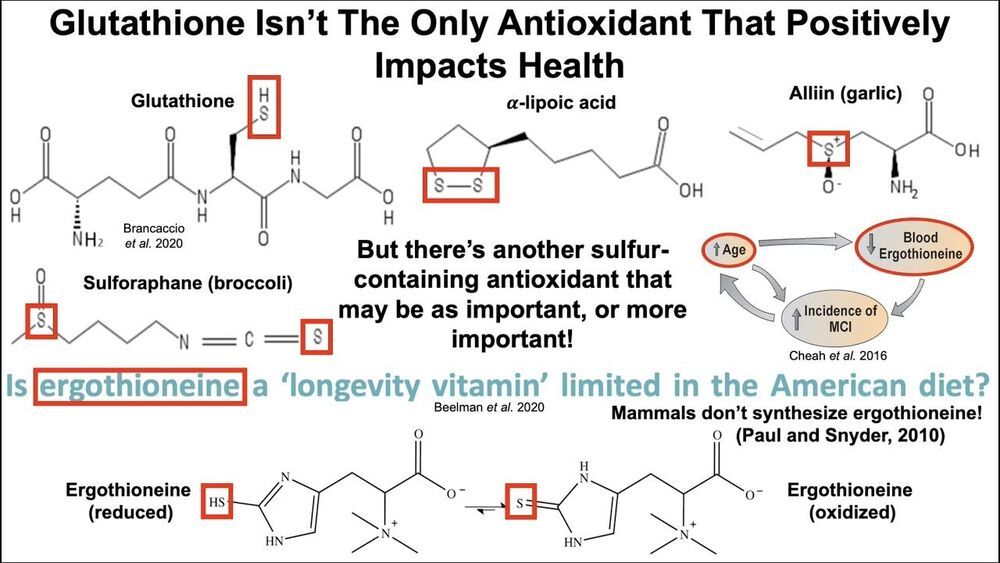
The more data collected, the better the results.
Understanding the genetics of complex diseases, especially those related to the genetic differences among ethnic groups, is essentially a big data problem. And researchers need more data.
1000, 000 genomes
To address the need for more data, the National Institutes of Health has started a program called All of Us. The project aims to collect genetic information, medical records and health habits from surveys and wearables of more than a million people in the U.S. over the course of 10 years. It also has a goal of gathering more data from underrepresented minority groups to facilitate the study of health disparities. The All of Us project opened to public enrollment in 2018, and more than 270000 people have contributed samples since. The project is continuing to recruit participants from all 50 states. Participating in this effort are many academic laboratories and private companies.