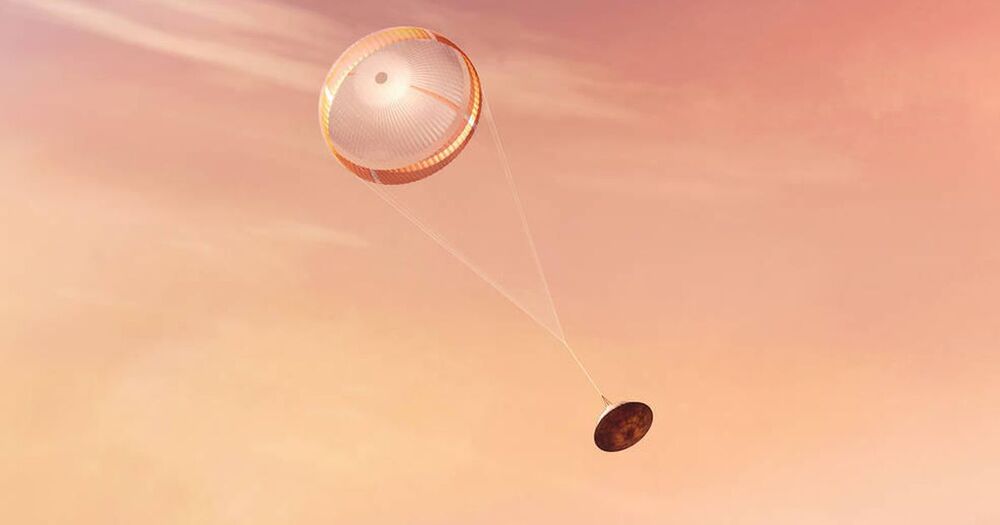
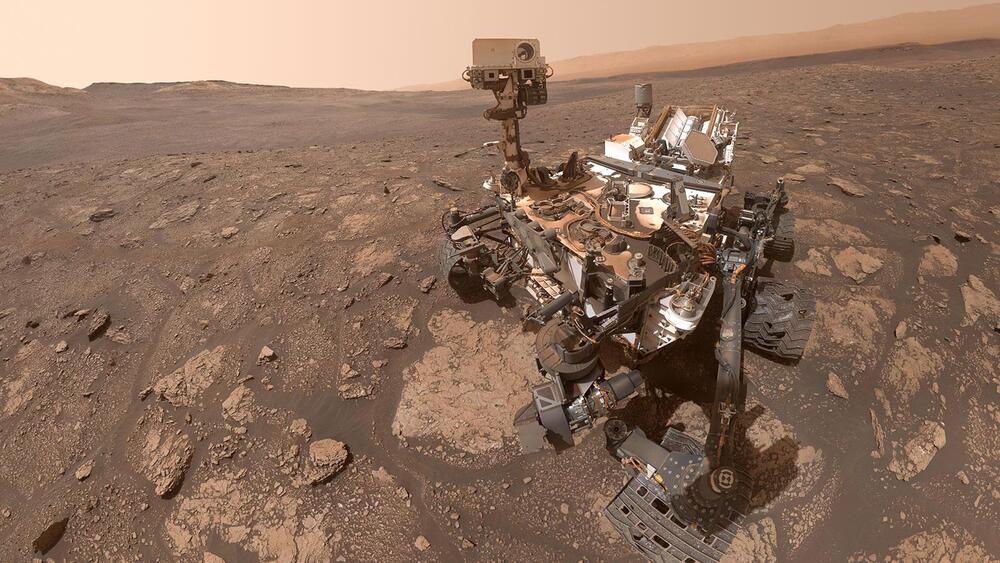
The next robot on Mars will touch down in a few weeks, and the views will be truly otherworldly.




Before the Apollo era, the moon was thought to be dry as a desert due to the extreme temperatures and harshness of the space environment. Many studies have since discovered lunar water: ice in shadowed polar craters, water bound in volcanic rocks, and unexpected rusty iron deposits in the lunar soil. Despite these findings, there is still no true confirmation of the extent or origin of lunar surface water.

China launched its first blockchain-based scientific data network on Wednesday to facilitate open and secured sharing of research information, which can help track and optimize the publishing process, as well as curb academic fraud, according to the Computer Network Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.

Law enforcement agencies dismantled the infrastructure of Emotet, a notorious email-based Windows malware behind several botnet-driven spam campaigns.
Researchers detail docker container escape bug affecting microsoft azure functions.


An international team of researchers has used modeling techniques borrowed from chemistry applications to create a new kind of city simulator. In their paper published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society A, the group describes using their models to create simulations of of COVID-19 spread for two real-world cities: Birmingham England and Bogota Columbia.
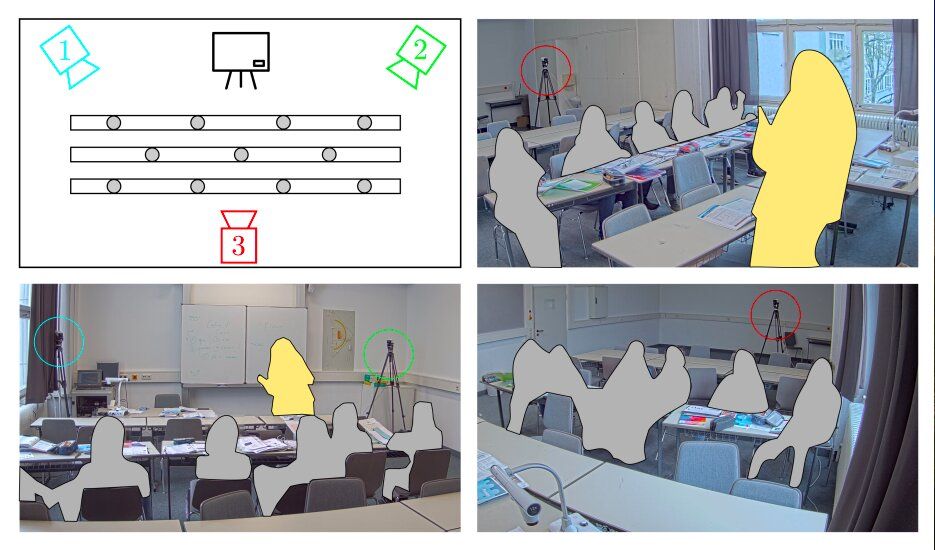
Past research has identified student engagement, or the extent to which students participate and are involved in classroom activities, as a crucial factor determining both the quality of education programs and the academic performance of individual students. As a result, many educators worldwide are actively trying to devise courses that maximize student engagement.