Putin might not use nukes. But someday, someone will.


Elliot Ackerman is following the crisis in Ukraine closely. The author and former U.S. marine served five tours of duty in Iraq and Afghanistan and has just spent two weeks in Kyiv. Ackerman joins Walter Isaacson to discuss Russia’s new tactics and the role of moral resolve in war.
Originally aired on March 30, 2022
For more from Amanpour and Company, including full episodes, click here: https://to.pbs.org/2NBFpjf.
Like Amanpour and Company on Facebook: https://bit.ly/2HNx3EF
How will it all end? By an asteroid, a science experiment gone wrong, or even a zombie invasion? Check out today’s insane new video to find out all the possible ways the world could actually come to an end!
🔔 SUBSCRIBE TO THE INFOGRAPHICS SHOW ►
🔖 MY SOCIAL PAGES
TikTok ► https://www.tiktok.com/@theinfographicsshow.
Discord ► https://discord.gg/theinfographicsshow.
Facebook ► https://www.facebook.com/TheInfographicsShow.
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/TheInfoShow.
💭 Find more interesting stuff on:
https://www.theinfographicsshow.com.
📝 SOURCES: https://pastebin.com/RAQwHgHz.
All videos are based on publicly available information unless otherwise noted.
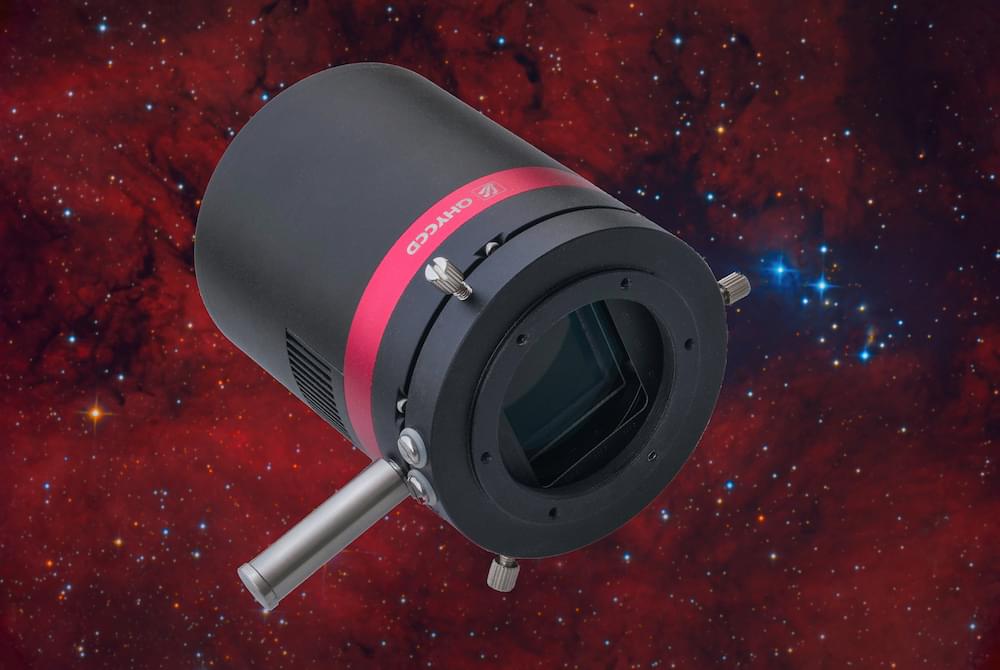

Move aside CCDs. Consumer CMOS cameras are here to stay.
For 20 years, I have been using charge-coupled device (CCD) cameras, and I currently own the top-of-the-line SBIG STX-16803. But while studying two images I recently made using the latest QHY 410C CMOS camera, I had to wonder: Is CCD dead?
For years, I lectured about the asymptotic boundary of noise in CCD images. In a basic sense, this means that no matter how many frames you take to increase your signal-to-noise ratio for a cleaner image, you will always run into a wall of noise when you stretch your image to bring out deep shadows. But with QHY’s new CMOS camera, this troublesome wall of noise is nonexistent.
The QHY 410C is a one-shot color camera that utilizes the back-illuminated Sony IMX410 CMOS chip found in high-end cameras like the Nikon Z6 and the Sony A7 III. But the 410C has taken the full-frame (35 millimeter) 24-megapixel chip and mounted it in a camera with regulated cooling and zero amplifier glow, helping drive the noise to such a low level.
