May 28, 2020
Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2
Posted by Nicholi Avery in category: biotech/medical
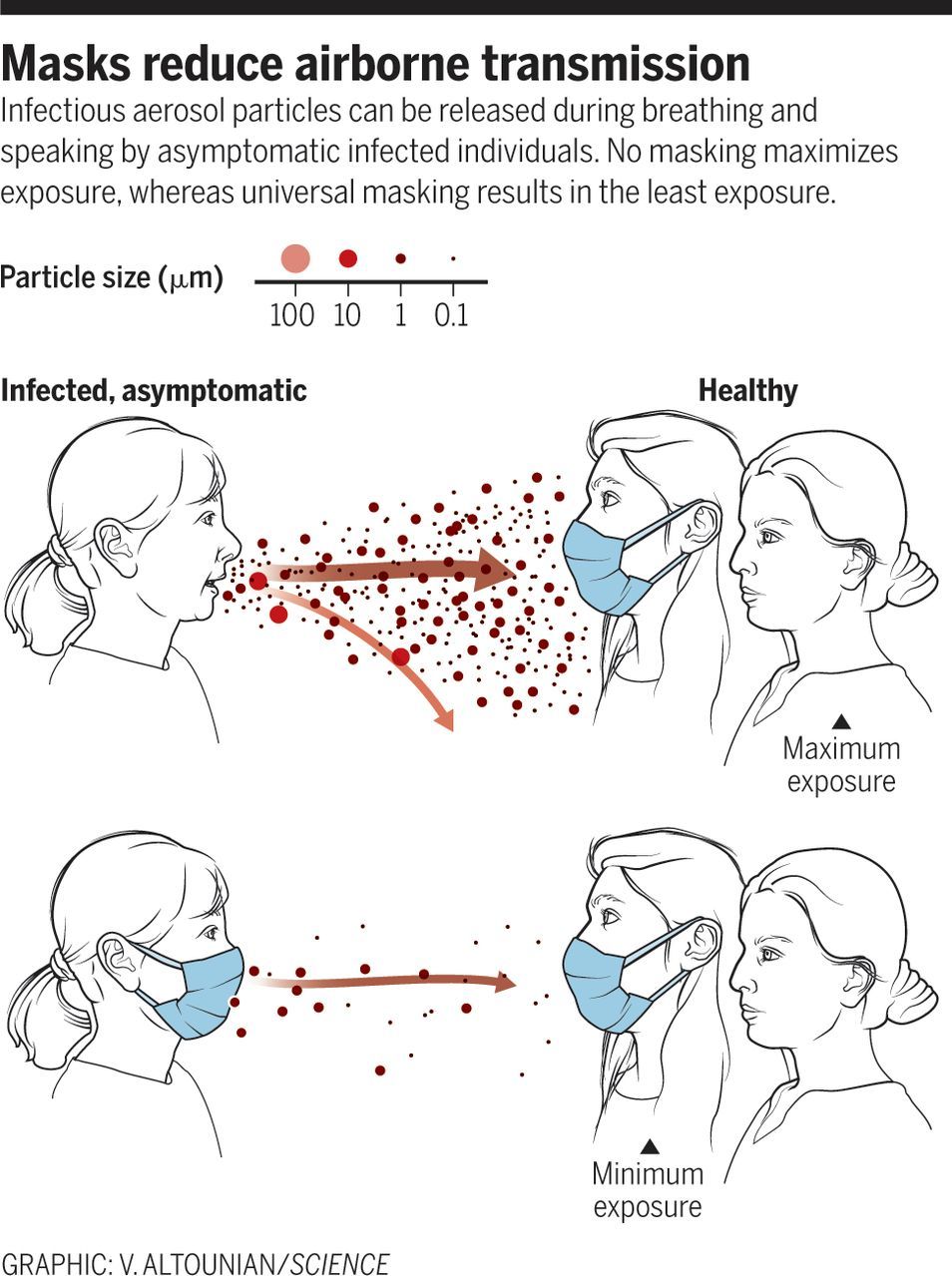
Masks and testing are necessary to combat asymptomatic spread in aerosols and droplets.
Respiratory infections occur through the transmission of virus-containing droplets (5 to 10 μm) and aerosols (≤5 μm) exhaled from infected individuals during breathing, speaking, coughing, and sneezing. Traditional respiratory disease control measures are designed to reduce transmission by droplets produced in the sneezes and coughs of infected individuals. However, a large proportion of the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) appears to be occurring through airborne transmission of aerosols produced by asymptomatic individuals during breathing and speaking (1–3). Aerosols can accumulate, remain infectious in indoor air for hours, and be easily inhaled deep into the lungs. For society to resume, measures designed to reduce aerosol transmission must be implemented, including universal masking and regular, widespread testing to identify and isolate infected asymptomatic individuals.
Humans produce respiratory droplets ranging from 0.1 to 1000 μm. A competition between droplet size, inertia, gravity, and evaporation determines how far emitted droplets and aerosols will travel in air (4, 5). Respiratory droplets will undergo gravitational settling faster than they evaporate, contaminating surfaces and leading to contact transmission. Smaller aerosols (≤5 μm) will evaporate faster than they can settle, are buoyant, and thus can be affected by air currents, which can transport them over longer distances. Thus, there are two major respiratory virus transmission pathways: contact (direct or indirect between people and with contaminated surfaces) and airborne inhalation.