These studies provide a clear proof of principle for a new type of gene therapy in which one copy of a mutated gene could be repaired from a partially intact second copy of the gene,” said Bier, senior author of the Nature Communications study and science director for the Tata Institute for Genetics and Society-UC San Diego. “The need for such a design occurs in genetic situations with patients with inherited genetic disorders, if their parents were carriers for two different mutations in the same gene.
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have laid the groundwork for a potential new type of gene therapy using novel CRISPR-based techniques.
Working in fruit flies and human cells, research led by UC San Diego Postdoctoral Scholar Zhiqian Li in Division of Biological Sciences Professor Ethan Bier’s laboratory demonstrates that new DNA repair mechanisms could be designed to address the effects of debilitating diseases and damaged cell conditions.
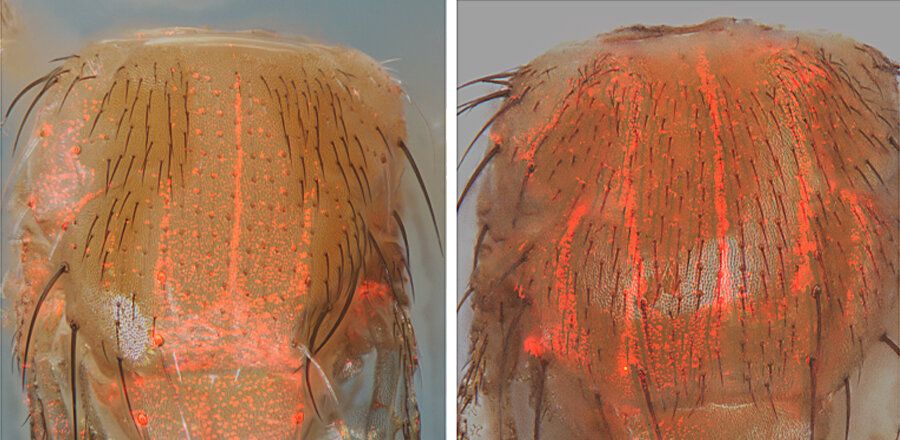
The scientists developed a novel genetic sensor called a ‘CopyCatcher,’ which capitalizes on CRISPR-based gene drive technology, to detect instances in which a genetic element is copied precisely from one chromosome to another throughout cells in the body of a fruit fly.