This novel material was made using a process that the team developed called a “float assembly method.” The float assembly takes advantage of the Marangoni effect, which occurs in two liquid phases with different surface tensions. When there is a gradient in surface tension, a Marangoni flow is generated away from the region with lower surface tension towards the region with higher surface tension. This means that dropping a liquid with lower surface tension on the water surface lowers the surface tension locally, and the resulting Marangoni flow causes the dropped liquid to spread thinly across the surface of the water.
The nanomembrane is created using a float assembly method which consists of a three-step process. The first step involves dropping a composite solution, which is a mixture of metal nanowires, rubber dissolved in toluene, and ethanol, on the surface of the water. The toluene-rubber phase remains above the water due to its hydrophobic property, while the nanowires end up on the interface between the water and toluene phases. The ethanol within the solution mixes with the water to lower the local surface tension, which generates Marangoni flow that propagates outward and prevents the aggregation of the nanowires. This assembles the nanomaterials into a monolayer at the interface between water and a very thin rubber/solvent film. In the second step, the surfactant is dropped to generate a second wave of Marangoni flow which tightly compacts the nanowires. Finally, in the third step, the toluene is evaporated and a nanomembrane with a unique structure in which a highly compacted monolayer of nanowires is partially embedded in an ultrathin rubber film is obtained.
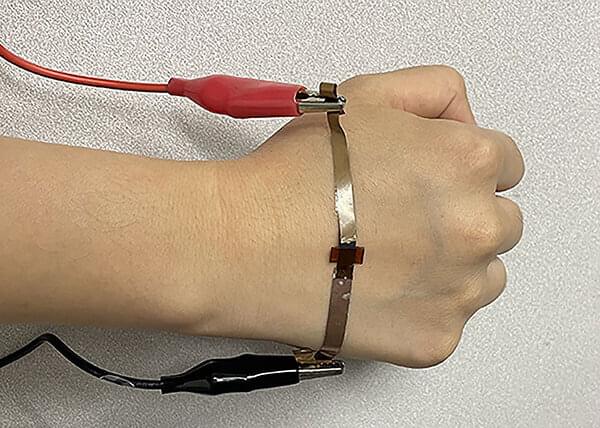
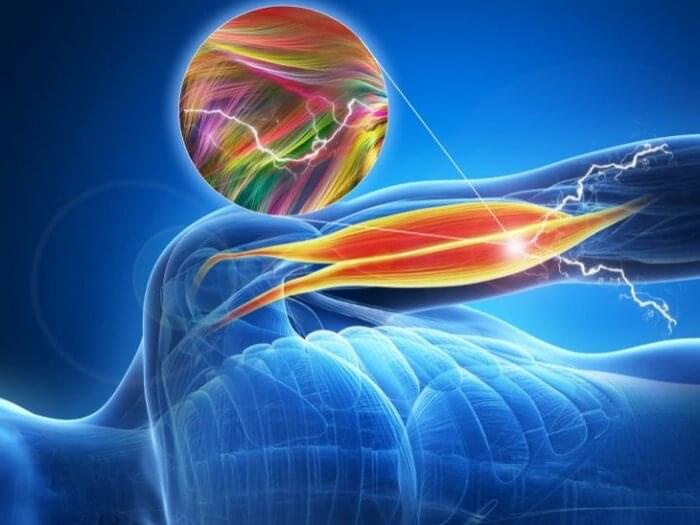
Its unique structure allows efficient strain distribution in ultrathin rubber film, leading to excellent physical properties, such as a stretchability of over 1,000%, and a thickness of only 250 nm. The structure also allows cold welding and bi-layer stacking of the nanomembrane onto each other, which leads to a metal-like conductivity over 100,000 S/cm. Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated that the nanomembrane can be patterned using photolithography, which is a key technology that is widely used for manufacturing commercial semiconductor devices and advanced electronics. Therefore, it is expected that the nanomembrane can serve as a new platform material for skin electronics.