The adhesion and colonization or biofilm formation include primary stage in bacterial infections. Major adhesion virulence factors in this step include type I fimbriae (FimH) and pilli structures for attachment to the host cells7,8. Furthermore, numerous bacteria secrete toxins and extracellular enzymes which play a crucial role in the apoptosis or necrosis of epithelial cells or immunocytes. Various virulence factors of A. baumannii such as adhesins genes like kpsMII (group 2 capsule synthesis) and fimH, tratT (serum resistance associated), fyuA (yersiniabactin receptor) and iutA (aerobactin receptor) have been investigated previously9,10. An important polysaccharide for biofilm formation is encoded by pgaABCD locus11. Biofilm production is a strategy to escape from harsh conditions and immune responses, hence play as reservoirs for drug-resistant systemic infections. Biofilm-producing A. baumannii has been isolated from several infectious origins such as pneumonia and devise-associated infections. Bacterial within biofilm can resist significantly more against antibiotics compared to planktonic mode of growth12. Hence, biofilm-mediated infections are in relapse more frequently13.
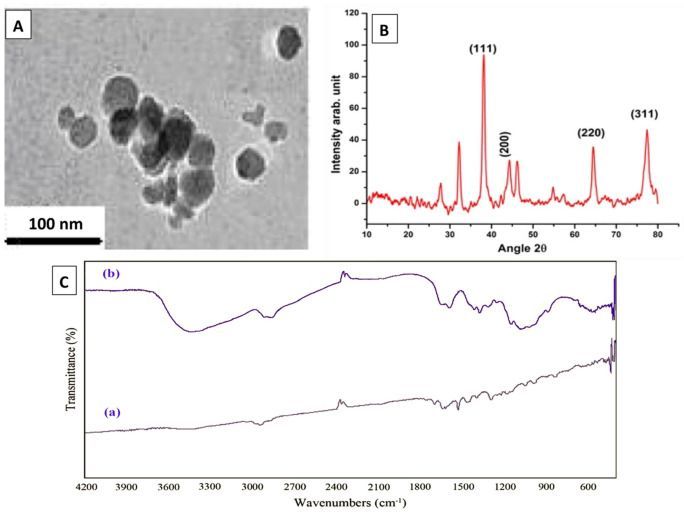
Therefore, there is an urgent need to enhance the effects of antimicrobials against pathogenic bacteria. In recent years, interest has enhanced towards application of nanoparticles as therapeutic regimens14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), which have low toxicity in ecosystems and have high rate of surface capacity, can inhibit accumulation of biofilm materials responsible for evasion and protection22,23,24.
The aim of this study was to isolate A. baumannii from wound infections, determine their resistance and virulence profile, and assess the impact of AgNPs on the bacterial growth, virulence and biofilm-related gene expressions in the isolated strains.