Perseverance will obtain additional imagery of the sample tube before potentially completing the process of collecting its first scientifically-selected Mars sample.
Mars feature.



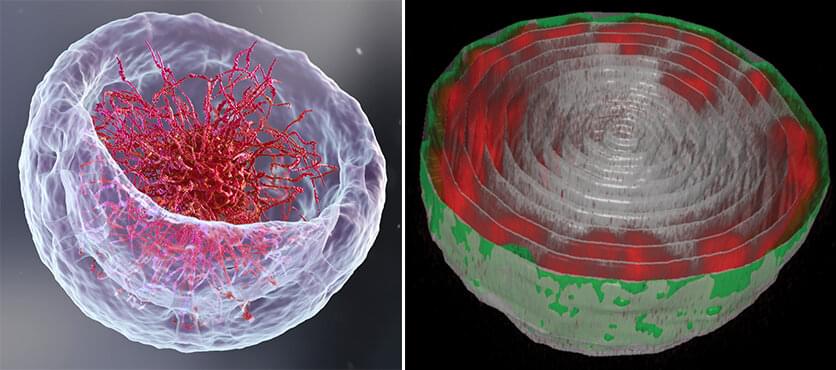
The groups also explained why in previous studies by other scientists, the chromatin appeared to fill the cell nuclei. “When scientists plate cells on a glass slide in order to study them under a microscope, they change their volume and physically flatten them. This may perturb some of the forces governing chromatin arrangement and reduce the distance between the upper part of the nucleus to its base,” Safran explains.
If you open a biology textbook and run through the images depicting how DNA is organized in the cell’s nucleus, chances are you’ll start feeling hungry; the chains of DNA would seem like a bowl of ramen: long strings floating in liquid. However, according to two new studies—one experimental and the other theoretical—that are the outcome of the collaboration between the groups of Prof. Talila Volk of the Molecular Genetics Department and Prof. Sam Safran of the Chemical and Biological Physics Department at the Weizmann Institute of Science, this image should be reconsidered. Clarifying it is essential since DNA’s spatial arrangement in the nucleus can affect the expression of genes contained within the DNA molecule, and hence the proteins found in the cell.
This story began when Volk was studying how mechanical forces influence cell nuclei in the muscle and found evidence that muscle contractions had an immediate effect on gene expression patterns. “We couldn’t explore this further because existing methods relied on imaging of chemically preserved cells, so they failed to capture what happens in the cell nuclei of an actual working muscle,” she says.
To address this issue, Dr. Dana Lorber, a research associate in Volk’s group, led the design of a device that makes it possible to study muscle nuclei in live fruit fly larvae. The device holds the tiny, translucent larva within a groove that allows it to contract and relax its muscles but keeps its movement constrained so that it can be scanned by a fluorescence microscope. Using the device, the researchers obtained images of the internal, linearly-organized complexes of DNA and its proteins (known as chromatin), surrounded by the membrane of the muscle nuclei.
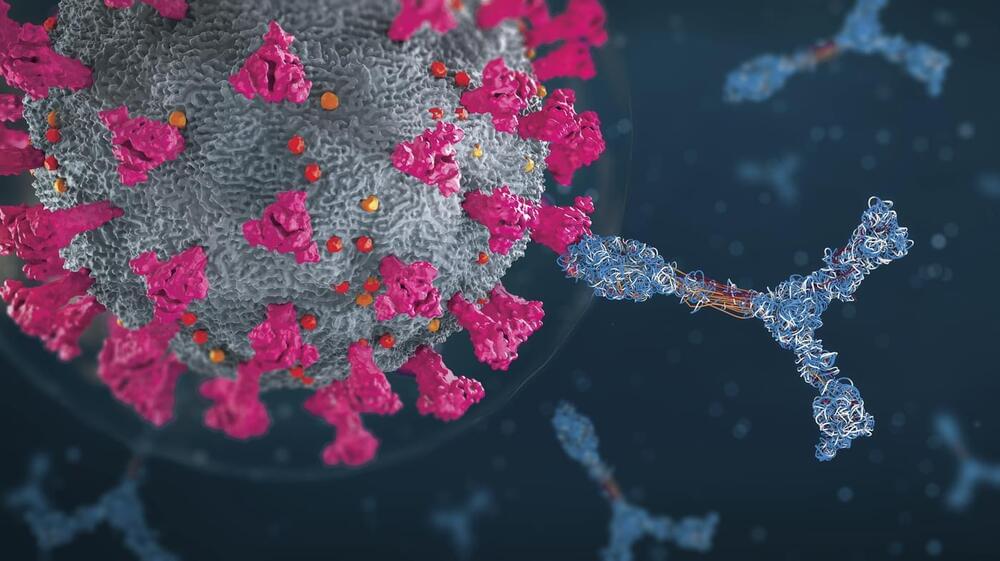
In fact, these antibodies could even fight off a virus engineered, on purpose, to be highly resistant to neutralization. This virus contained 20 mutations that are known to prevent SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from binding to it. Antibodies from people who were only vaccinated or only had prior COVID infections were essentially useless against this mutant virus. But antibodies in people with the “hybrid immunity” could neutralize it.
That’s how one scientist describes the findings of a series of studies looking at the antibodies created by individuals who were infected by the virus and then had an mRNA vaccine.
A genomic analysis of lung cancer in people with no history of smoking has found that a majority of these tumors arise from the accumulation of mutations caused by natural processes in the body. This study was conducted by an international team led by researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and describes for the first time three molecular subtypes of lung cancer in people who have never smoked.
These insights will help unlock the mystery of how lung cancer arises in people who have no history of smoking and may guide the development of more precise clinical treatments. The findings were published September 6 2021, in Nature Genetics.
“What we’re seeing is that there are different subtypes of lung cancer in never smokers that have distinct molecular characteristics and evolutionary processes,” said epidemiologist Maria Teresa Landi, M.D., Ph.D., of the Integrative Tumor Epidemiology Branch in NCI’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, who led the study, which was done in collaboration with researchers at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, another part of NIH, and other institutions. “In the future we may be able to have different treatments based on these subtypes.”
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed COVID-19 vaccine candidates that can take the heat. Their key ingredients? Viruses from plants or bacteria.
The new fridge-free COVID-19 vaccines are still in the early stage of development. In mice, the vaccine candidates triggered high production of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. If they prove to be safe and effective in people, the vaccines could be a big game changer for global distribution efforts, including those in rural areas or resource-poor communities.
“What’s exciting about our vaccine technology is that is thermally stable, so it could easily reach places where setting up ultra-low temperature freezers, or having trucks drive around with these freezers, is not going to be possible,” said Nicole Steinmetz, a professor of nanoengineering and the director of the Center for Nano-ImmunoEngineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.



Jeff Falk 713−348−6775 [email protected]
Jade Boyd 713−348−6778 [email protected]
HOUSTON – (Sept. 1 2021) – Rice physicists have confirmed the topological origins of magnons, magnetic features they discovered three years ago in a 2D material that could prove useful for encoding information in the spins of electrons.