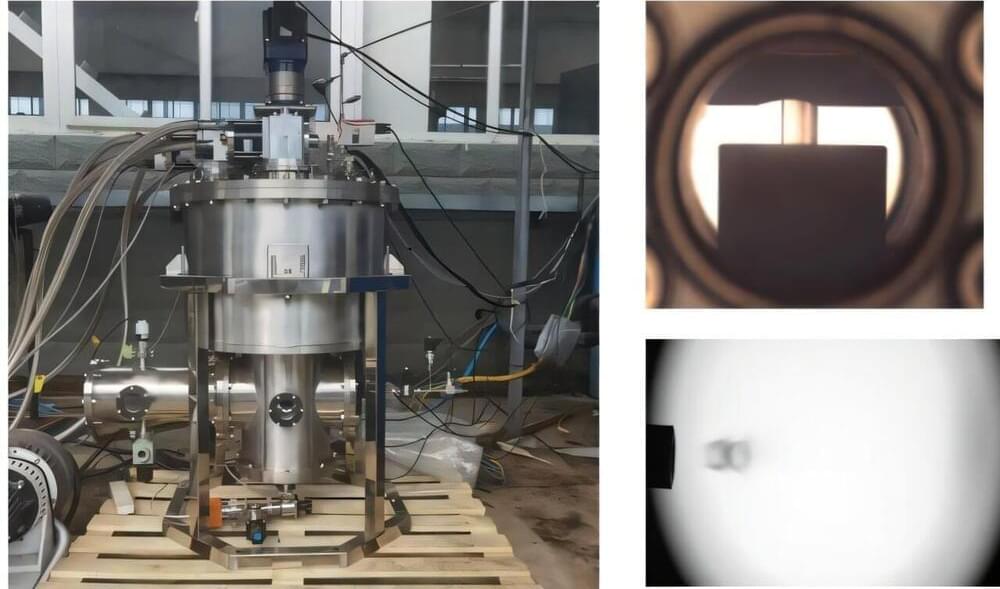
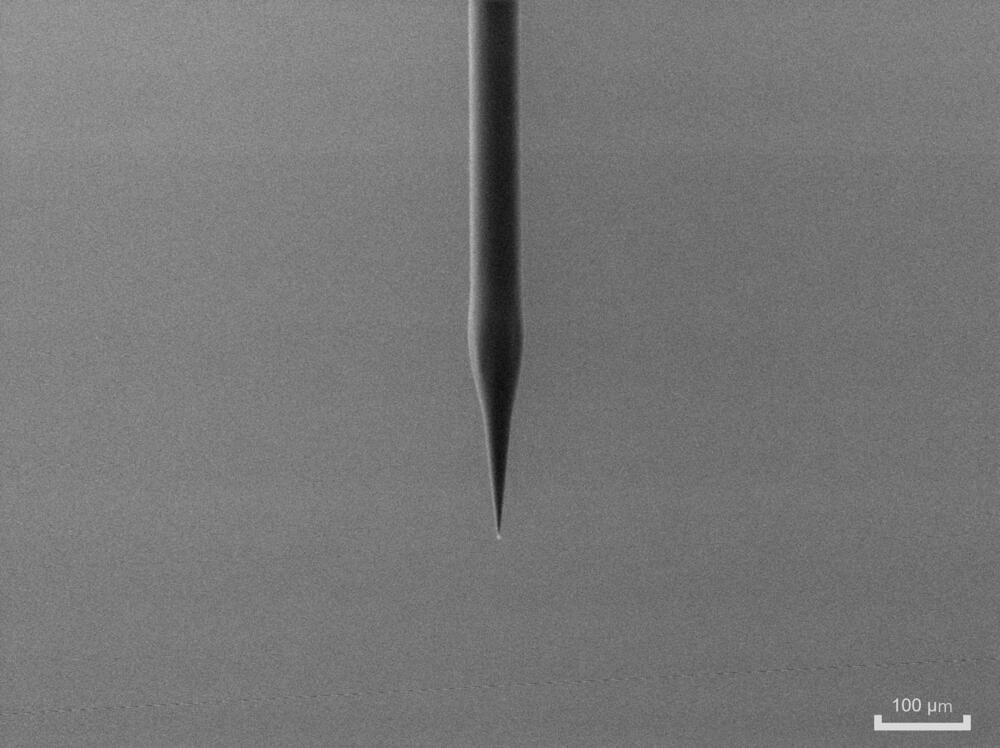
Researchers have developed a reliable and reproducible way to fabricate tapered polymer optical fibers that can be used to deliver light to the brain. These fibers could be used in animal studies to help scientists better understand treatments and interventions for various neurological conditions.
The tapered fibers are optimized for neuroscience research techniques, such as optogenetic experiments and fiber photometry, which rely on the interaction between genetically modified neurons and visible light delivered to and/or collected from the brain.
“Unlike standard optical fibers, which are cylindrical, the tapered fibers we developed have a conical shape, which allows them to penetrate the tissue with more ease and to deliver light to larger volumes of the brain,” said research team member Marcello Meneghetti from the Neural Devices and Gas Photonics group at the Technical University of Denmark.