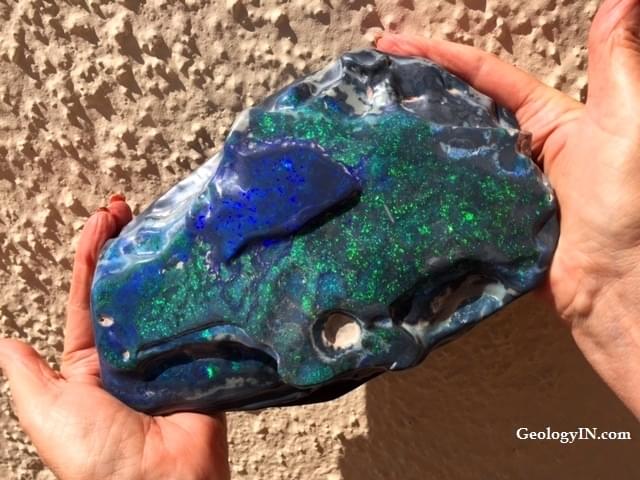
The largest black opal weighs 11,340.95 carats (2,268.19 grams; 80 oz) and measures 2,450 × 1,460 × 527 mm.


We’re all used to swapping RAM in our desktops and laptops. What about a GPU, though? [dosdude1] teaches us that soldered-on RAM is merely a frontier to be conquered. Of course, there’s gotta be a good reason to undertake such an effort – in his case, he couldn’t find the specific type of Nvidia GT640 that could be flashed with an Apple BIOS to have his Xserve machine output the Apple boot screen properly. All he could find were 1GB versions, and the Apple BIOS could only be flashed onto a 2GB version. Getting 2GB worth of DDR chips on Aliexpress was way too tempting!
The video goes through the entire replacement process, to the point where you could repeat it yourself — as long as you have access to a preheater, which is a must for reworking relatively large PCBs, as well as a set of regular tools for replacing BGA chips. In the end, the card booted up, and, flashed with a new BIOS, successfully displayed the Apple bootup logo that would normally be missing without the special Apple VBIOS sauce. If you ever want to try such a repair, now you have one less excuse — and, with the GT640 being a relatively old card, you don’t even risk all that much!
This is not the first soldered-in RAM replacement journey we’ve covered recently — here’s our write-up about [Greg Davill] upgrading soldered-in RAM on his Dell XPS! You can upgrade CPUs this way, too. While it’s standard procedure in sufficiently advanced laptop repair shops, even hobbyists can manage it with proper equipment and a good amount of luck, as this EEE PC CPU upgrade illustrates. BGA work and Apple computers getting a second life go hand in hand — just two years ago, we covered this BGA-drilling hack to bypass a dead GPU in a Macbook, and before that, a Macbook water damage revival story.
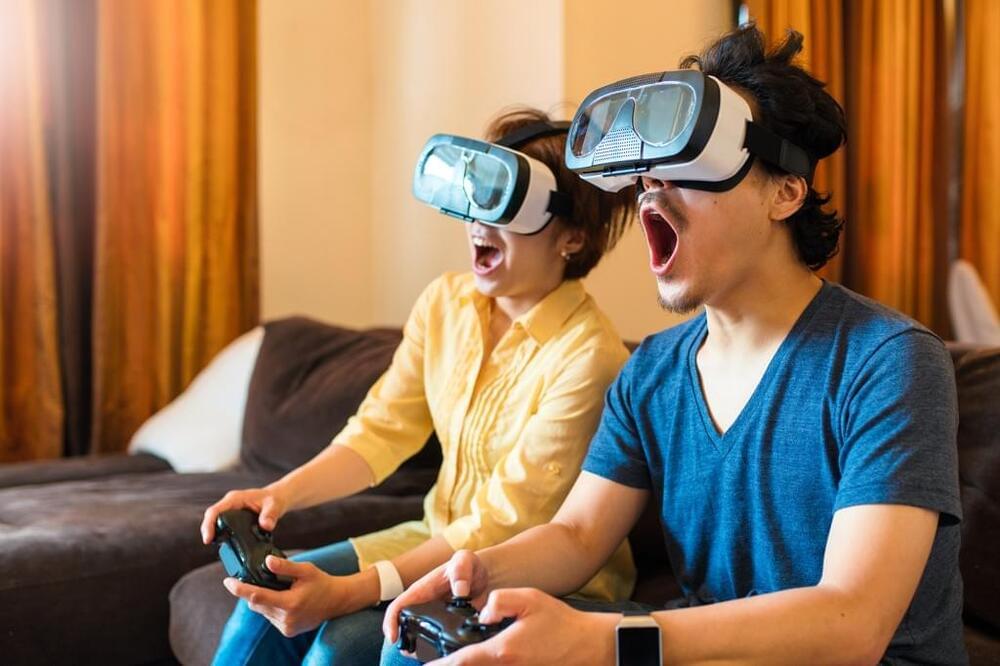

