The space rock (7482) 1994 PC1, which is more than twice the height of the Empire State Building, will whiz by our planet on Jan. 18.



Technology changes every day. And faster and faster with every passing year. There is no denying it: the singularity is coming. The robot revolution is marching ever closer. And it all begins here. Here are some examples of future technology that will change the world!
► For copyright matters please contact us: [email protected]

The Neuro-Network.
𝐓𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐬𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐚 𝐩𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬 𝐦𝐚𝐲 𝐛𝐞 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐜𝐢𝐨𝐮𝐬 𝐛𝐮𝐭 𝐰𝐞’𝐫𝐞 𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐦, 𝐬𝐚𝐲𝐬 𝐩𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐧𝐞𝐮𝐫𝐨𝐬𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐬𝐭
𝙄𝙩’𝙨 𝙪𝙨𝙪𝙖𝙡𝙡𝙮 𝙖𝙨𝙨𝙪𝙢𝙚𝙙 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙖 𝙥𝙚𝙧𝙨𝙤𝙣 𝙞𝙣 𝙖 𝙫𝙚𝙜𝙚𝙩𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝙨𝙩𝙖𝙩𝙚 𝙝𝙖𝙨… See more.
It’s usually assumed that a person in a vegetative state has no awareness of the world around them. Dr Adrian Owen, who pioneered groundbreaking research that has proven otherwise, explains why we need to be talking to these patients.


🌱 🤓 This week I helped with the latest experiment going on in the International Space Station plant habitat which cultivates several cotton genotypes. Each of these petri dishes contains undifferentiated masses of cotton cells known as a calli. Cotton is highly resistant to the process of plant regeneration, making it difficult to engineer stable, reproducing plants that have specific or enhanced traits such as drought resistance. The investigation could provide a better understanding of this behavior and could ultimately improve our ability to grow crop plants on Earth and in space.
Photo credit: Mark Vande Hei.
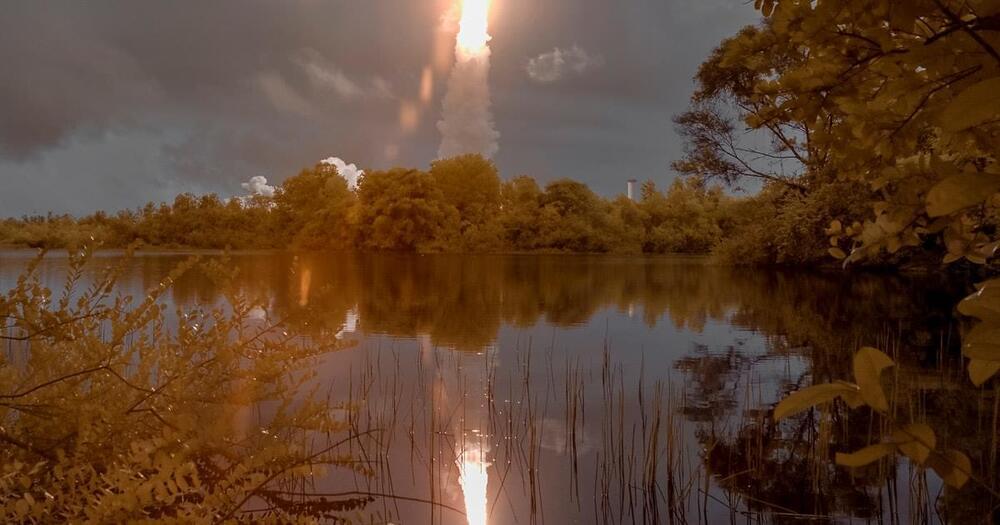
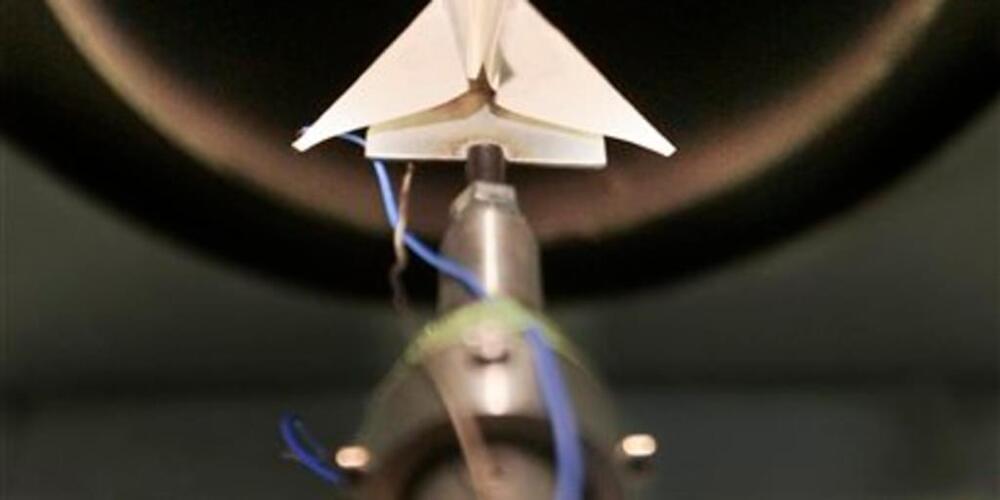

NASA announced that James Webb telescope course corrections used less fuel than expected, which means Webb can expect to work for more than 10 years.
And as NASA announced Wednesday morning, Webb may get to peer deep into the universe for even longer than expected: Webb used less of its limited supply of propellant during two course-correction thruster burns after launch than expected, and the space agency says it should have enough left over to enable operations “significantly” longer than the expected 10-year mission.

The James Webb just deployed another important instrument — the aft momentum flap — that will keep the telescope steady as it makes its groundbreaking observations.
On December 25th, 2021, astronomers and space exploration enthusiasts got the greatest Christmas present of all! After years of delays, cost overruns, and additional testing, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) launched from Europe’s Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana. In what was a real nail-biter, the Ariane 5 rocket and its precious payload reached orbit without a hitch. But as is so often the case, the deployment of the JWST was just the first in a series of “hurry up and wait” episodes.
Typically, periods of waiting are seeing are accompanied by plenty of worry and doubt. Luckily, there have been several positive developments since the JWST launched that could help alleviate these anxieties. The latest is how the telescope successfully deployed its aft momentum flap, an instrument that will keep the telescope oriented during its mission. The news was announced yesterday (December 30th) via @NASAWebb, NASA’s official Twitter account for the Webb telescope, and the JWST page at NASA Blogs.
According to NASA Blogs, the deployment of the aft momentum flap began at 09:00 AM EST (06:00 AM PST) and lasted about eight minutes. During this time, the mission team released the flap’s hold-down devices while a spring brought the flap into its final position. The purpose of this flap is to maintain the observatory’s orientation to minimize the fuel engineers will need to make corrective adjustments throughout the mission.