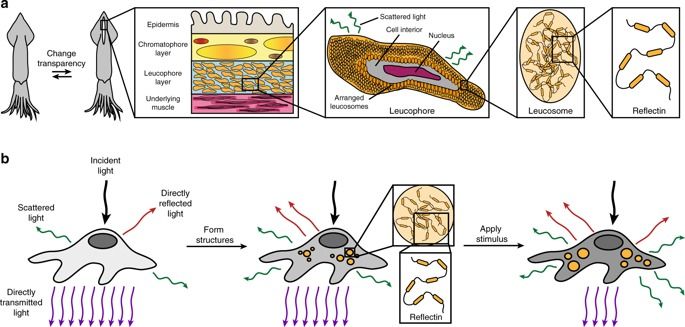
Although many animals have evolved intrinsic transparency for the purpose of concealment, the development of dynamic, that is, controllable and reversible, transparency for living human cells and tissues has remained elusive to date. Here, by drawing inspiration from the structures and functionalities of adaptive cephalopod skin cells, we design and engineer human cells that contain reconfigurable protein-based photonic architectures and, as a result, possess tunable transparency-changing and light-scattering capabilities. Our findings may lead to the development of unique biophotonic tools for applications in materials science and bioengineering and may also facilitate an improved understanding of a wide range of biological systems.
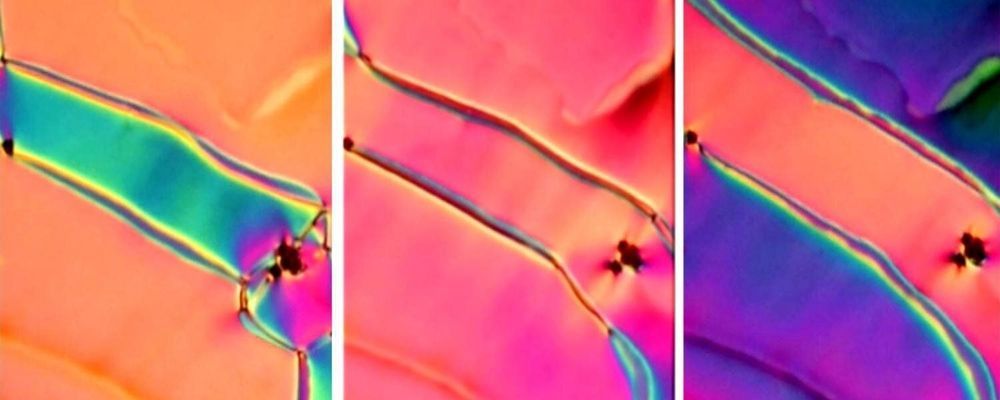
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder’s Soft Materials Research Center (SMRC) have discovered an elusive phase of matter, first proposed more than 100 years ago and sought after ever since.
The team describes the discovery of what scientists call a “ferroelectric nematic” phase of liquid crystal in a study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The discovery opens a door to a new universe of materials, said co-author Matt Glaser, a professor in the Department of Physics.
Nematic liquid crystals have been a hot topic in materials research since the 1970s. These materials exhibit a curious mix of fluid- and solid-like behaviors, which allow them to control light. Engineers have used them extensively to make the liquid crystal displays (LCDs) in many laptops, TVs and cellphones.
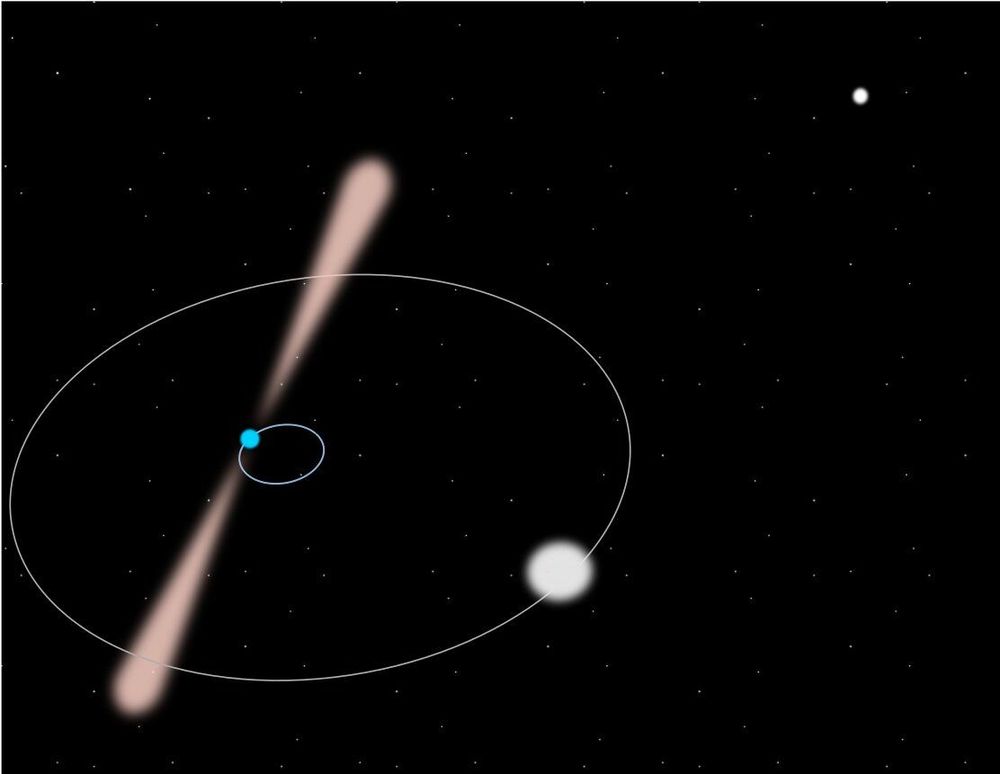
An international collaboration of scientists has recorded the most accurate confirmation to date for one of the cornerstones of Einstein’s theory of general relativity, ‘the universality of free fall.”
