Working out buffs up the body — and perhaps the mind, too.


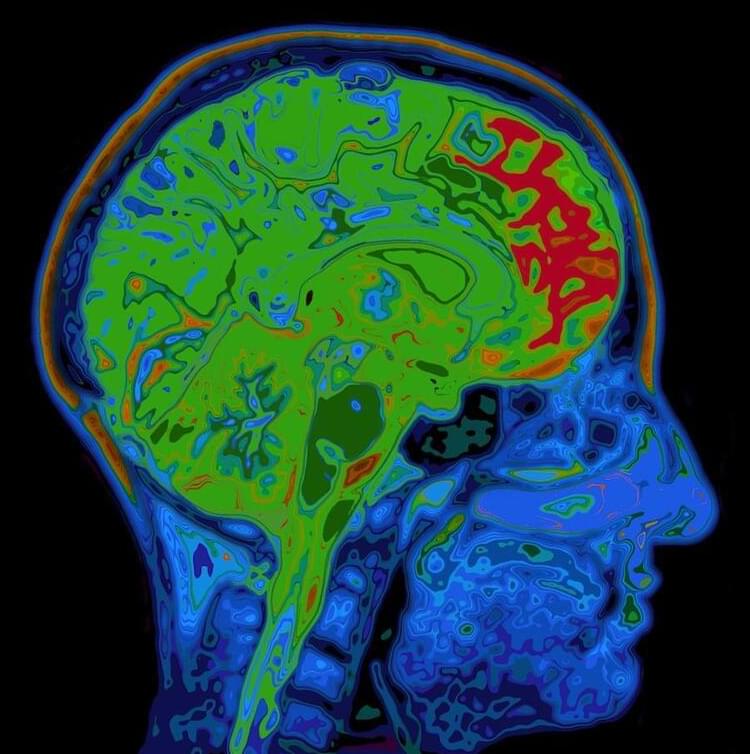
Grief can be overwhelming. Here’s what’s going on in the brain when you’re heartsick.
28:49 minutes.
But having strong relationships also means the possibility of experiencing loss. Grief is one of the hardest things people go through in life. Those who have lost a loved one know the feeling of overwhelming sadness and heartache that seems to well up from the very depths of the body.