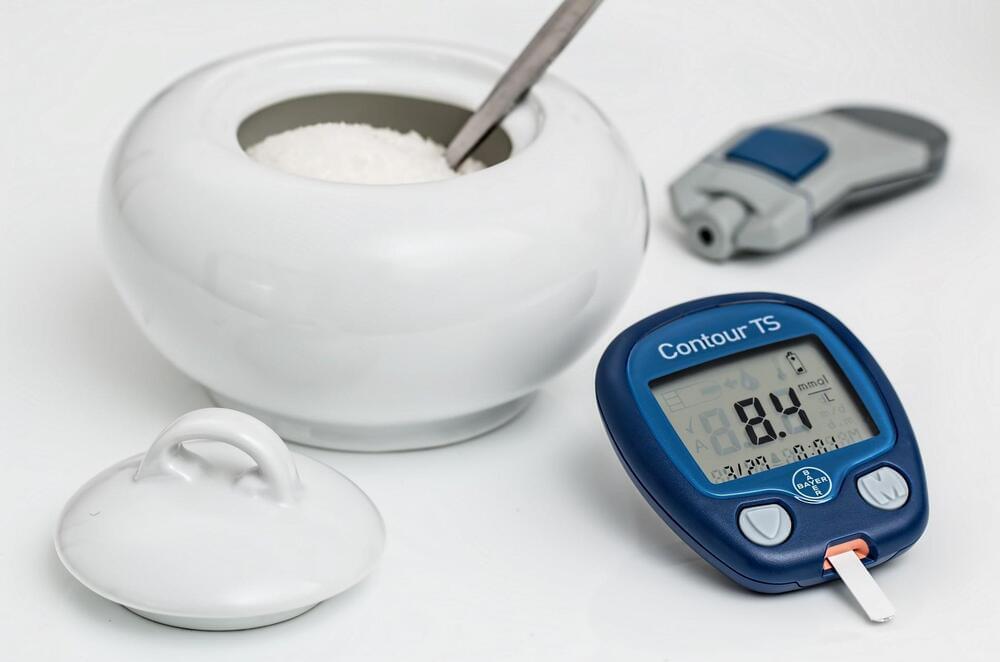
Some diabetes therapies work by ramping up the body’s secretion of insulin to counteract high blood sugar levels. | Preserving insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells—rather than exhausting them—might be a better strategy in the treatment of diabetes. Following that thinking, scientists at the Karolinska Institute found a cancer drug by Seagen holds promise for the metabolic disease.


►Is faster-than-light (FTL) travel possible? In most discussions of this, we get hung up on the physics of particular ideas, such as wormholes or warp drives. But today, we take a more zoomed out approach that addresses all FTL propulsion — as well as FTL messaging. Because it turns out that they all allow for time travel. Join us today as we explore why this is so and the profound consequences that ensue. Special thanks to Prof Matt.
Written & presented by Prof David Kipping. Special thanks to Prof Matt Buckley for fact checking and his great blog article that inspired this video (http://www.physicsmatt.com/blog/2016/8/25/why-ftl-implies-time-travel)
→ Support our research program: https://www.coolworldslab.com/support.
→ Get Stash here! https://teespring.com/stores/cool-worlds-store.
THANK-YOU to our supporters D. Smith, M. Sloan, C. Bottaccini, D. Daughaday, A. Jones, S. Brownlee, N. Kildal, Z. Star, E. West, T. Zajonc, C. Wolfred, L. Skov, G. Benson, A. De Vaal, M. Elliott, B. Daniluk, M. Forbes, S. Vystoropskyi, S. Lee, Z. Danielson, C. Fitzgerald, C. Souter, M. Gillette, T. Jeffcoat, H. Jensen, J. Rockett, N. Fredrickson, D. Holland, E. Hanway, D. Murphree, S. Hannum, T. Donkin, K. Myers, A. Schoen, K. Dabrowski, J. Black, R. Ramezankhani, J. Armstrong, K. Weber, S. Marks, L. Robinson, F. Van Exter, S. Roulier, B. Smith, P. Masterson, R. Sievers, G. Canterbury, J. Kill, J. Cassese, J. Kruger, S. Way, P. Finch, S. Applegate, L. Watson, T. Wheeler, E. Zahnle, N. Gebben, J. Bergman, E. Dessoi, J. Alexander, C. Macdonald, M. Hedlund, P. Kaup, C. Hays, S. Krasner, W. Evans, J. Curtin, J. Sturm, RAND Corp, T. Kordell, T. Ljungberg & M. Janke.
