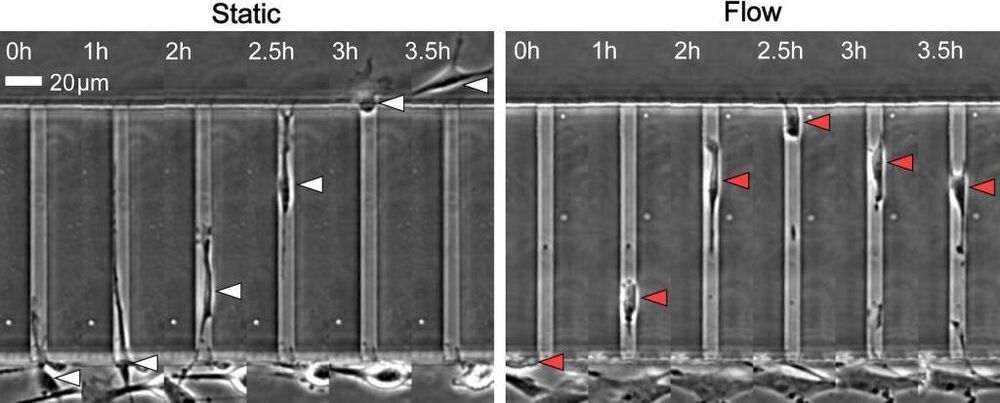
Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body.
“We have discovered that this protein, TRPM7, senses the pressure of fluid flowing in the circulation and stops the cells from spreading through the vascular system,” said Kaustav Bera, a Image 1: Overexpressing protein TRPM7 in cancer cells greatly reduces entry into the blood vessels. Image 2: In static conditions, cells enter microchannels, whereas 40-60% reverse direction when fluid is flowing. Courtesy of Johns Hopkins University.
Johns Hopkins University news releases are available online, as is information for reporters. To arrange an interview with a Johns Hopkins expert, contact a media representative listed above. Find more Johns Hopkins experts on the Experts Hub, and more Johns Hopkins stories on the Hub.