Researchers have released genetic and behavioral data from over 1,500 children and adolescents with autism who were hospitalized in psychiatric units across the U.S.


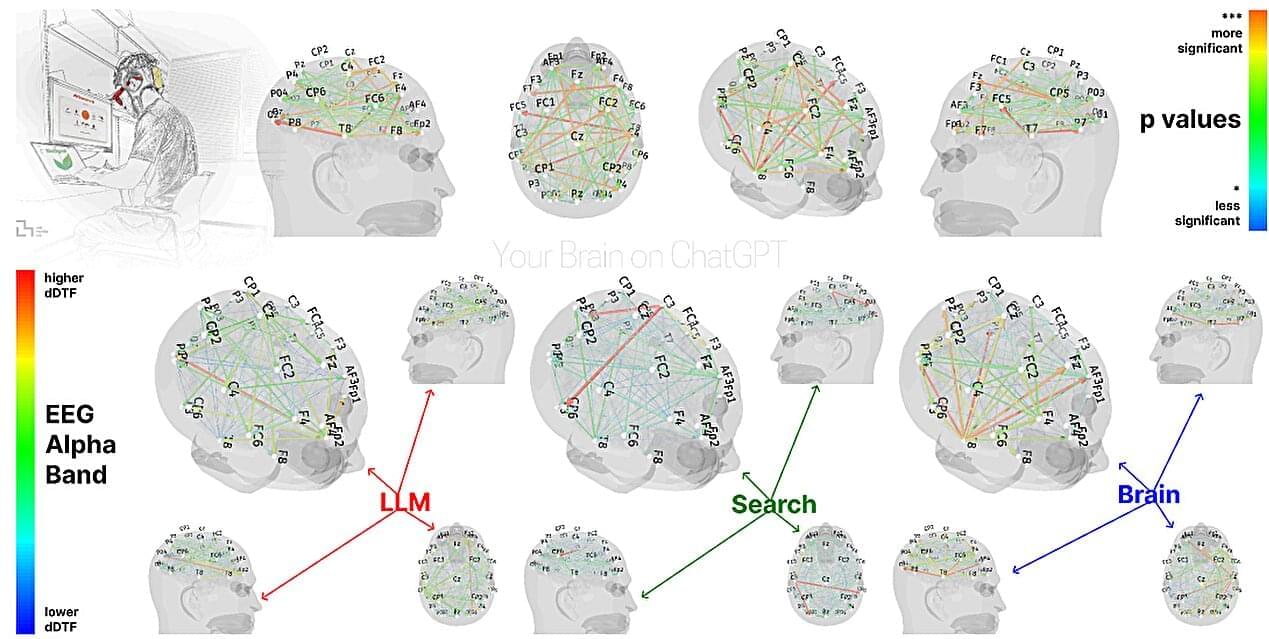
A team of neurologists and AI specialists at MIT’s Media Lab has led a study looking into the brain impacts of large language model (LLM) use among people who engage with them for study or work. They report evidence that the use of LLMs may lead to an erosion of critical thinking skills. In their study, posted on the arXiv preprint server, the researchers asked groups of volunteers to write essays while connected to EEG monitors.
Over the past few years, the use of LLMs such as ChatGPT has become commonplace. Some use them for fun, while others use them to help with school or work responsibilities, and the team at MIT wondered what sort of impact LLM use might have on the brain.
To find out, they recruited 54 volunteers. The initial group was then split into three small groups, all of whom were asked to write a 20-minute essay on the topic of philanthropy—one group was asked to use ChatGPT for help, the second was asked to use Google Search, and the third “Brain-only” group was given no tools or resources at all. The participants remained in these same groups for three writing sessions.