In addition to securities fraud and obstruction of justice, James Velissaris has been charged with wire fraud and lying to auditors.
The founder and manager of a $1.7 billion mutual fund that collapsed last year has been charged by federal prosecutors with securities fraud and obstruction of justice for allegedly inflating fund asset values to keep investor money flowing, then falsifying records to conceal the improprieties.
The Infinity Q Diversified Alpha Fund halted investor redemptions in February 2021, roughly seven years after it was co-founded by James Velissaris, 37, its chief investment officer. A government inquiry began, Velissaris stepped down and the mutual fund and a parallel hedge fund he oversaw began liquidating.
It was a rare example of a big mutual fund failure amid a roaring bull market. And the collapse ensnared billionaire investor David Bonderman, co-founder of TPG, a huge private-equity firm that went public this year. The Bonderman Family was a major investor in Infinity Q Capital Management, the investment company overseen by Velissaris, regulatory documents show. Velissaris had worked for the Bonderman family before he co-founded Infinity Q Capital Management.
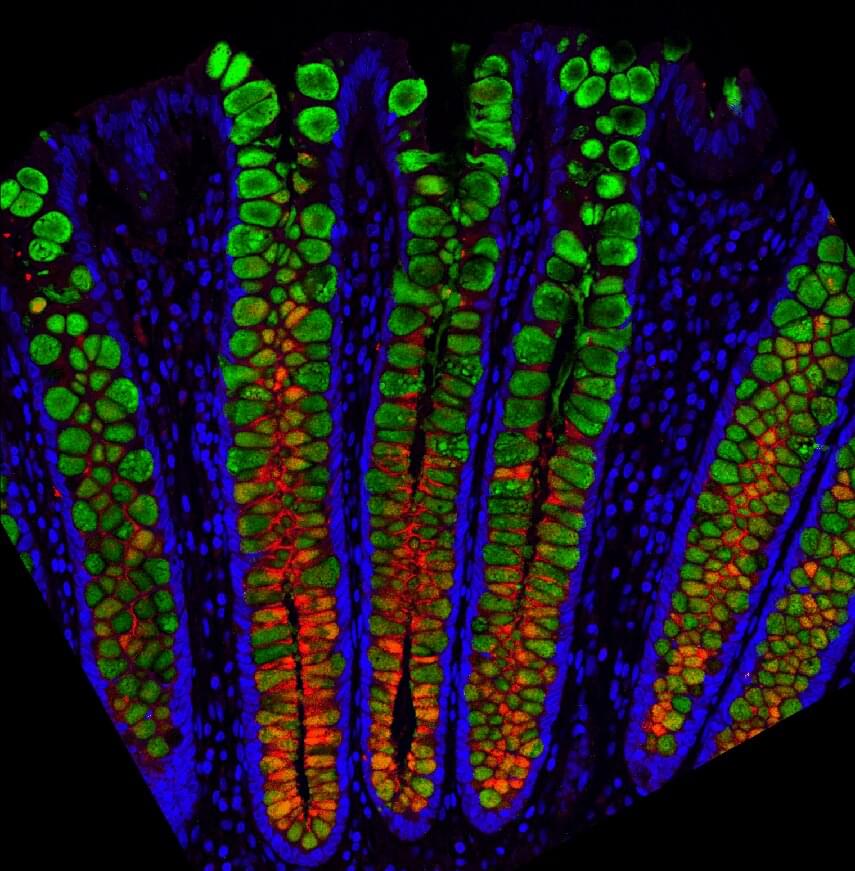
If you get nervous, you might feel it in your gut. If you eat chili, your gut might revolt, but your friend can eat anything and feel great. You can pop ibuprofen like candy with no ill effects, but your friend’s belly might bleed and might get no pain relief. Why is this? The quick answer is because we’re all different. The next questions are how different exactly, and what do these differences mean for health and disease? Answering these is much more difficult, but the UNC School of Medicine lab of Scott Magness, Ph.D., is revealing some interesting scientific answers.
For the first time, the Magness lab used entire human GI tracts from three organ donors to show how cell types differ across all regions of the intestines, to shed light on cellular functions, and to show gene expression differences between these cells and between individuals.
This work, published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, opens the door to exploring the many facets of gut health in a much more precise manner at greater resolution than ever before.
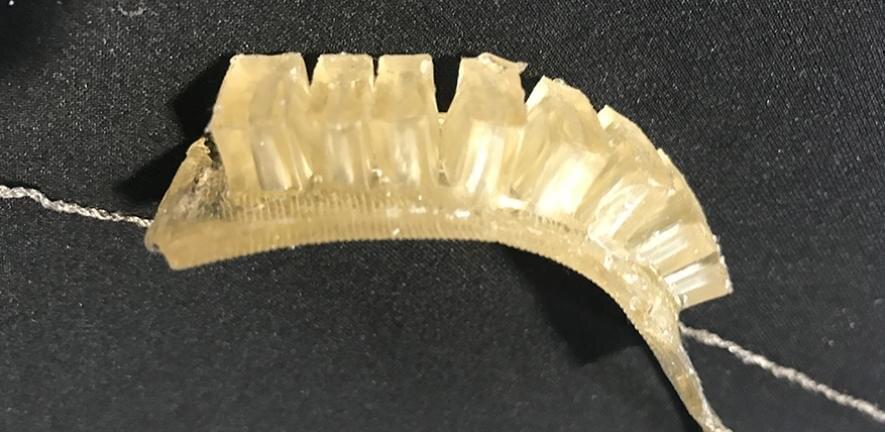