A German gamer has broken his neck while wearing a virtual reality headset after he moved too “intensely.”
Doctors claim the 31-year-old’s “repetitive” movements led to the neck being damaged — before part of the bone finally “cracked.”
The man went to the hospital after experiencing a piercing pain in his shoulders.
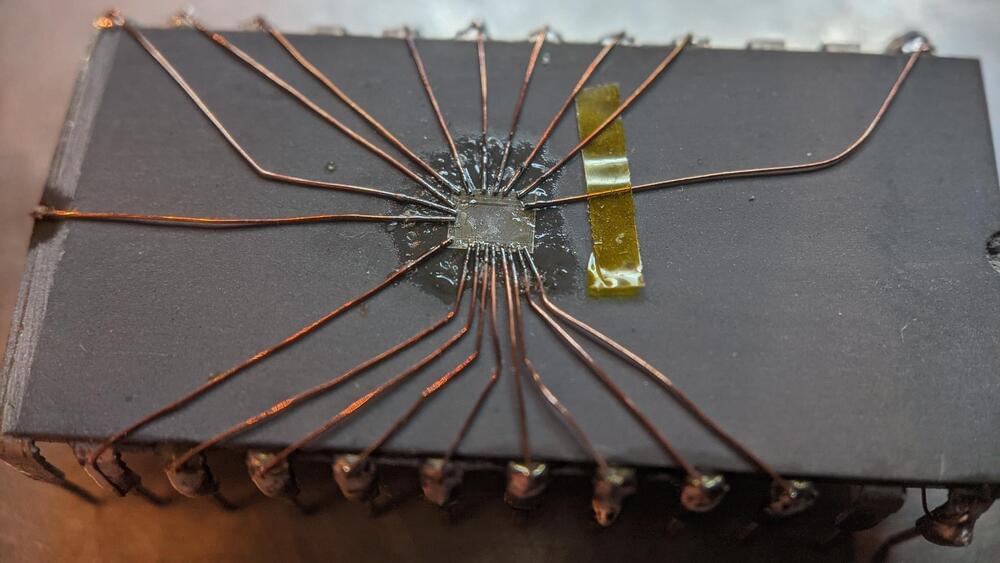
We might be amidst a chip shortage, but if you enjoy reverse-engineering, there’s never a shortage of intriguing old chips to dig into – and the 2513N 5×7 character ROM is one such chip. Amidst a long thread probing a few of these (Twitter, ThreadReader link), [TubeTime] has realized that two address lines were shorted inside of the package. A Twitter dopamine-fueled quest for truth has led them to try their hand at making the chip work anyway. Trying to clear the short with an external PSU led to a bond wire popping instead, as evidenced by the ESD diode connection disappearing.
A dozen minutes of sandpaper work resulted in the bare die exposed, making quick work of the bond wires as a side effect. Apparently, having the bond pads a bit too close has resulted in a factory defect where two of the pads merged together. No wonder the PSU wouldn’t take that on! Some X-acto work later, the short was cleared. But without the bond wires, how would [TubeTime] connect to it? This is where the work pictured comes in. Soldering to the remains of the bond wires has proven to be fruitful, reviving the chip enough to continue investigating, even if, it appears, it was never functional to begin with. The thread continued on with comparing ROMs from a few different chips [TubeTime] had on hand and inferences on what could’ve happened that led to this IC going out in the wild.
Such soldering experiments are always fun to try and pull off! We rarely see soldering on such a small scale, as thankfully, it’s not always needed, but it’s a joy to witness when someone does IC or PCB microsurgery to fix factory defects that render our devices inoperable before they were even shipped. Each time that a fellow hacker dares to grind the IC epoxy layers down and save a game console or an unidentified complex board, the world gets a little brighter. And if you aren’t forced to do it for repair reasons, you can always try it in an attempt to build the smallest NES in existence!


A team of scientists at Tufts University and Harvard University “have brought us a step closer to the goal of regenerative medicine” by using a drug cocktail to regrow a frog’s amputated legs.
Peer-reviewed study: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abj2164
Scientists say they have been able to help frogs regrow their legs for the first time. The next step? Try the procedure on mammals.

Chinese mobility manufacturer BYD has introduced its new “Type A” electric school bus to transport up to thirty US students at a time. Furthermore, the new zero-emission bus is ADA capable up to 800 lbs and can travel 140 miles on a single charge. What may be most appealing to school districts, however, is the vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities BYD’s Type A school bus will provide.
BYD is an acronym for “Build Your Dreams,” a motto the Chinese automaker has followed since 1995 when it was founded. BYD Auto, the subsidiary of BYD Co. Ltd. will be celebrating its 20th anniversary next year, as it sits as one of the largest auto manufacturers in China. In 2021, BYD produced over 320,000 BEVs, second in the country only to SAIC.
In addition to manufacturing unique “blade” EV batteries, BYD Auto develops and manufactures electric cars, buses, trucks, bicycles, and even forklifts – under its own monicker as well as for other OEMs like Toyota.