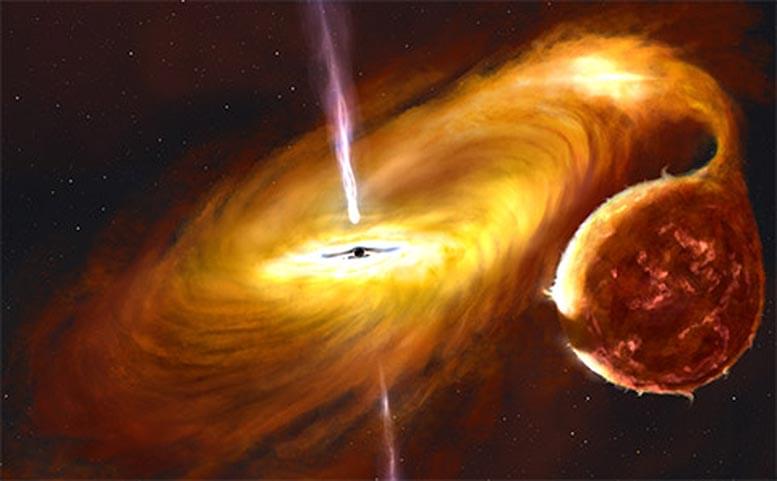
An international team of astrophysicists from South Africa, the UK, France and the US have found large variations in the brightness of light seen from around one of the closest black holes in our Galaxy, 9,600 light-years from Earth, which they conclude is caused by a huge warp in its accretion disc.
This object, MAXI J1820+070, erupted as a new X-ray transient in March 2018 and was discovered by a Japanese X-ray telescope onboard the International Space Station. These transients, systems that exhibit violent outbursts, are binary stars, consisting of a low-mass star, similar to our Sun and a much more compact object, which can be a white dwarf 0 neutron star 0 or black hole. In this case, MAXI J1820+070 contains a black hole that is at least 8 times the mass of our Sun.
The first findings have now been published in the international highly ranked journal, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, whose lead author is Dr. Jessymol Thomas, a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO).