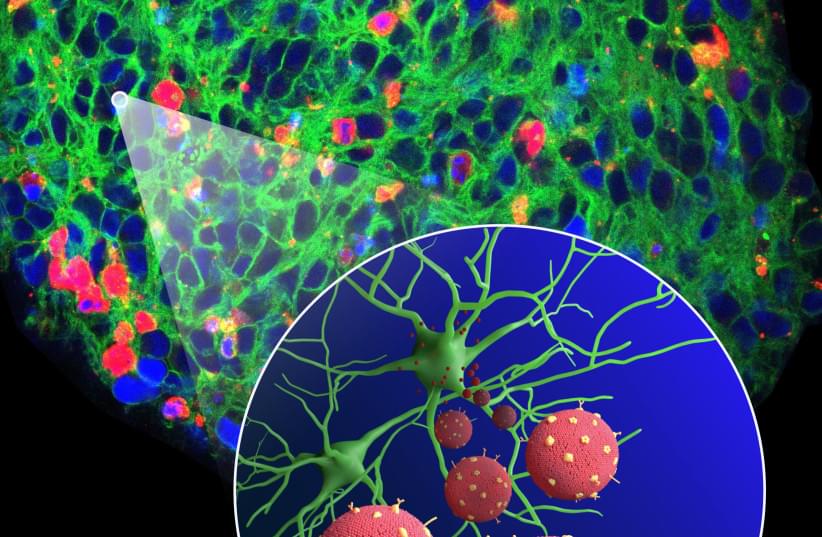
Researchers from the Technion and the Houston Methodist Research Institute have developed microscopic machines that can deliver drugs to parts of the brain in order to treat injuries and diseases.

Researchers have identified a potential new treatment that suppresses the replication of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes Covid-19.
In order to multiply, all viruses, including coronaviruses, infect cells and reprogramme them to produce novel viruses.
The research revealed that cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 can only produce novel coronaviruses when their metabolic pentose phosphate pathway is activated.
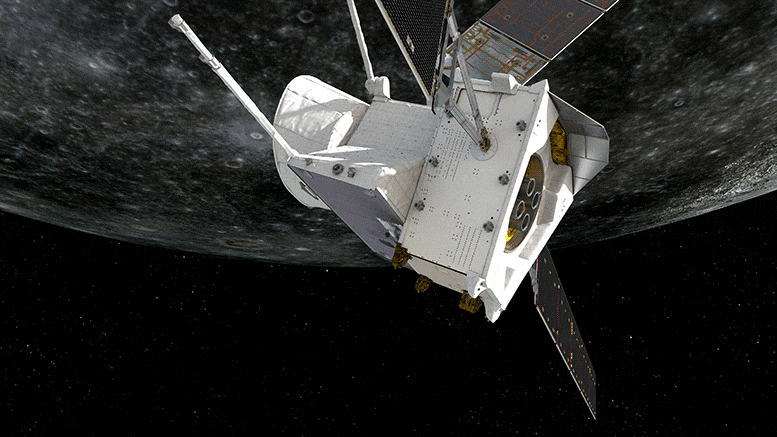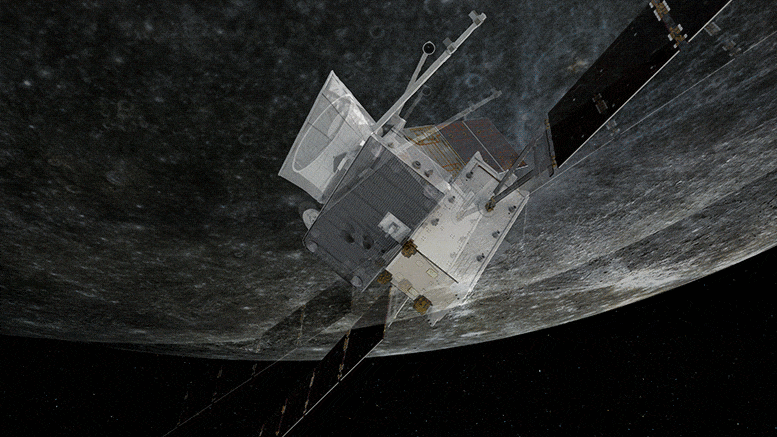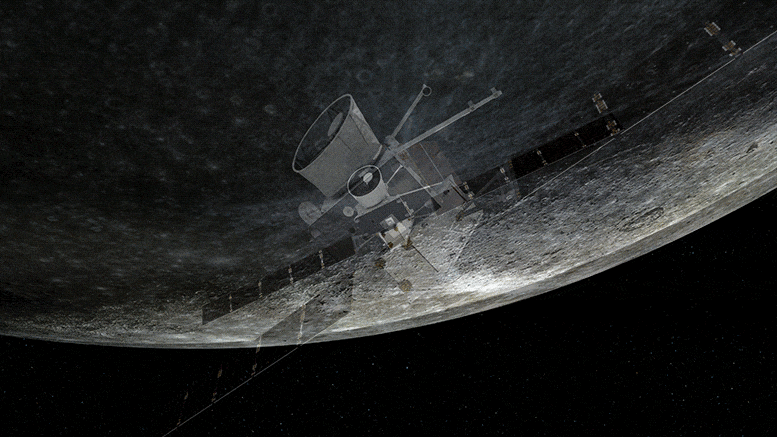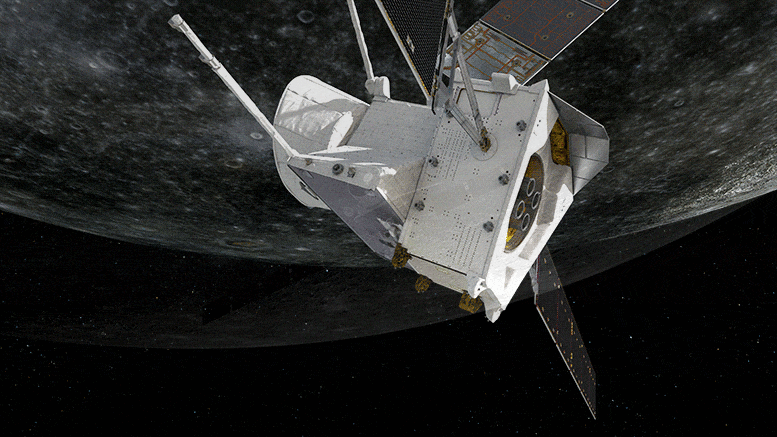
The magnetic and particle environment around Mercury was sampled by BepiColombo for the first time during the mission’s close flyby of the planet at 199 km on 1–2 October 2,021 while the huge gravitational pull of the planet was felt by its accelerometers.
