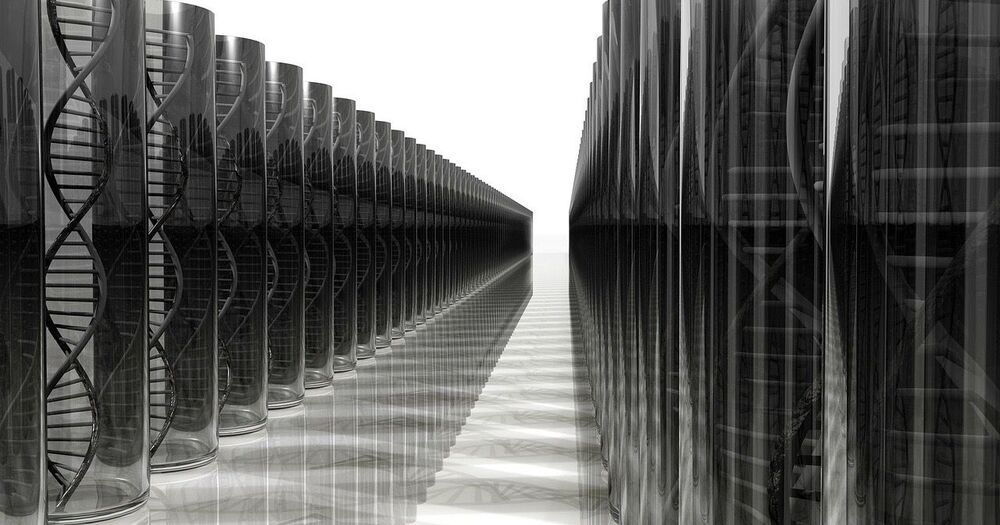
Intelligent Design
DNA is already known to be an ideal storage medium. Why not use cells to do the hard work?
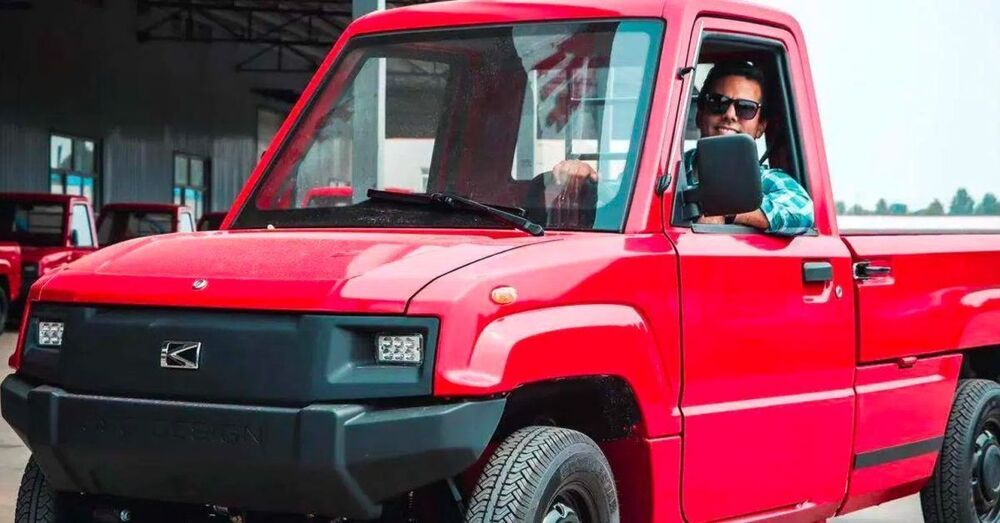


Alibaba is one of the best places around to find the coolest and sometimes weirdest electric vehicles in the world. As part of a new series known as Awesomely weird Alibaba electric vehicle of the week, we’re taking a look at some of our favorites.
This week’s feature is a small-yet-mighty electric pickup truck designed for utility and off-road usage, though it may even be street legal as an NEV in the US.
If the proportions look at bit odd on this electric pickup truck, that’s because they are.


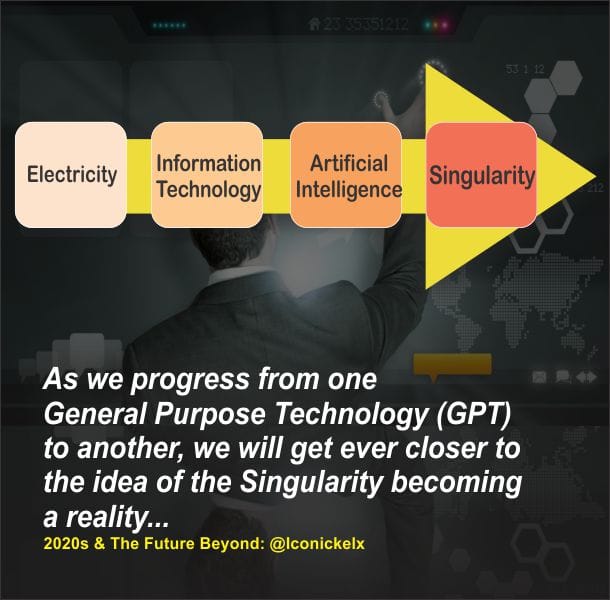
From self-driving cars, to the many automated production processes we will end up creating; we will allow AI drive us into the next era of human civilization.
We will allow the creation to create, and according to futurist and technologists’ world over, there is only one likely path where this road will lead to — the Singularity (the point where computer intelligence surpasses human intelligence).
- The Above is an excerpt from the book, 2020s & The Future Beyond.
Will be happy to hear the thoughts of group members.
#Iconickelx.
#AI #Singularity #Future
This trend needs to stop.
I like this idea. I don’t want AI to be a black box, I want to know what’s happening and how its doing it.
The field of artificial intelligence has created computers that can drive cars, synthesize chemical compounds, fold proteins, and detect high-energy particles at a superhuman level.
However, these AI algorithms cannot explain the thought processes behind their decisions. A computer that masters protein folding and also tells researchers more about the rules of biology is much more useful than a computer that folds proteins without explanation.
Therefore, AI researchers like me are now turning our efforts toward developing AI algorithms that can explain themselves in a manner that humans can understand. If we can do this, I believe that AI will be able to uncover and teach people new facts about the world that have not yet been discovered, leading to new innovations.
It is true. From its effect on biomarkers such as heat shock proteins and Fox 03, through to real world impacts on cardiovascular health, to improving mood, helping you live longer healthier and reducing your chance of dying before your time. I think we all know saunas are really great for you, but this will give you all the scientific reasons why… Taking it easy and relaxing for half an hour… Is not just wasting your time… Changes today will make tomorrow better. #saunas
I am going to give you the best reasons in the world to sit back and take it easy in a nice warm environment, and to just forget the troubles of the world.
Maybe play some music, or a podcast, or listen to a book, or just meditate, just relax and take it easy.
It is for your own health after all!!
How about clicking here and watching the video I did on good and bad stress.
The science in the video.
Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons.
We are targeting a two-hour test window that opens at 4 p.m. EST on Sat., Jan. 16, for the hot fire test of the NASA’s Space Launch System rocket core stage at our Stennis Space Center. The hot fire is the eighth and final test of the Green Run series, to ensure the core stage of the SLS is ready to launch NASA’s Artemis Program missions to the Moon. This will be the first time that all four RS-25 engines will be fired at once in order to simulate a launch, generating 1.6 million pounds of thrust.
Live coverage begins at 3:20 p.m. EST. Use the hashtag #AskNASA and your questions might be answered on air 🚀