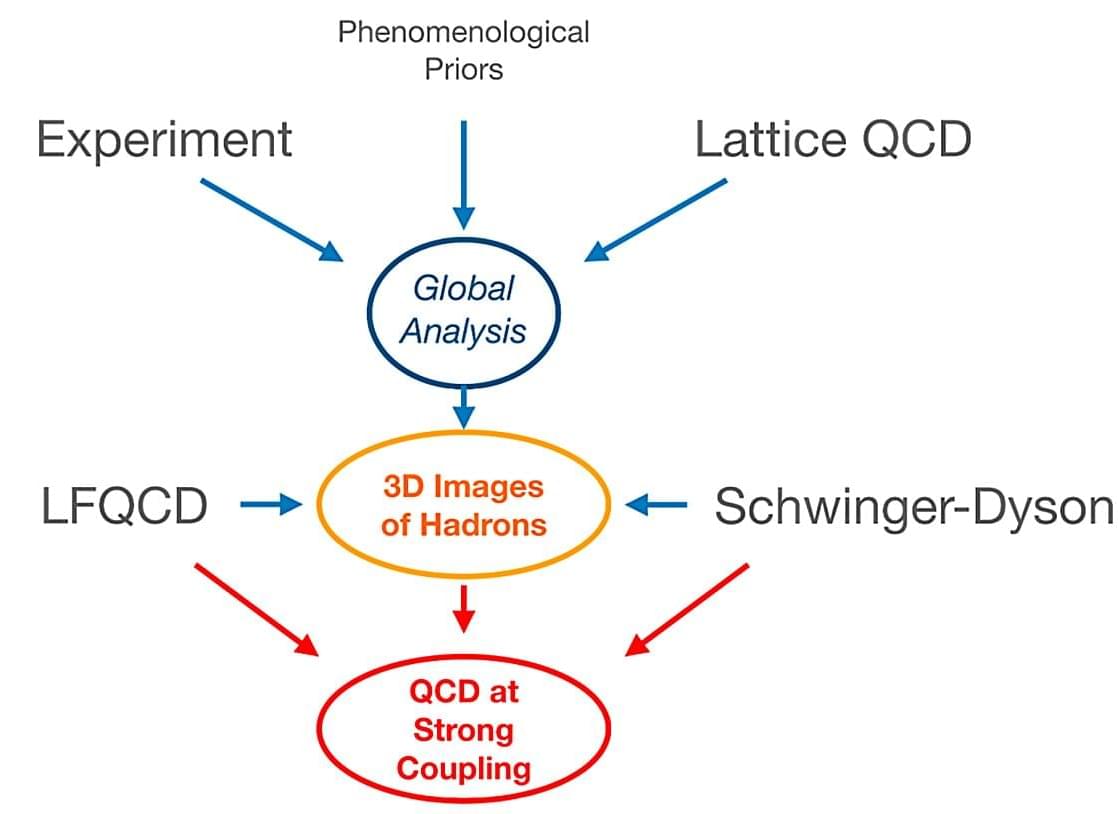
Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with collaborators from the Instituto Tecnológico de Aeronáutica in Brazil and Iowa State University, have theoretically explored the influence mechanism of quark-gluon interactions on the parton distribution functions (PDFs) within hadrons, providing new insights into first-principles calculations of hadron structure.
Their findings are published as a letter in Physical Review D.
Hadrons are essential building blocks of the universe. These composite particles, which are composed of quarks and gluons, include protons, neutrons, pions, and others. Investigating the behavior of quarks and gluons within hadrons is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the microscopic structure of matter.
