Mar 18, 2020
A new computer chip mimics the neurocircuitry of our noses to smell
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: computing, neuroscience
It draws inspiration from the structure and electrical activity of the brain to distinguish between odors.
It draws inspiration from the structure and electrical activity of the brain to distinguish between odors.
:ooooooo.
The quantum spin Hall insulator is characterized by a bandgap in the two-dimensional (2D) interior and helical 1D edge states1,2,3. Inducing superconductivity in the helical edge state results in a 1D topological superconductor, a highly sought-after state of matter at the core of many proposals for topological quantum computing4. In the present study, we report the coexistence of superconductivity and the quantum spin Hall edge state in a van der Waals heterostructure, by placing a monolayer of 1T′-WTe2, a quantum spin Hall insulator1,2,3, on a van der Waals superconductor, NbSe2. Using scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy (STM/STS), we demonstrate that the WTe2 monolayer exhibits a proximity-induced superconducting gap due to the underlying superconductor and that the spectroscopic features of the quantum spin Hall edge state remain intact. Taken together, these observations provide conclusive evidence for proximity-induced superconductivity in the quantum spin Hall edge state in WTe2, a crucial step towards realizing 1D topological superconductivity and Majorana bound states in this van der Waals material platform.
Despite the crashing markets, companies are working hard to boost the further adoption of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. In two separate announcements, Coinbase and the popular internet browser Opera revealed that they’ve made serious strides in this regard.
Coinbase Card Usable With Google Pay
The leading cryptocurrency exchange in the US, Coinbase, allows its users to get a cryptocurrency card through a partnership with Visa. Now, the card has enabled users to spend Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies directly from their Coinbase account using Google Pay.
Location data from Facebook and Google could clarify whether people are actually social distancing, and whether it’s working.

The increasing number of coronavirus cases in Italy has brought the entire country to a standstill. According to the Live Tracking Dashboard, there are 27,980 confirmed cases as of now and 2,158 people have succumbed to the infection. However, a total of 2,749 people have also recovered from the illness.
Since people are socially distancing themselves to avoid the virus from spreading, a lot of them are also losing business with every passing minute. There’s panic and tension all around. However, there is a piece of good news that’s become the silver lining at this time of misery.
Hope on the horizon:
1. Researcher make a breakthrough: Professor Katherine Kedzierska leads research at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity that discovers how the human body overcomes coronavirus.
Melbourne researchers have mapped immune responses from one of Australia’s first novel coronavirus (COVID-19) patients, showing the body’s ability to fight the virus and recover from the infection.
Continue reading “COVID-19: the immune system can fight back” »
A preprint of a study conducted by researchers from Utrecht University, in collaboration with Erasmus MC and Harbor BioMed, outlines the first report of a human monoclonal antibody that can block SARS-CoV-2.
Understanding antibodies: Terms and definitions
Antibodies are proteins that are produced by certain cells of the immune system known as B cells. They are able to bind to “foreign” material that tries to invade the body, such as pathogens, and directly neutralize them or trigger an immune response. This is achieved by binding of the antibody to an antigen, a specific molecule present on the pathogen.
This video was made possible thanks to the kind donations of our supporters on Patreon and Ko-fi. Join them in supporting us.
Buy the team a coffee — or a meal! https://ko-fi.com/transportevolved
Follow our ‘second’ channel — Transport Evolved Take Two, at https://www.youtube.com/transportevolvedtake2
Follow the show on Twitter https://www.twitter.com/TransportEvolve
Buy Transport Evolved SWAG : https://teespring.com/stores/transport-evolved
Join our Discord Channel: https://discord.gg/9WAjfQn
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/transportevolved
Follow Nikki’s personal channel at https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCZWSrDEYcNoio7QaetV_JKA
——
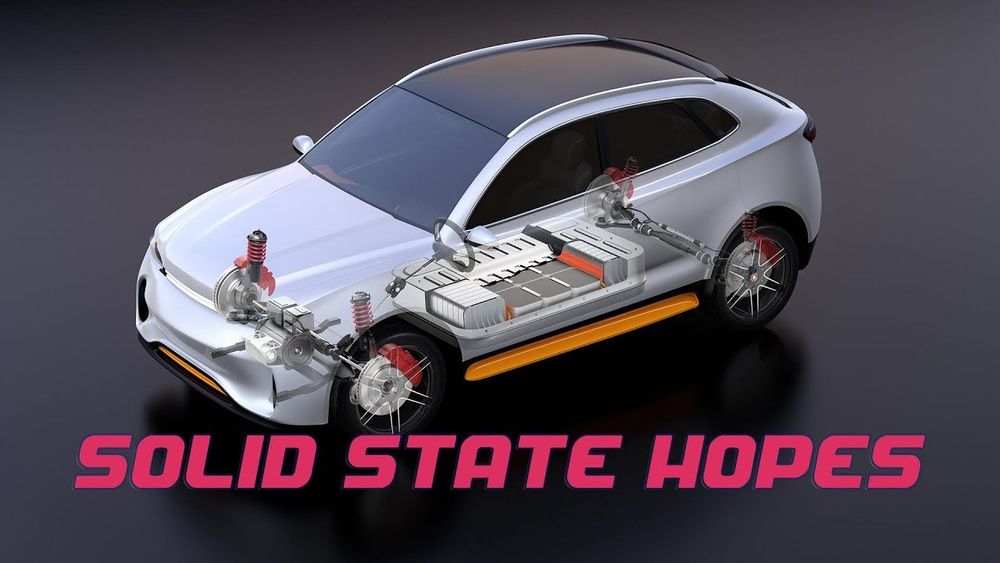
While most electric cars already travel further per charge than most people need them to on a daily basis, there’s still a massive hunt to find the longest-range, cheapest, longest-life battery pack possible for future generations of EVs.
Continue reading “Has Samsung Found The Holy Grail Of Solid State Batteries?” »
Now, in an important new resource for the scientific community published today in Nature Biotechnology, researchers in the lab of Neville Sanjana, PhD, at the New York Genome Center and New York University have developed a new kind of CRISPR screen technology to target RNA.
The researchers capitalized on a recently characterized CRISPR enzyme called Cas13 that targets RNA instead of DNA. Using Cas13, they engineered an optimized platform for massively-parallel genetic screens at the RNA level in human cells. This screening technology can be used to understand many aspects of RNA regulation and to identify the function of non-coding RNAs, which are RNA molecules that are produced but do not code for proteins.
By targeting thousands of different sites in human RNA transcripts, the researchers developed a machine learning-based predictive model to expedite identification of the most effective Cas13 guide RNAs. The new technology is available to researchers through an interactive website and open-source toolbox to predict guide RNA efficiencies for custom RNA targets and provides pre-designed guide RNAs for all human protein-coding genes.

On March 9, 2016, the worlds of Go and artificial intelligence collided in South Korea for an extraordinary best-of-five-game competition, coined The DeepMind Challenge Match. Hundreds of millions of people around the world watched as a legendary Go master took on an unproven AI challenger for the first time in history.
Directed by Greg Kohs with an original score by Academy Award nominee, Hauschka, AlphaGo chronicles a journey from the halls of Oxford, through the backstreets of Bordeaux, past the coding terminals of DeepMind in London, and ultimately, to the seven-day tournament in Seoul. As the drama unfolds, more questions emerge: What can artificial intelligence reveal about a 3000-year-old game? What can it teach us about humanity?
