We’ve created a new way to explore the fundamental constituents of the universe.

*BLACK FRIDAY DROP Out Now*: http://seek-discomfort.com/yes-theory.
This week only, with every purchase about $35, you’ll get a Free Seeker necklace.
The World Islands. A collection of 300 man-made islands built off the coast of Dubai to resemble an outline of the EARTH FROM THE SKY… Yet, after $13 billion was spent to complete them they’ve mostly been sitting there empty… I couldn’t believe this place actually existed.
So as a first stop on my trip I flew to Dubai to understand what happened and what their future holds… What are your thoughts? Amazing or too crazy of an idea?
Thank you to @MyDubai and @VisitDubai for helping us get in touch with the creators of these islands and for letting us go out to see the restricted areas.
Who are we?
We believe that life’s greatest moments and deepest connections exist outside of your comfort zone.
We have a 2nd channel! Make sure to subscribe to it here:
Nad plus works for alzheimers.
In June of 2,018 the World Health Organization (WHO) released the 11th edition of its International Classification of Diseases, and for the first time added aging.1 The classification of aging as a disease paves the way for new research into novel therapeutics to delay or reverse age-related illnesses such as cancer, cardiovascular and metabolic disease, and neurodegeneration.2,3 Nutrient sensing systems have been an intense focus of investigation, including mTOR (the mammalian target of rapamycin) for regulating protein synthesis and cell growth; AMPK (activated protein kinase) for sensing low energy states; and sirtuins, a family of seven proteins critical to DNA expression and aging, which can only function in conjunction with NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme present in all living cells.4
Across the kingdom of life, an increase in intracellular levels of NAD+ triggers shifts that enhance survival, including boosting energy production and upregulating cellular repair.5 In fact, the slow, ineluctable process of aging has been described as a “cascade of robustness breakdown triggered by a decrease in systemic NAD+ biosynthesis and the resultant functional defects in susceptible organs and tissues.”6 Aging is marked by epigenetic shifts, genomic instability, altered nutrient sensing ability, telomere attrition, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and dysregulated intercellular communication.7,8
By middle age, our NAD+ levels have plummeted to half that of our youth.9 Numerous studies have demonstrated that boosting NAD+ levels increases insulin sensitivity, reverses mitochondrial dysfunction, and extends lifespan.10,11 NAD+ levels can be increased by activating enzymes that stimulate synthesis of NAD+, by inhibiting an enzyme (CD38) that degrades NAD+, and by supplementing with NAD precursors, including nicotinamide riboside(NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).12,13 A conceptual framework called NAD World, formulated over the last decade by developmental biologist Shin-ichiro Imai, MD, PhD, of Washington University School of Medicine, posits NMN as a critical, systemic signaling molecule that maintains biological robustness of the communication network supporting NAD+.6.
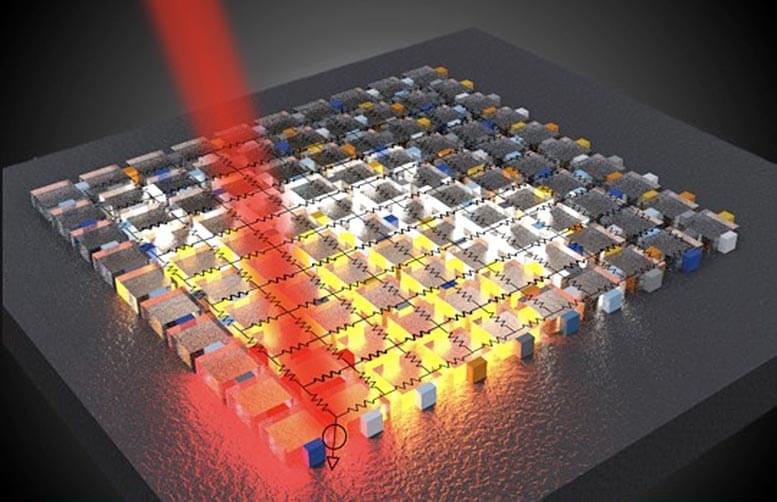
Analog photonic solutions offer unique opportunities to address complex computational tasks with unprecedented performance in terms of energy dissipation and speeds, overcoming current limitations of modern computing architectures based on electron flows and digital approaches.
In a new study published on August 26 2021, in the journal Nature Communications Physics, researchers led by Volker Sorger, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at the George Washington University, reveal a new nanophotonic analog processor capable of solving partial differential equations. This nanophotonic processor can be integrated at chip-scale, processing arbitrary inputs at the speed of light.
The research team also included researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles, and City College of New York.
Because we can’t possibly absorb every single stimulus, our brain lets some of these signals filter through to our consciousness while others don’t.
But where specifically in the brain does that filtering take place? If somewhere in the brain exists the gateway to consciousness, which part of the brain functions as the gatekeeper?
Researchers at the University of Michigan Medical School set out to answer this question. Their study, published Tuesday in Cell Reports, suggests they’ve found the answer.
The global revenue of the pharmaceutical market is 1.2 trillion dollars. With such capital at stake and with the pace of technological disruption, the pharma industry has to embrace new technologies, therapies, and innovations and put a greater focus on prevention and digital health.
In this video, we take a dive into the five trends of how big pharma will adapt to these changing times:
1. Artificial intelligence for drug research and development.
2. Patient design — DIY medicine movements.
3. In silico trials to bypass in vivo clinical testing.
4. New technologies, such as blockchain, in the supply chain.
5. New drug strategies by big pharma companies.
Get access to exclusive content and express your support for The Medical Futurist by joining our Patreon community: https://www.patreon.com/themedicalfuturist.
Read our magazine for further updates and analyses on the future of healthcare:
https://medicalfuturist.com/magazine.
#pharmaceutics #digitalhealth #pharma
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Papers referenced in the video:
Human microbiome: an academic update on human body site specific surveillance and its possible role.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32524177/
Taxonomic signatures of cause-specific mortality risk in human gut microbiome.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33976176/
The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32082260/
Inhibiting antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae by microbiota-mediated intracellular acidification.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30563917/
Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood.
A new coronavirus variant, C.1.2, has been detected in South Africa and a number of other countries, with concerns that the variant could be more infectious and evade vaccines, according to a new preprint study by South Africa’s National Institute for Communicable Diseases and the KwaZulu-Natal Research Innovation and Sequencing Platform. The study is awaiting peer review.
The C.1.2 variant first detected in South Africa is more mutated compared to the original virus than any other known variant.

Circa 2017
Transformers are found at generating stations and distribution substations. Their primary function is to reduce the high voltages used to transport electricity long distances to the lower voltages needed by homes and businesses. But today’s transformers only operate in one direction. They are poorly equipped for boosting electricity from local sources — typically wind and solar — to the higher voltages needed to mesh efficiently with the larger grid.
Beginning in 2,010 researchers at the National Science Foundation’s FREEDM Systems Center at NC State introduced the first solid state transformer. It could perform all of the functions of a traditional transformer, but could also redirect power as needed to address changes in supply and demand.
“The SST is a fundamental building block in the smart-grid concept,” says Iqbal Husain, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the school and director of the FREEDM Center. “It can scale down voltage for use in homes and businesses, but it can also scale up voltage from solar panels or other residential-scale renewable sources in order to feed that power back into the grid. And because the SST is a smart technology, it can switch back and forth between those two functions as needed.”
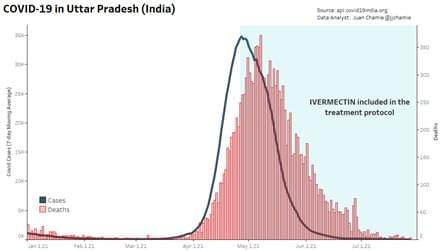
Article at gnews reports on announcement by Dr. Ozaki, chairman of the Tokyo Metropolitan Medical Association Greenlight for Ivermectin in Japan. Excerpts in italics with my bolds.
Since Tokyo summer Olympic Game ended on August 8 2021, the urgent status of the pandemic as Japan is now in its worst surge of the COVID-19 pandemic since the onset of the crisis in such a megacity of 14 million. Most recently, a record number of new cases were reported at 20,140 on August 14. Deaths aren’t as high as successive waves of the pandemic from February2021to the end of May, but nerves are frayed with record numbers of infections. Dr. Ozaki, The chairman of the Tokyo Metropolitan Medical Association, recently led an emergency press conference on August 13 Dr. Haruo Ozaki shared those 18,000 new infections are reported daily. However, the death count has eased as compared to previous surges.
How to deal with the current dilemma is a huge challenge to Japanese government and medical agencies? Fortunately, India has an excellent testimonial. Since April 28 India medical officials started providing Hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin to its massive population. As India is the major pharmaceutical manufacture in the world, they were ready for this massive drug distribution. Miraculously, COVID cases have plummeted quickly since then thanks to the new rules.