Researchers have developed self-healing, biodegradable, 3D-printed materials that could be used in the development of realistic artificial hands and other soft robotics applications.
The low-cost jelly-like materials, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, can sense strain, temperature and humidity. And unlike earlier self-healing robots, they can also partially repair themselves at room temperature.
The results are reported in the journal NPG Asia Materials.
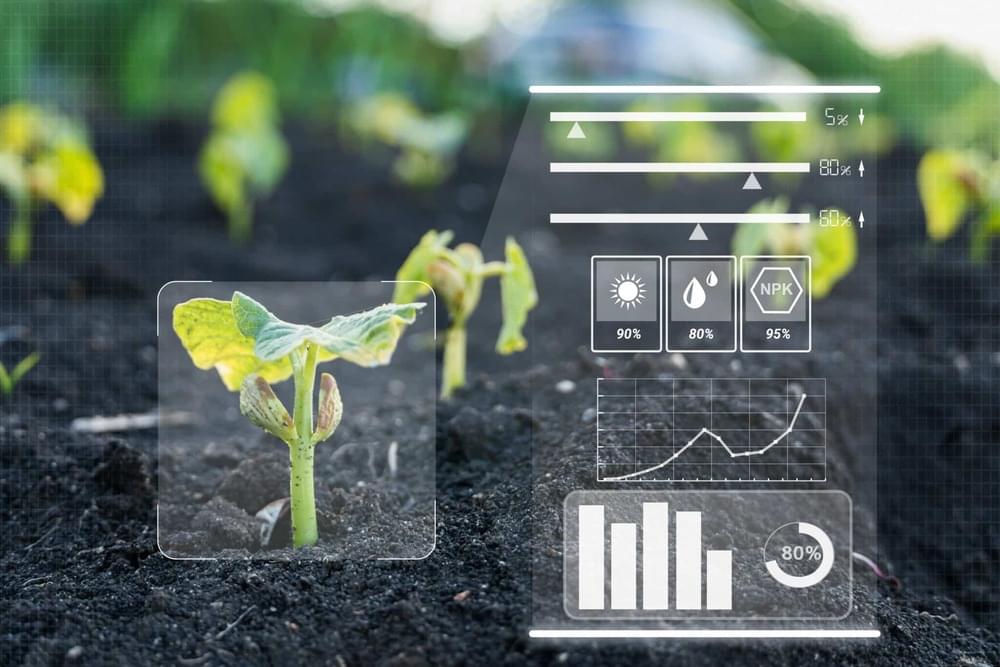



Electronic components applied to implement IoT based smart farming systems, ranging from processors, sensors, signal conditioning, power management, connectivity, and positioning.
The IoT systems in smart farming have been depicted in six main sections by EET India, which are processors, sensors, signal conditioning, power management, connectivity, and positioning. Common use cases like automatic fertilization, automatic irrigation, crop management, precision farming, and livestock monitoring all can be realized through IoT systems. After sensors detect the environmental phenomena and target objects, the information will be transmitted to controlled processors through wireless connectivity. Then, the processors can collect and analyze these data, or even help farmers with further decision making.
Fig. 1 An IoT system in smart farming (Source: EET India, TECHDesign)
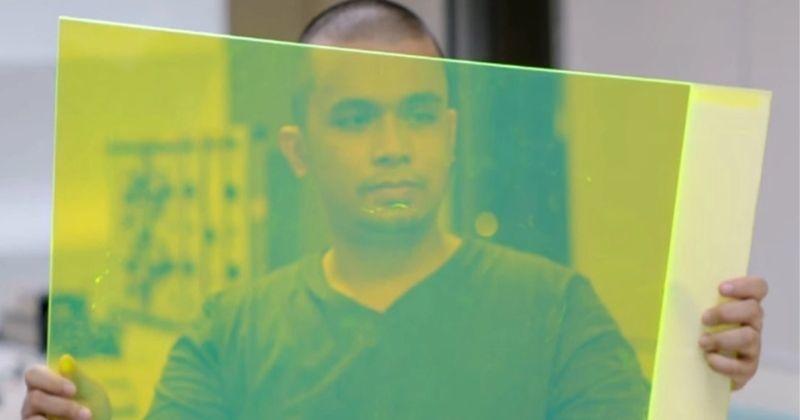

Also read: IIT delhi built solar panels that track sun’s movement to generate more electricity.
However, now an engineer from the Philippines has developed a new kind of solar panel that doesn’t really need sunlight to generate electricity. At least not directly.
Developed by Carvey Ehren Maigue, a student at Mapua University in the Philippines, the novel solar panels (called AuRES) are designed to feed off the UV rays of the sun — something that even dense cloudy days cannot block.