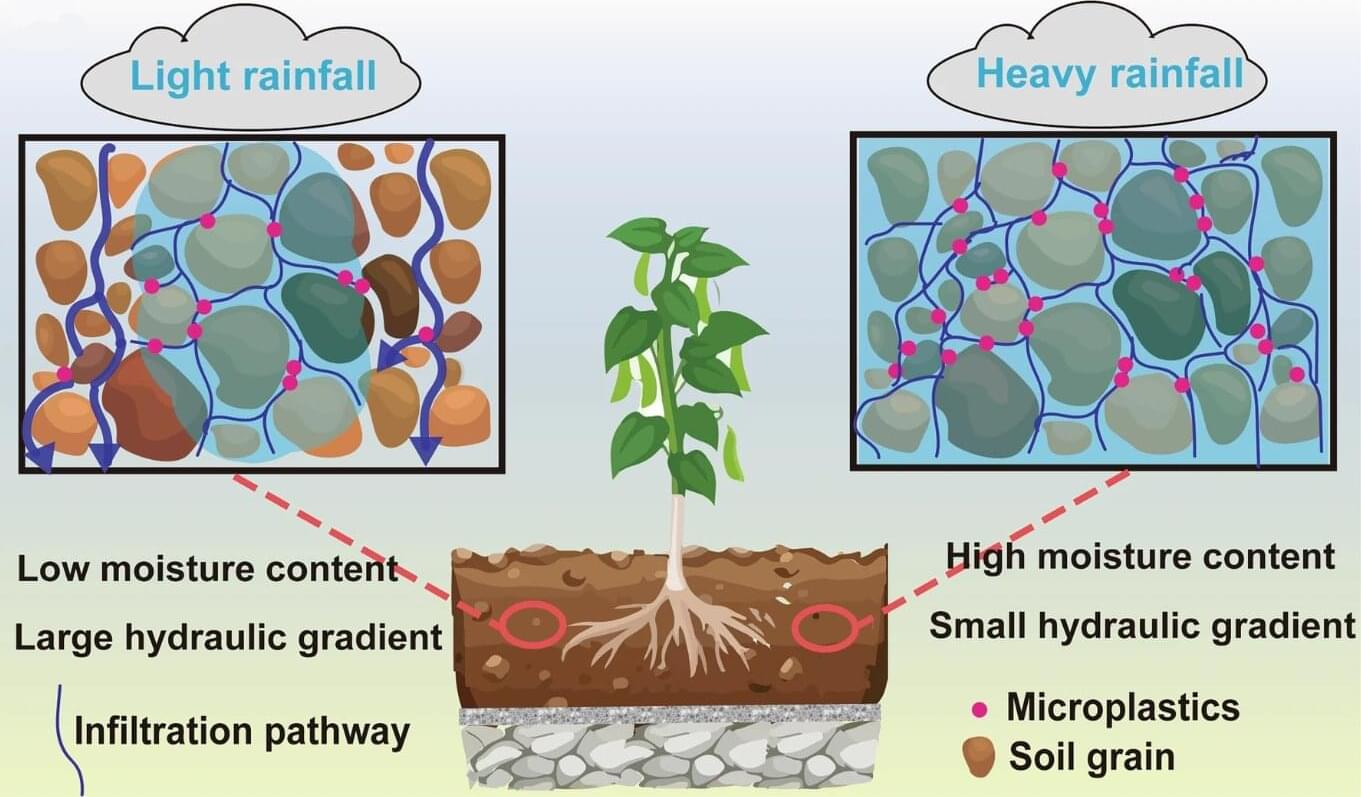
A small team of researchers at Tongji University, working with a colleague from the Shanghai Academy of Landscape Architecture Science and Planning, both in China, has found that growing plants on roofs can serve as an effective way to remove microplastics from the air. In their study, published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, the group measured the amounts of microplastics found on plants and the soil in which they grow.
Prior research has shown that growing plants on roofs can reduce heating and cooling bills and also clear pollution from the surrounding air. The research team wondered if that also included microplastics.
To find out, they built a simulated roof environment in their lab, where, in a thin layer of fresh soil, they planted two kinds of plants commonly used on rooftops in the city of Shanghai. They also introduced microplastic particles into the air above the plants at levels common to Shanghai. They then conducted simulated rains, measuring microplastic levels on the plants and in the soil.

