor of biology at UMD and co-lead author of the paper. “But now we have the data to show that instead of having to follow animals over their lifetime to be sure of their age, you can just go out and take a tiny sample of an individual in the wild and be able to know its age, which allows us to ask all kinds of questions we couldn’t before.”