The new research shows that the theory holds for strongly self-gravitating objects such as neutron stars. Using a radio telescope, scientists can very accurately observe the signal produced by pulsars, a type of neutron star and test the validity of Einstein’s theory of gravity for these extreme objects. In particular, the team analyzed the signals from a pulsar named “PSR J0337+1715’ recorded by the large radio telescope of Nançay, located in the heart of Sologne (France).
The universality of free fall principle states that two bodies dropped in a gravitational field undergo the very same acceleration independently of their composition. This was first demonstrated by Galileo who famously would have dropped objects of different masses from the top of Pisa’s tower to verify that they both reach the ground simultaneously.
At Imperial College we’ve been comparing psilocybin to conventional antidepressants – and the results are likely to be game-changing, says Robin Carhart-Harris.
(Reuters) — Johnson & Johnson moved up the start of human clinical trials for its experimental vaccine against the highly contagious coronavirus by two months to the second half of July, as the drugmaker rushes to develop a prevention for COVID-19, the company said on Wednesday.
The acceleration should allow J&J to take part in the massive clinical trials program planned by the U.S. government, which aims to have an effective vaccine by year end.
J&J shares rose nearly 2% to $148.69.
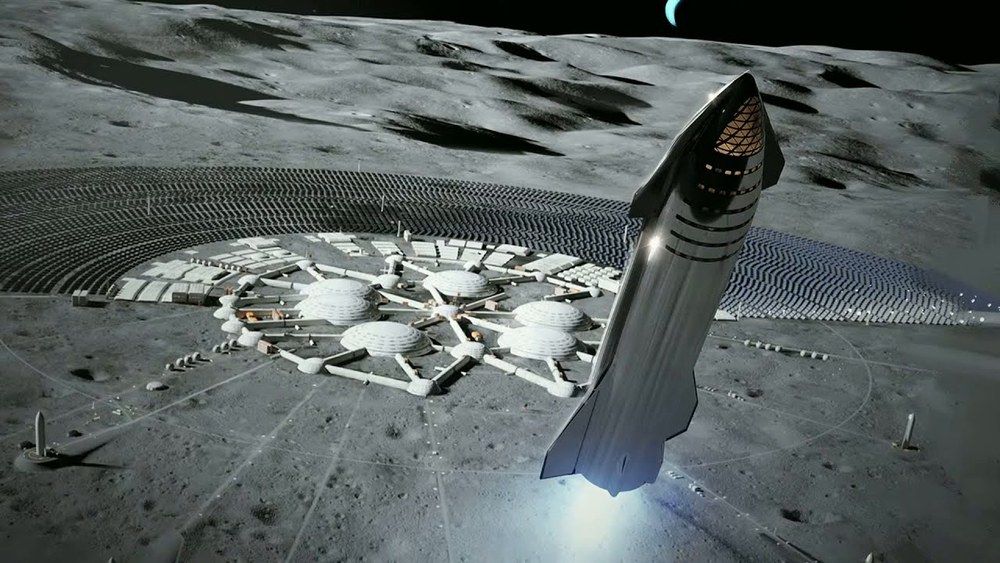
Good idea. I wonder how much of his attention will shift from Mars to the Moon.
Elon has tweeted out that early Starships will stay on the moon as part of moon base alpha.
The SpaceX plan is what Nextbigfuture described in last months article “A Sky Full of Starships”.
The SpaceX Starship will have six Raptor engines but will still be larger and cheaper than the external fuel tanks of the Space Shuttle. Elon Musk has a goal of building Starships for $5 million.
In the March 1988 issue of Popular Mechanics, the legendary science fiction author Isaac Asimov wrote an article describing his vision for humanity’s return to the moon.
