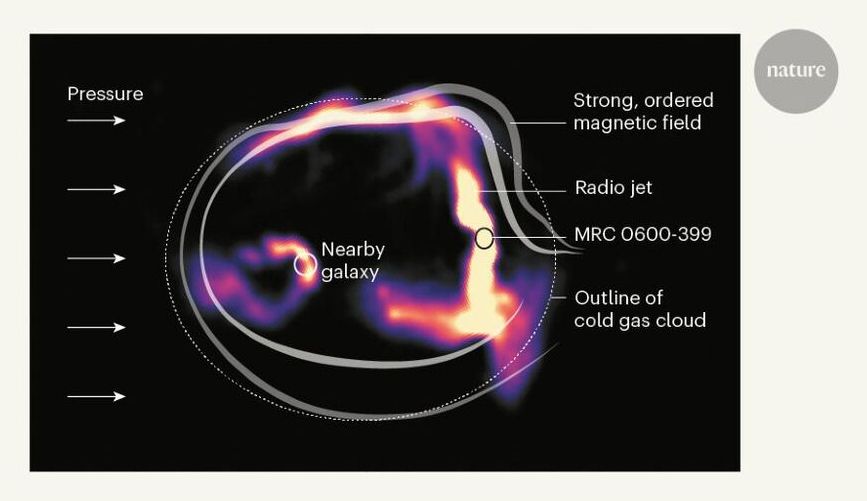
Observational evidence of cosmic magnetic fields in a galaxy cluster.
If the authors’ interpretation is correct, it is a remarkable finding, because it implies that relatively strong, ordered magnetic fields (of a few tens of microgauss in strength) exist in the highly disrupted environments of galaxy clusters such as Abell 3376. For comparison, relatively weak magnetic fields (of a few microgauss) have been detected13 in the gas at the centres of clusters less disrupted than Abell 3376. So far, it has proved extremely challenging to detect and measure magnetic fields in clusters and in the space between galaxies, and the origin of cosmic magnetic fields is still mysterious. Consequently, any observational evidence for such fields in cluster environments is valuable.
However, there is another plausible explanation for the bent jets, referred to as the slingshot model. In this scenario, MRC 0600‑399 and the nearby radio galaxy are falling back towards the centre of Abell 3376 after being ejected from the centre at supersonic speed. The radio jets of MRC 0600‑399 are bent simply by the pressure of gaseous wind acting in the opposite direction to the galaxy’s motion. Although this alternative model can explain the bent jets, it cannot account for the peculiar double-scythe structures, which suggest that the jets are interacting with a layer of strong, ordered magnetic fields. One limitation of the current work is that the magnetic-field strength in the jet-interaction region was not measured directly but was obtained from numerical simulations.
The most exciting aspect of Chibueze and colleagues’ finding is that the observations of radio jets from SMBHs in galactic centres might help to explain poorly understood processes involving gas dynamics in galaxy-cluster formation. Sensitive measurements of the polarization of radio waves could confirm the strength and ordering of the magnetic fields in the magnetic boundary layer. Moreover, the discovery of other examples of strongly distorted radio jets might enable scientists to, for example, measure the total energy injected into jets by SMBHs, understand the role of magnetic fields in jet stabilization and determine the magnetic-field strength of the gas inside clusters. In the upcoming years, the most sensitive radio telescopes ever built will reveal many spectacular processes in the Universe that cannot be seen using optical instruments.