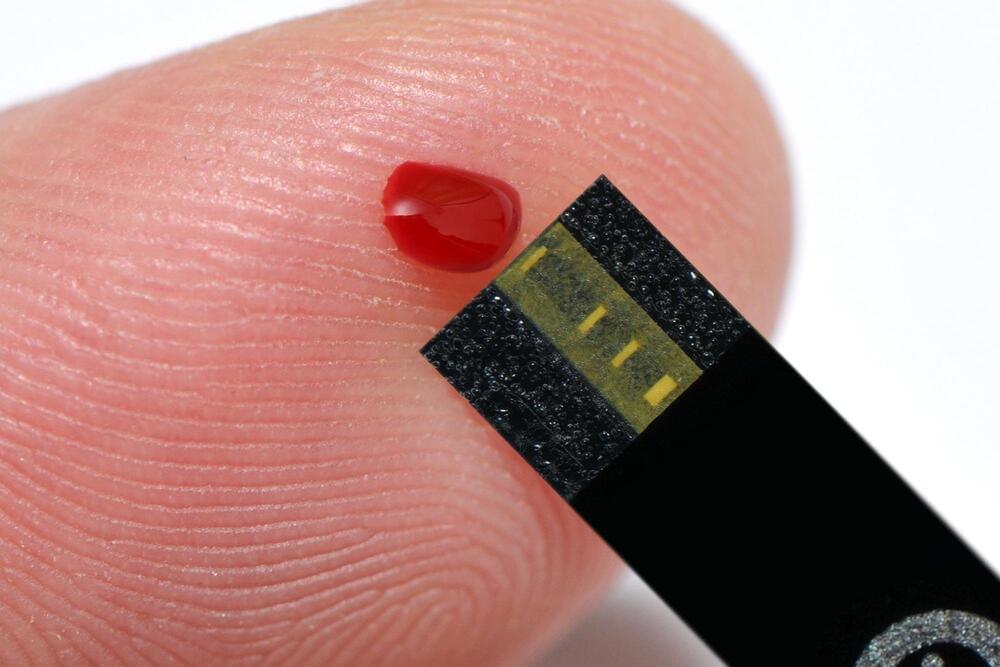
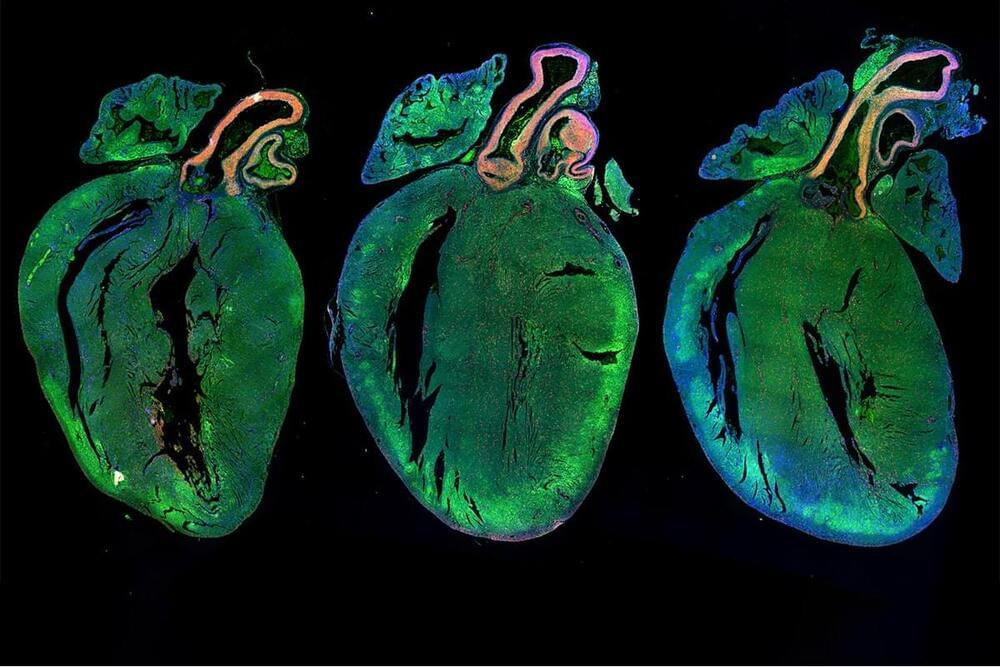
Eight cutting-edge heart failure projects are set to receive millions of pounds’ worth of funding from the British Heart Foundation (BHF) this year, with the money raised, fittingly enough, by the London Marathon.
Longevity. Technology: Heart disease is the world’s greatest killer, with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year [1]. With organs for transplant in short supply, the focus is turning to regenerative medicine – getting the heart to repair itself – and the BHF is planning to fund eight projects all aimed at finding ways to cure heart failure. Given that a picture paints a thousand words, BHF has made the smart move of showcasing this regenerative research through a stunning set of images that shows the Foundation’s desire to not just ameliorate the symptoms of heart disease, or to extend patients’ lives, but to cure heart disease by regenerating, regrowing or replacing damaged cells and tissues.
“Heart failure is a debilitating condition that dramatically affects the lives of almost 1 million people in the UK,” commented Professor Metin Avkiran, BHF Associate Medical Director. “BHF-funded research has spear-headed treatments to give people with heart failure longer, healthier lives, but there is no cure. Regenerative medicine offers that hope.