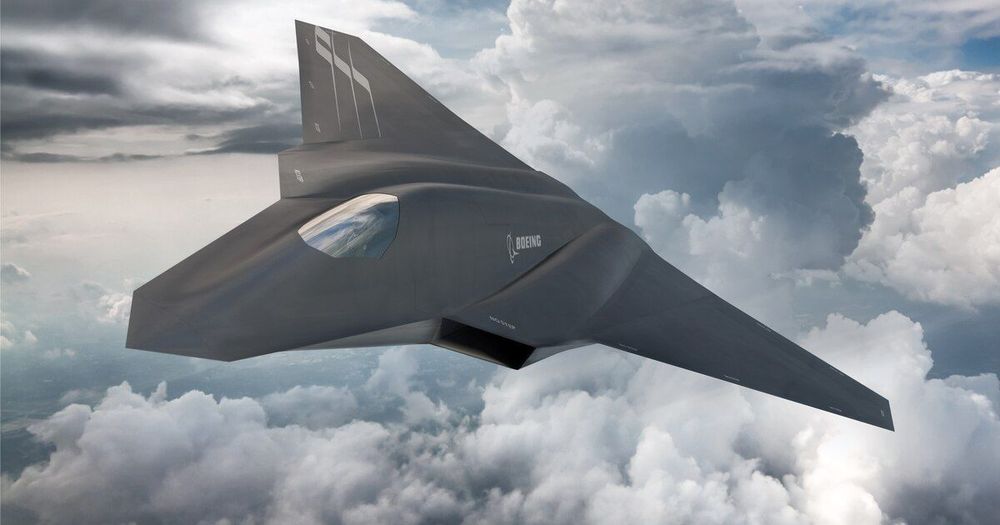
The Next Generation Air Dominance program is set to have a finalized acquisition strategy within the next few months.
Plug And Play
The underlying mechanics of a quantum computer won’t be any less difficult to comprehend under Gil’s vision of the future. But, he argues, it won’t matter because programming quantum computing software would become far more automated along the way.
“You’ll simply have to write a line of code in any programming language you work with,” Gil wrote, “and the system will match it with the circuit in the library and the right quantum computer.”
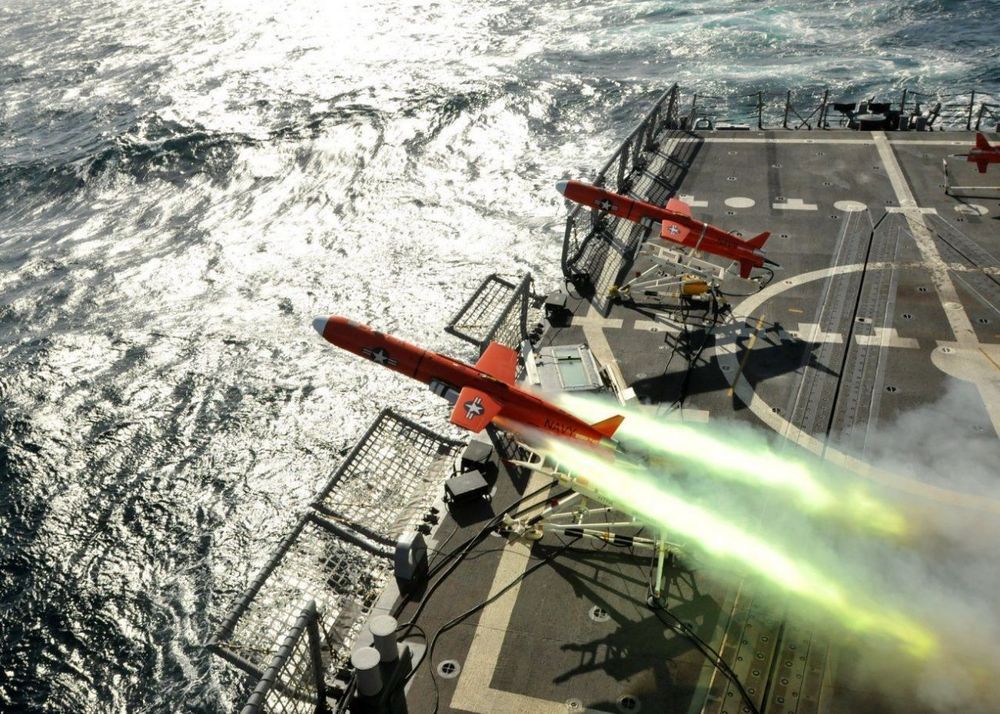
Here’s What You Need To Remember: Chinese so-called “carrier-killer” missiles could, quite possibly, push a carrier back to a point where its fighters no longer have range to strike inland enemy targets from the air. The new drone is being engineered, at least in large measure, as a specific way to address this problem. If the attack distance of an F-18, which might have a combat radius of 500 miles or so, can double — then carrier-based fighters can strike targets as far as 1000 miles away if they are refueled from the air.
The Navy will choose a new carrier-launched drone at the end of this year as part of a plan to massively expand fighter jet attack range and power projection ability of aircraft carriers.
The emerging Navy MQ-25 Stingray program, to enter service in the mid-2020s, will bring a new generation of technology by engineering a first-of-its-kind unmanned re-fueler for the carrier air wing.