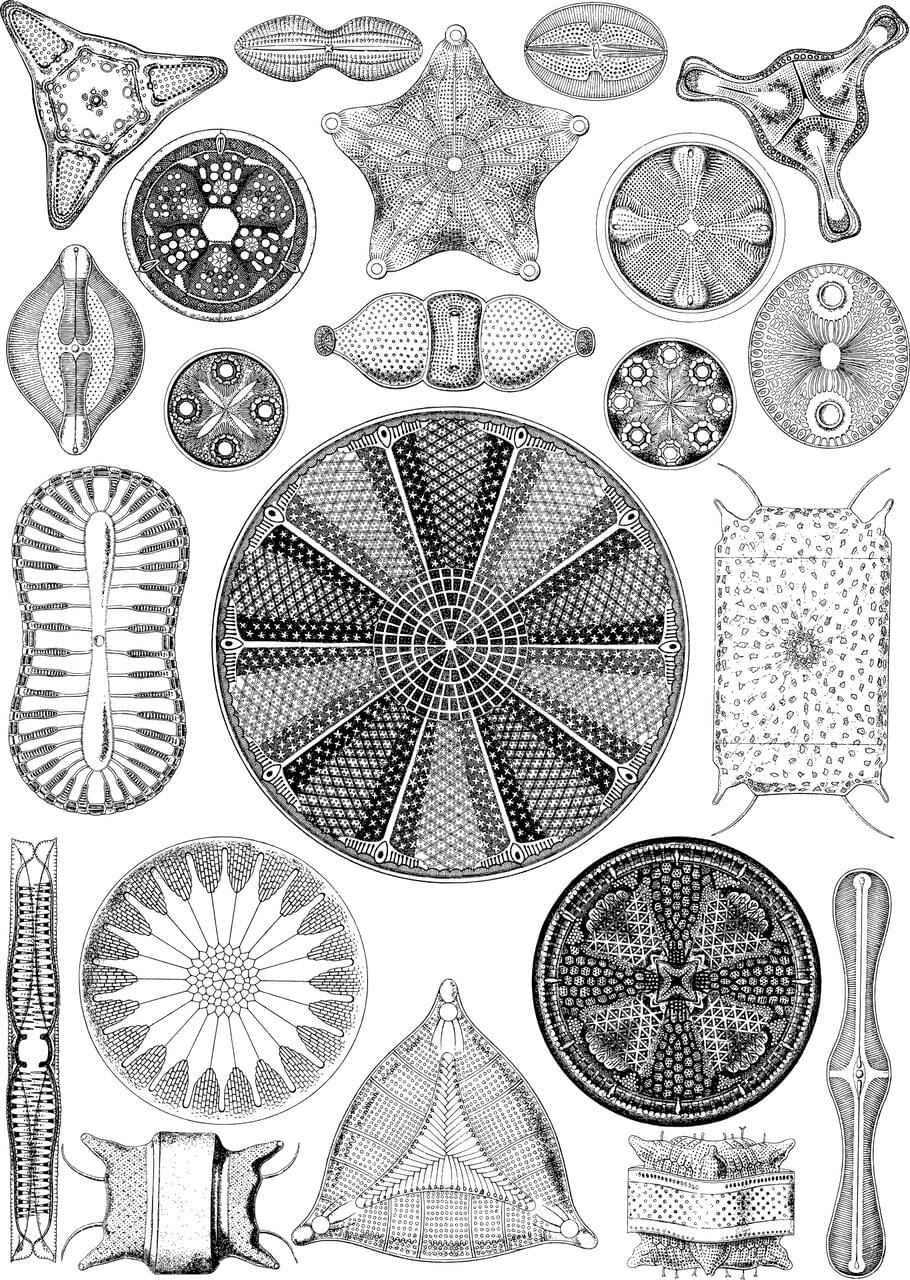
Trees get most of the love, but diatoms, a group of photosynthetic microalgae, produce 20% of Earth’s oxygen and are the foundation of aquatic food webs. The prevalence and diversity of diatoms have made them highly successful, suggesting the evolutionary history of diatoms is worth understanding as an important piece of the larger puzzle of life on Earth.
A new study led by researchers from the U of A found that diatoms evolved slowly for the first 100 million years of their existence. Then, 170 million years ago, they reached an inflection point characterized by a burst of rapid speciation orders of magnitude faster than anything that had preceded it. This included changes to their shape, size and mode of reproduction, as well as repeated movements from oceans into freshwater systems, a typically difficult barrier for aquatic species to cross.
With an estimated 100,000 species, diatoms are now one of the most diverse groups of microalgae. They are small enough that dozens could fit on the head of a pin and are found almost anywhere there is water and sunlight.