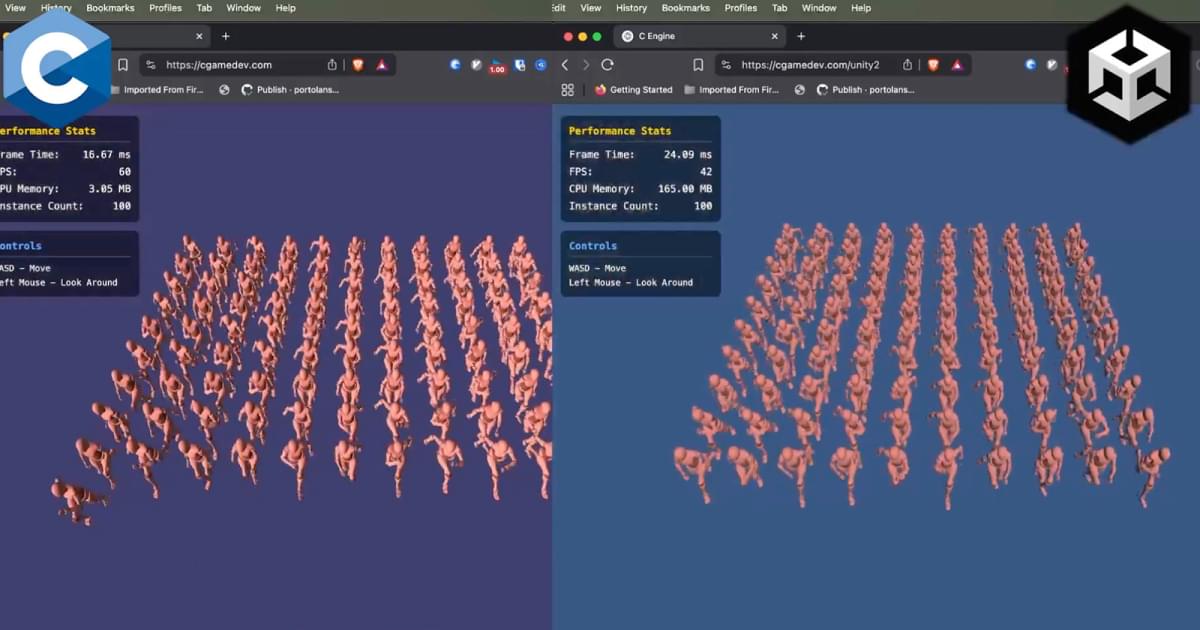
Gabriel Dechichi, a developer you might know from his challenge of making an Unreal Engine game in 4 weeks, is building his own C engine, and he’s ready to prove it’s better than Unity, at least in web space.
Dechichi made a demo where you can add hundreds of running mannequins and see how your system reacts to the stress. The creator claims his engine is “10x faster, 10x lighter, 10x better” than other software, and 14 times quicker than Unity in particular.
It’s obvious from first glance even at 100 characters that Dechichi’s engine runs smoother, but I tested it on my MacBook Pro, and while the C engine works with 1,000 units at 250 ms and 1 FPS, Unity took forever to load so many characters at 1,300 ms and 1 FPS. So, I guess, Dechichi is right, and we’ll see a nice addition to the gamedev world soon.

Stephen Wolfram joins Brian Greene to explore the computational basis of space, time, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and reality itself.
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participant: Stephen Wolfram.
Moderator: Brian Greene.
0:00:00 — Introduction.
01:23 — Unifying Fundamental Science with Advanced Mathematical Software.
13:21 — Is It Possible to Prove a System’s Computational Reducibility?
24:30 — Uncovering Einstein’s Equations Through Software Models.
37:00 — Is connecting space and time a mistake?
49:15 — Generating Quantum Mechanics Through a Mathematical Network.
01:06:40 — Can Graph Theory Create a Black Hole?
01:14:47 — The Computational Limits of Being an Observer.
01:25:54 — The Elusive Nature of Particles in Quantum Field Theory.
01:37:45 — Is Mass a Discoverable Concept Within Graph Space?
01:48:50 — The Mystery of the Number Three: Why Do We Have Three Spatial Dimensions?
01:59:15 — Unraveling the Mystery of Hawking Radiation.
02:10:15 — Could You Ever Imagine a Different Career Path?
02:16:45 — Credits.
VISIT our Website: http://www.worldsciencefestival.com.
FOLLOW us on Social Media:
Facebook: / worldsciencefestival.
Twitter: / worldscifest.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/worldscifest/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@worldscifest.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/world-science-festival.
#worldsciencefestival #briangreene #cosmology #astrophysics
Does the use of computer models in physics change the way we see the universe? How far reaching are the implications of computation irreducibility? Are observer limitations key to the way we conceive the laws of physics?
In this episode we have the difficult yet beautiful topic of trying to model complex systems like nature and the universe computationally to get into; and how beyond a low level of complexity all systems, seem to become equally unpredictable. We have a whole episode in this series on Complexity Theory in biology and nature, but today we’re going to be taking a more physics and computational slant.
