« In the form it is known today, macroeconomics began in 1936 with the publication of John Maynard Keynes’s “The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money”. Its subsequent history can be divided into three eras. The era of policy which was guided by Keynes’s ideas began in the 1940s. By the 1970s it had encountered problems that it could not solve and so, in the 1980s, the monetarist era, most commonly associated with the work of Milton Friedman, began. In the 1990s and 2000s economists combined insights from both approaches. But now, in the wreckage left behind by the coronavirus pandemic, a new era is beginning. What does it hold? »
It is not yet clear where it will lead.



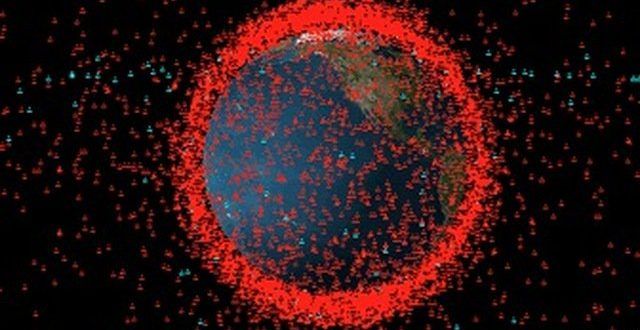
 As part of the partnership between SpaceWatch. Global and Joint Air Power Competence Centre, we have been granted permission to publish selected articles and texts. We are pleased to present “Space Traffic Management – Impact of Large Constellations on Military Operations in Space”, originally published by the Joint Air Power Competence Centre for the Conference Read Ahead 2020.
As part of the partnership between SpaceWatch. Global and Joint Air Power Competence Centre, we have been granted permission to publish selected articles and texts. We are pleased to present “Space Traffic Management – Impact of Large Constellations on Military Operations in Space”, originally published by the Joint Air Power Competence Centre for the Conference Read Ahead 2020.