America’s Office of Science and Technology Policy, the National Science and Technology Council, and the National Security Council prioritize.

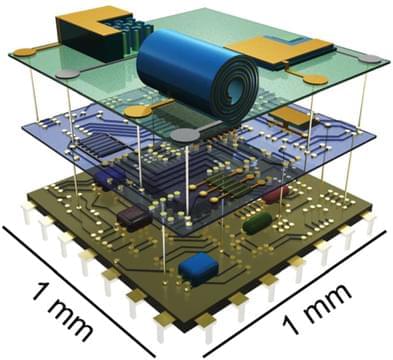
And it’s the size of a grain of dust. Energy storage might have been revolutionized thanks to a common dessert dish.
Advances in microelectronics have enabled the use of miniaturized computers for autonomous intelligence at the size of a dust particle less than one square millimeter across and a few hundred micrometers thick, creating an environment for ubiquitous computing. However, the size mismatch between microbatteries and microelectronics has emerged as a fundamental barrier against the take-off of tiny intelligent systems requiring power anytime anywhere. Mainstream microbattery structures include stacked thin films on the chip or electrode pillars and on-chip interdigitated microelectrodes. Nevertheless, available technologies cannot shrink the footprint area of batteries while maintaining adequate energy storage. Alternatively, the on-chip self-assembly process known as micro-origami is capable of winding stacked thin films into Swiss-roll structures to reduce the footprint area, which exactly mimics the manufacture of the most successful full-sized batteries—cylinder batteries. In addition to discussing in detail the technical difficulties of reducing the size of on-chip microbatteries with various structures and potential solutions, this Perspective highlights the following two basic requirements for eventual integration in microcomputers: minimum energy density of 100 microwatt-hour per square centimeter and monolithic integration with other functional electric circuits on the chip.
Space Race 2.0 is heating up.
There’s no use denying it: Space Race 2.0 is heating up.
But while the focus remains on public-private partnerships in low-Earth orbit, space junk, and finally human settlements on the moon and Mars, a remnant of that original space race spirit is beginning to awaken: the push to explore the outer edges of our solar system, and beyond.
Last year, China announced it was developing a pair of spacecraft capable of exploring the very edge of our solar system. According to an official industry newspaper called *China Space News Friday*, the mission “Interstellar Express” promised the potential to enter interstellar space by the middle of the century.
Of course, NASA already did it.
‘NASA launched Voyager 1 in 1977, in addition to Voyager 2 a month earlier — two intrepid spacecraft that toured the outer solar system through the late eighties. Both spacecraft are now in interstellar space and still sending what data they can back, with most equipment shut down to preserve power. But NASA might not be done with deep space missions yet.
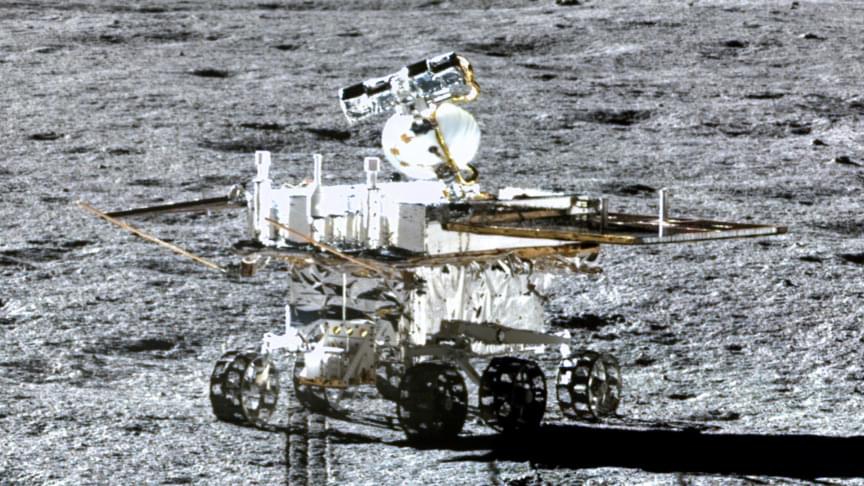
Glass isn’t uncommon on the Moon. But these spheres are.
China’s Yutu-2 lunar rover on a mission to find out more about the far side of the Moon has made a startling new discovery. It has found mysterious glass spheres that may have captured within them important information about the Moon’s composition and history of its impact events, * Science Alert* reported.
Originally scheduled to be operational on the lunar surface for just three months, the Yutu-2 now holds the record of being the longest operational rover on the Moon. When it landed in 2019, it became the first rover to reach the far side of the Moon and has since been providing us insights about the side we cannot see from Earth. Last month, we learned that the soil on the far side is a lot stickier, and now there is the mystery of the glass spheres on the Moon aren’t a new finding. But the nature of these spheres makes them interesting and possibly a gateway for future missions.



The researcher also told BleepingComputer that websites, such as LinkedIn, detect man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks and deactivate accounts after successful logins.
To overcome this obstacle, mr.d0x came up with a devious new phishing technique that uses the noVNC remote access software and browsers running in kiosk mode to display email login prompts running on the attacker’s server but shown in the victim’s browser.
VNC is a remote access software that allows remote users to connect to and control a logged-in user’s desktop. Most people connect to a VNC server through dedicated VNC clients that open the remote desktop in a similar manner to Windows Remote Desktop.

Billionaire Elon Musk has long been vocal about his ambitions for colonizing Mars – here’s everything we know about his plan.
Musk founded SpaceX in 2002 and since then has constantly reiterated one of his biggest goals is to help make humankind a multi-planetary species.
In order to achieve this otherworldly feat, the world’s richest man (at the time of publishing) turned his attention to the red planet, located approximately 33.9 million miles away from Earth.