Another key element to this episode is Observer Theory, because we have to take into account the perceptual limitations of our species’ context and perspective, if we want to understand how the laws of physics that we’ve worked out from our environment, are not and cannot be fixed and universal but rather will always be perspective bound, within a multitude of alternative branches of possible reality with alternative possible computational rules. We’ll then connect this multi-computational approach to a reinterpretation of Entropy and the 2nd law of thermodynamics.
The fact that my guest has been building on these ideas for over 40 years, creating computer language and AI solutions, to map his deep theories of computational physics, makes him the ideal guest to help us unpack this topic. He is physicist, computer scientist and tech entrepreneur Stephen Wolfram. In 1987 he left academia at Caltech and Princeton behind and devoted himself to his computer science intuitions at his company Wolfram Research. He’s published many blog articles about his ideas, and written many influential books including “A New kind of Science”, and more recently “A Project to Find the Fundamental Theory of Physics”, and “Computer Modelling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems”, and just out in 2023 “The Second Law” about the mystery of Entropy.
One of the most wonderful things about Stephen Wolfram is that, despite his visionary insight into reality, he really loves to be ‘in the moment’ with his thinking, engaging in socratic dialogue, staying open to perspectives other than his own and allowing his old ideas to be updated if something comes up that contradicts them; and given how quickly the fields of physics and computer science are evolving I think his humility and conceptual flexibility gives us a fine example of how we should update how we do science as we go.
What we discuss:
00:00 Intro.
07:45 The history of scientific models of reality: structural, mathematical and computational.
14:40 Late 2010’s: a shift to computational models of systems.
20:20 The Principle of Computational Equivalence (PCE)
24:45 Computational Irreducibility — the process that means you can’t predict the outcome in advance.
27:50 The importance of the passage of time to Consciousness.
28:45 Irreducibility and the limits of science.
33:30 Godel’s Incompleteness Theorem meets Computational Irreducibility.
42:20 Observer Theory and the Wolfram Physics Project.
45:30 Modelling the relations between discrete units of Space: Hypergraphs.
47:30 The progress of time is the computational process that is updating the network of relations.
50:30 We ’make’ space.
51:30 Branchial Space — different quantum histories of the world, branching and merging.
54:30 We perceive space and matter to be continuous because we’re very big compared to the discrete elements.
56:30 Branchial Space VS Many Worlds interpretation.
58:50 Rulial Space: All possible rules of all possible interconnected branches.
01:07:30 Wolfram Language bridges human thinking about their perspective with what is computationally possible.
01:11:00 Computational Intelligence is everywhere in the universe. e.g. the weather.
01:19:30 The Measurement problem of QM meets computational irreducibility and observer theory.
01:20:30 Entanglement explained — common ancestors in branchial space.
01:32:40 Inviting Stephen back for a separate episode on AI safety, safety solutions and applications for science, as we did’t have time.
01:37:30 At the molecular level the laws of physics are reversible.
01:40:30 What looks random to us in entropy is actually full of the data.
01:45:30 Entropy defined in computational terms.
01:50:30 If we ever overcame our finite minds, there would be no coherent concept of existence.
01:51:30 Parallels between modern physics and ancient eastern mysticism and cosmology.
01:55:30 Reductionism in an irreducible world: saying a lot from very little input.
References:
“The Second Law: Resolving the Mystery of the Second Law of Thermodynamics”, Stephen Wolfram.
“A New Kind of Science”, Stephen Wolfram.
Observer Theory article, Stephen Wolfram.
Neil deGrasse Tyson breaks down intriguing new evidence along with other curious parallels that could point to the universe being inside a black hole. Is the edge of our universe an event horizon on a black hole in some other universe?
Timestamps:
00:00 — What is a Black Hole?
1:26 — Mass of the Universe vs. A Black Hole This Size.
2:36 — The Net Rotation of the Universe.
5:55 — What This Means.
6:48 — Closing.
Check out our second channel, @StarTalkPlus.
Get the NEW StarTalk book, ‘To Infinity and Beyond: A Journey of Cosmic Discovery’ on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3PL0NFn.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/startalkradio.
FOLLOW or SUBSCRIBE to StarTalk: