CERT-UA alerts on fake AnyDesk requests posing as audits; 1,042 cyber incidents hit Ukraine in 2024.
4.2M hosts, including VPNs and routers, face risks from unencrypted tunneling protocols like GRE6 enabling DDoS.
Gould’s thesis has sparked widespread debate ever since, with some advocating for determinism and others supporting contingency. In his 1952 short story A Sound of Thunder, science fiction author Ray Bradbury recounted how a time traveler’s simple act of stepping on a butterfly in the age of the dinosaurs changed the course of the future. Gould made a similar point: “Alter any early event, ever so slightly and without apparent importance at the time, and evolution cascades into a radically different channel.”
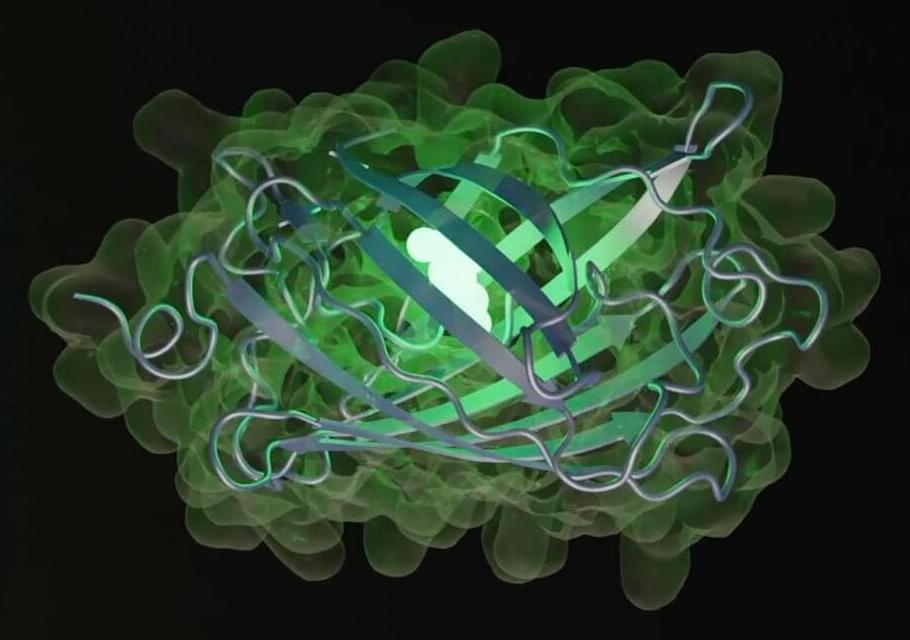
Scientists have been exploring this problem through experiments designed to recreate evolution in the lab or in nature, or by comparing species that have emerged under similar conditions. Today, a new avenue has opened up: AI. In New York, a group of former researchers from Meta — the parent company of social networks Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp — founded EvolutionaryScale, an AI startup focused on biology. The EvolutionaryScale Model 3 (ESM3) system created by the company is a generative language model — the same kind of platform that powers ChatGPT. However, while ChatGPT generates text, ESM3 generates proteins, the fundamental building blocks of life.
ESM3 feeds on sequence, structure, and function data from existing proteins to learn the biological language of these molecules and create new ones. Its creators have trained it with 771 billion data packets derived from 3.15 billion sequences, 236 million structures, and 539 million functional traits. This adds up to more than one trillion teraflops (a measure of computational performance) — the most computing power ever used in biology, according to the company.
Harnessing Terahertz Light for Magnetic Control
MIT physicists have discovered a way to create a new, long-lasting magnetic state in a material using only light.
HERSHEY, Pa. — Immunotherapies that mobilize a patient’s own immune system to fight cancer have become a treatment pillar. These therapies, including CAR T-cell therapy, have performed well in cancers like leukemias and lymphomas, but the results have been less promising in solid tumors.
A team led by researchers from the Penn State College of Medicine has re-engineered immune cells so that they can penetrate and kill solid tumors grown in the lab. They created a light-activated switch that controls protein function associated with cell structure and shape and incorporated it into natural killer cells, a type of immune cell that fights infections and tumors. When these cells are exposed to blue light, they morph and can then migrate into tumor spheroids — 3D tumors grown in the lab from either mouse or human cell lines — and kill tumor cells. This novel approach could improve cell-based immunotherapies, the researchers said.
The findings were published today (Oct 23) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The researchers also filed a provisional application to patent the technology described in the paper.
On a broader level, by pushing AI toward more human-like processing, Titans could mean AI that thinks more deeply than humans — challenging our understanding of human uniqueness and our role in an AI-augmented world.
At the heart of Titans’ design is a concerted effort to more closely emulate the functioning of the human brain. While previous models like Transformers introduced the concept of attention—allowing AI to focus on specific, relevant information—Titans takes this several steps further. The new architecture incorporates analogs to human cognitive processes, including short-term memory, long-term memory, and even the ability to “forget” less relevant information. Perhaps most intriguingly, Titans introduces a concept that’s surprisingly human: the ability to prioritize surprising or unexpected information. This mimics the human tendency to more easily remember events that violate our expectations, a feature that could lead to more nuanced and context-aware AI systems.
The key technical innovation in Titans is the introduction of a neural long-term memory module. This component learns to memorize historical context and works in tandem with the attention mechanisms that have become standard in modern AI models. The result is a system that can effectively utilize both immediate context (akin to short-term memory) and broader historical information (long-term memory) when processing data or generating responses.
I was recently a co-author on a paper about anticipatory governance and genome editing. The lead author was Jon Rueda, and the others were Seppe Segers, Jeroen Hopster, Belén Liedo, and Samuela Marchiori. It’s available open access here on the Journal of Medical Ethics website. There is a short (900 word) summary available on the JME blog. Here’s a quick teaser for it:
Transformative emerging technologies pose a governance challenge. Back in 1980, a little-known academic at the University of Aston in the UK, called David Collingridge, identified the dilemma that has come to define this challenge: the control dilemma (also known as the ‘Collingridge Dilemma’). The dilemma states that, for any emerging technology, we face a trade-off between our knowledge of its impact and our ability to control it. Early on, we know little about it, but it is relatively easy to control. Later, as we learn more, it becomes harder to control. This is because technologies tend to diffuse throughout society and become embedded in social processes and institutions. Think about our recent history with smartphones. When Steve Jobs announced the iPhone back in 2007, we didn’t know just how pervasive and all-consuming this device would become. Now we do but it is hard to put the genie back in the bottle (as some would like to do).
The field of anticipatory governance tries to address the control dilemma. It aims to carefully manage the rollout of an emerging technology so as to avoid the problem of losing control just as we learn more about the effects of the technology. Anticipatory governance has become popular in the world of responsible innovation and design. In the field of bioethics, approaches to anticipatory governance often try to anticipate future technical realities, ethical concerns, and incorporate differing public opinion about a technology. But there is a ‘gap’ in current approaches to anticipatory governance.
It has gotten to the point now that I find myself trying to make sense of them all. If you were to read them, what would you learn about me and my beliefs? Are there any coherent themes and patterns within these papers? I think there are and this is my attempt to hunt them out. I’m sure this will seem self-indulgent to some of you. I can only apologise. It is a deliberately self-indulgent exercise, but hopefully the thematic organisation is of interest to people other than myself, and some of the arguments may be intriguing or pique your curiosity. I’m going to keep this overview updated.
Reading note: There is some overlap in content between the sections below since some papers belonged to more than one theme. Also, clicking on the titles of the papers will take you directly to an open access version of them.
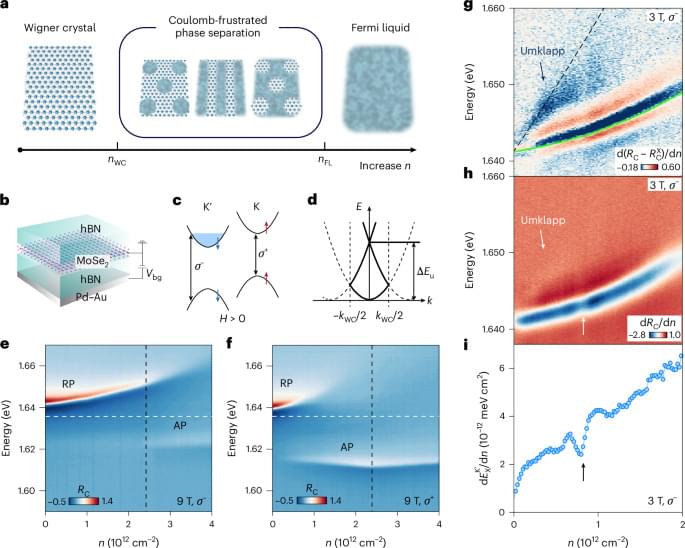
Competition between different possible ground states of strongly correlated electron systems can lead to the emergence of mixed states called microemulsions. Now this phenomenon is reported at the meltingion of a Wigner crystal.
In the world of tiny particles and quantum physics, scientists often study how electrons—the fundamental particles that carry electricity—behave under different conditions. When electrons interact strongly with each other, they can form various states of matter, much like how water can turn into ice or steam. Sometimes, these states compete, leading to complex and fascinating patterns. One such pattern is called a microemulsion phase, where tiny regions of different electron states mix together, creating a kind of quantum “patchwork quilt.”
In this study, researchers explored a special material called a MoSe₂ monolayer, which is an ultra-thin layer of atoms that can host electrons. By cooling this material to extremely low temperatures and using advanced light-based techniques, they observed something remarkable: aion between two electron states—a rigid Wigner crystal (where electrons are locked in place) and a flowing electron liquid. During thision, the electrons formed a microemulsion phase, blending crystal-like and liquid-like regions in a unique, self-organized pattern.
The team detected this phase by looking for specific clues, such as changes in how light reflects off the material, how the electrons respond to magnetic fields, and how they scatter off each other. These clues confirmed that the microemulsion is a distinct and exotic state of electronic matter, offering new insights into how electrons can organize themselves in surprising ways. This discovery not only deepens our understanding of quantum materials but also opens the door to exploring new phases of matter that could one day power advanced technologies.
Women are now being diagnosed with cancer more often than men in certain age groups, according to a new report from the American Cancer Society.
Among adults aged 50–64, cancer rates are slightly higher in women, and women under 50 are almost twice as likely as men in the same age group to receive a cancer diagnosis.
The report, released Thursday, found that while deaths continue to decrease, troubling racial disparities persist, with white Americans more likely to survive cancer than other groups.