::References::
► Alcubierre, M., 1994, “The warp drive: hyper-fast travel within general relativity”, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 11 L73: https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/0009013
► Pfenning, M. & Ford, L., 1997, “The unphysical nature of Warp Drive”, Classical and Quantum Gravity, 14, 1743: https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9702026
► Finazzi, S., Liberati, S., Barceló, C., 2009, “Semiclassical instability of dynamical warp drives”, Physical Review D., 79, 124017: https://arxiv.org/abs/0904.0141
► McMonigal, B., Lewis, G., O’Byrne, P., 2012, “Alcubierre warp drive: On the matter of matter”, Physical Review D., 85, 064024: https://arxiv.org/abs/1202.5708
► Everett, A., 1996, “Warp drive and causality”, Physical Review D, 53, 7365: https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.53.
::Music::
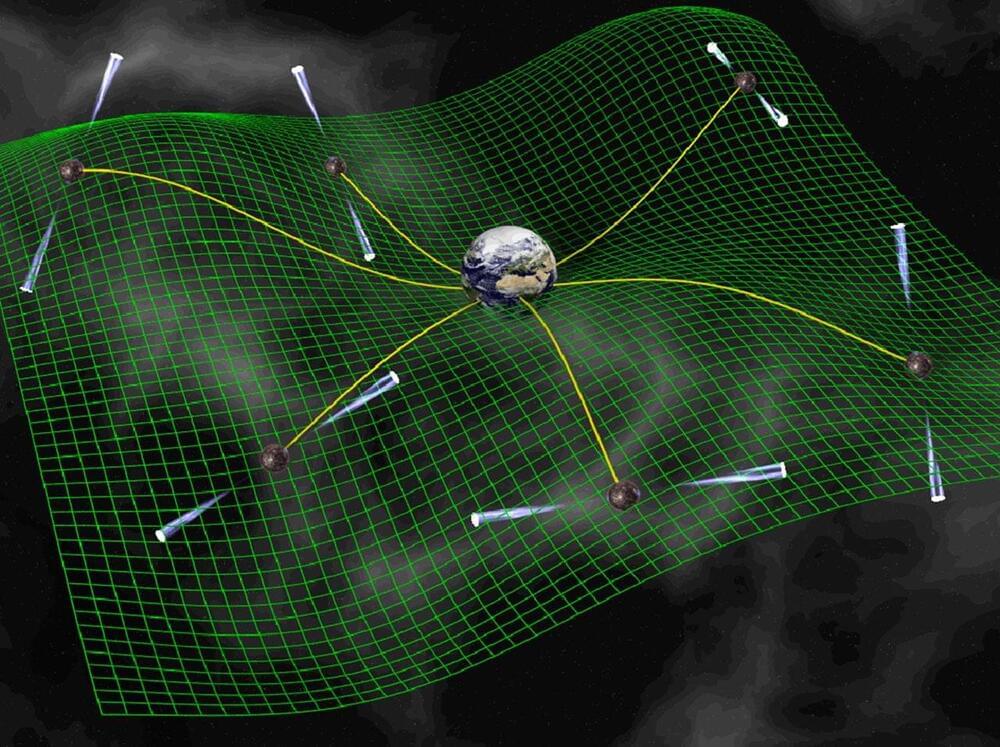
Stephen Taylor, assistant professor of physics and astronomy and former astronomer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), said, “Using the pulsars we observe across the Milky Way galaxy, we are trying to be like a spider sitting in stillness in the middle of her web. How well we understand the solar system barycenter is critical as we attempt to sense even the smallest tingle to the web. The solar system barycenter, its center of gravity, is the location where the masses of all planets, moons, and asteroids balance out.”
So, where is the center of the solar system?
It is not in the center of the Sun as many might assume, instead it is closer to the surface of the star. This is due to Jupiter’s mass and our imperfect knowledge of its orbit.