The dream of transforming windows into active power generators has just edged one step closer to realization.
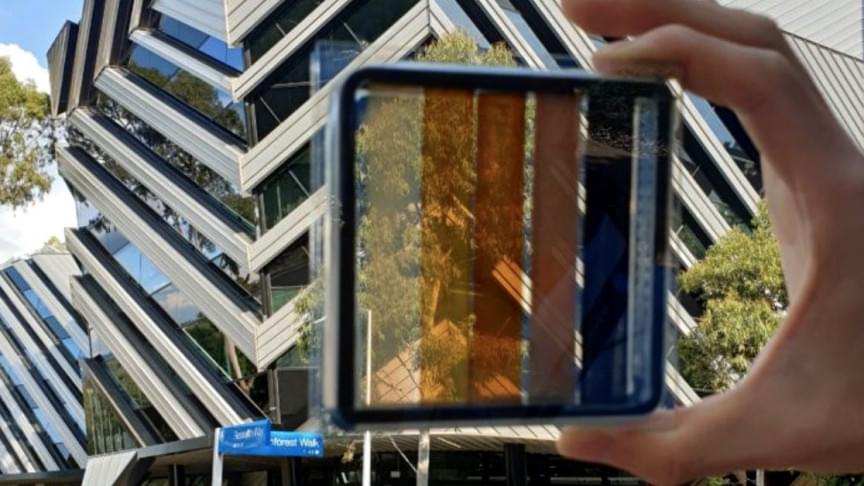
A team of researchers from ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science led by Professor Jacek Jasieniak from Monash University’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering has created perovskite cells with a conversion efficiency of 15.5 percent that allows more than 20 percent of visible light through, a press release states.
This improves the stability of solar windows while allowing more natural light in, which means the amount of visible light passing through the cells is remarkably now reaching glazing levels, increasing their potential for usage in a wide range of real-world applications.