
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.




Dead eyes brought back to life
“This new study joins a growing body of scientific evidence that raises questions about the irreversible nature of death…”
Scientists have revived light-sensing neuron cells in organ donor eyes and restored communication between them as part of a series of discoveries that could transform research into the brain-vision system.
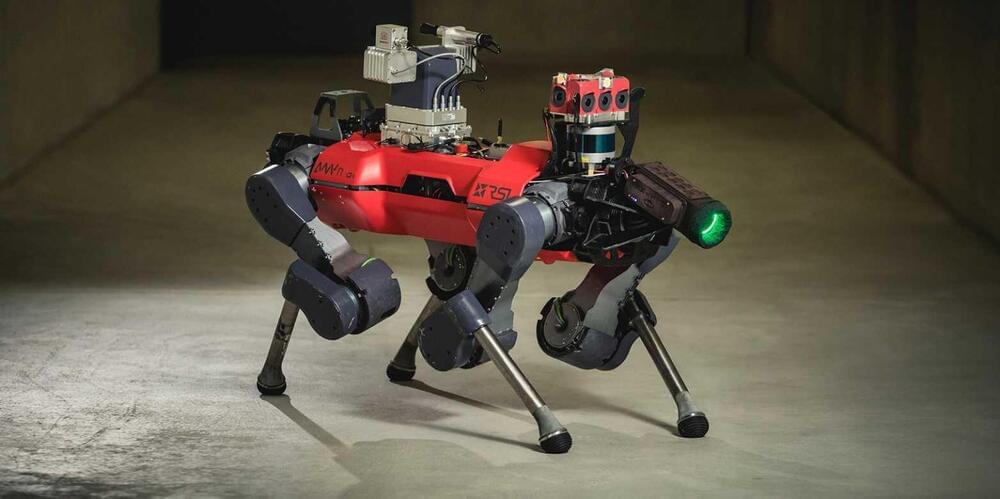


Robot dog may get to go to the moon
The robotic explorer GLIMPSE, created at ETH Zurich and the University of Zurich, has made it into the final round of a competition for prospecting resources in space. The long-term goal is for the robot to explore the south polar region of the moon.
The south polar region of the moon is believed to contain many resources that would be useful for lunar base operations, such as metals, water in the form of ice, and oxygen stored in rocks. But to find them, an explorer robot that can withstand the extreme conditions of this part of the moon is needed. Numerous craters make moving around difficult, while the low angle of the sunlight and thick layers of dust impede the use of light-based measuring instruments. Strong fluctuations in temperature pose a further challenge.
The European Space Agency (ESA) and the European Space Resources Innovation Center ESRIC called on European and Canadian engineering teams to develop robots and tools capable of mapping and prospecting the shadowy south polar region of the moon, between the Shoemaker and the Faustini craters. To do this, the researchers had to adapt terrestrial exploration technologies for the harsh conditions on the moon.
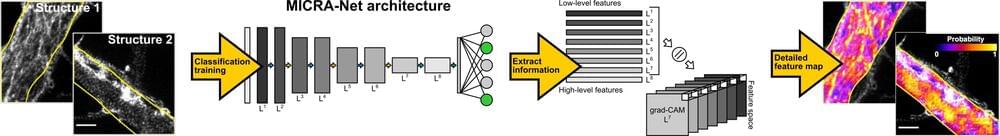
A weakly supervised machine learning model to extract features from microscopy images
Deep learning models have proved to be highly promising tools for analyzing large numbers of images. Over the past decade or so, they have thus been introduced in a variety of settings, including research laboratories.
In the field of biology, deep learning models could potentially facilitate the quantitative analysis of microscopy images, allowing researchers to extract meaningful information from these images and interpret their observations. Training models to do this, however, can be very challenging, as it often requires the extraction of features (i.e., number of cells, area of cells, etc.) from microscopy images and the manual annotation of training data.
Researchers at CERVO Brain Research Center, the Institute for Intelligence and Data, and Université Laval in Canada have recently developed an artificial neural network that could perform in-depth analyses of microscopy images using simpler, image-level annotations. This model, dubbed MICRA-Net (MICRoscopy Analysis neural network), was introduced in a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence.

Eavesdroppers can hack 6G frequency with DIY metasurface
Crafty hackers can make a tool to eavesdrop on some 6G wireless signals in as little as five minutes using office paper, an inkjet printer, a metallic foil transfer and a laminator.
The wireless security hack was discovered by engineering researchers from Rice University and Brown University, who will present their findings and demonstrate the attack this week in San Antonio at ACM WiSec 2022, the Association for Computing Machinery’s annual conference on security and privacy in wireless and mobile networks.
“Awareness of a future threat is the first step to counter that threat,” said study co-author Edward Knightly, Rice’s Sheafor-Lindsay Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering. “The frequencies that are vulnerable to this attack aren’t in use yet, but they are coming and we need to be prepared.”

Rapid Neutron Capture: Astronomers Discover “Gold Standard” Star in Milky Way
A team of astronomers led by University of Michigan’s Ian Roederer and including Carnegie’s Erika Holmbeck have identified the widest range of elements yet observed in a star beyond our own Sun. Their findings will be published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series.
The researchers identified 65 elements in the star, which is called HD 222925. Of these, 42 are from the bottom of the periodic table. Their identification will help astronomers better understand rapid neutron capture process — one of the main methods by which the universe’s heavy elements were created.
“To the best of my knowledge, that’s a record for any object beyond our Solar System. And what makes this star so unique is that it has a very high relative proportion of the elements listed along the bottom two-thirds of the periodic table. We even detected gold,” explained Roederer, a former Carnegie postdoc. “These elements were made by the rapid neutron capture process. That’s really the thing we’re trying to study: the physics in understanding how, where and when those elements were made.”

Lighting up artificial neural networks with optomemristors
A team of international scientists have performed difficult machine learning computations using a nano-scale device, named an “optomemristor.”
The chalcogenide thin-film device uses both light and electrical signals to interact and emulate multi-factor biological computations of the mammalian brain while consuming very little energy.
To date, research on hardware for artificial intelligence and machine learning applications has concentrated mainly on developing electronic or photonic synapses and neurons, and combining these to carry out basic forms of neural-type processing.