Aug 27, 2019
Nanoparticles could someday give humans built-in night vision
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: entertainment, nanotechnology, space
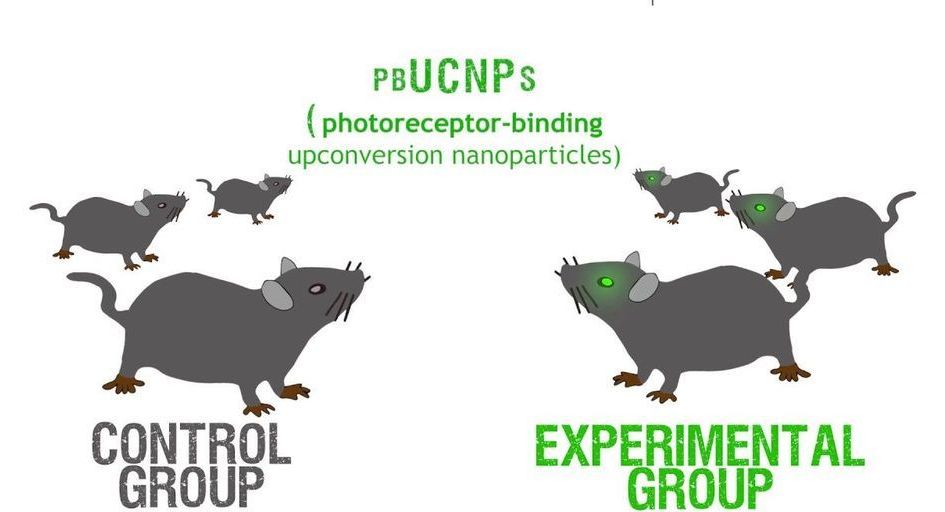
Movies featuring heroes with superpowers, such as flight, X-ray vision or extraordinary strength, are all the rage. But while these popular characters are mere flights of fancy, scientists have used nanoparticles to confer a real superpower on ordinary mice: the ability to see near-infrared light. Today, scientists report progress in making versions of these nanoparticles that could someday give built-in night vision to humans.
The researchers will present their results at the American Chemical Society (ACS) Fall 2019 National Meeting & Exposition.
Continue reading “Nanoparticles could someday give humans built-in night vision” »