The magnetic and accelerometer data have been converted into sound files and presented here for the first time. They capture the ‘sound’ of the solar wind as it bombards a planet close to the Sun, the flexing of the spacecraft as it responded to the change in temperature as it flew from the night to dayside of the planet, and even the sound of a science instrument rotating to its ‘park’ position.

The first artificial Lab-Grown Meats have recently gotten into stores and markets for everyone to buy and eat. But until now, those meats were largely just chicken nuggets or similar types of meat. But with Future Meat Technologies’ latest crazy invention, this has changed. They managed to create a system that actually involves Artificial Intelligence, which grows almost 5,000 fully-fledged hamburgers a day without the environmental impact or regular food and meat.
Cultured meat is meat produced by in vitro cell cultures of animal cells (as opposed to meat obtained from animals). It is a form of cellular agriculture.
Cultured meat is produced using many of the same tissue engineering techniques traditionally used in regenerative medicines. It’s also occasionally called lab grown meat.
–
Every day is a day closer to the Technological Singularity. Experience Robots learning to walk & think, humans flying to Mars and us finally merging with technology itself. And as all of that happens, we at AI News cover the absolute cutting edge best technology inventions of Humanity.
If you enjoyed this video, please consider rating this video and subscribing to our channel for more frequent uploads. Thank you! smile
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 The Best Burger of the Future.
01:29 History of Future Meat Technologies.
02:53 How Cultured Meat is made.
04:37 Where you can buy cultured Meat.
05:52 Advantages of Cultured Meat.
07:44 Last Words.
–
#weird #food #cultured
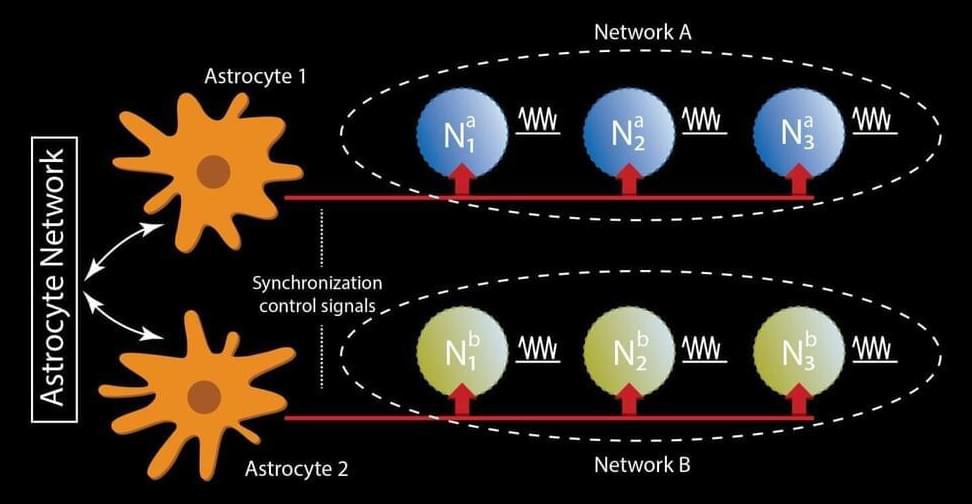
A clearer understanding of how a type of brain cell known as astrocytes function and can be emulated in the physics of hardware devices, may result in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning that autonomously self-repairs and consumes much less energy than the technologies currently do, according to a team of Penn State researchers.
Astrocytes are named for their star shape and are a type of glial cell, which are support cells for neurons in the brain. They play a crucial role in brain functions such as memory, learning, self-repair and synchronization.
“This project stemmed from recent observations in computational neuroscience, as there has been a lot of effort and understanding of how the brain works and people are trying to revise the model of simplistic neuron-synapse connections,” said Abhronil Sengupta, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science. “It turns out there is a third component in the brain, the astrocytes, which constitutes a significant section of the cells in the brain, but its role in machine learning and neuroscience has kind of been overlooked.”
Until real windows are eventually all replaced with ultra-high-resolution screens (mark my words, it’s gonna happen) Skyline Robotics hopes to solve the window washer dilemma with robots: specifically, what appears to be KUKA Robotics arms outfitted with a large cleaning brush and a system that automatically pumps clean water through it.
Officially named Ozmo, the robot can be mounted to the same lift mechanisms that carry multiple window washers up and down the side of a building through the use of a motorized crane system on the roof. Unlike humans, however, Ozmo has a much longer reach, allowing one or two of the robotic arms to potentially clean a much larger region on every pass. As with other robotic workers, Ozmo doesn’t take breaks, need lunch, or ever have to go to the bathroom. And since it’s permanently bolted to the lift it’s riding, there are no harnesses to check and re-check before a shift, and should something go wrong, there’s less risk to human life.
If you live in New York and work in a high-rise structure, there’s a good chance you might get a chance to see one of the Ozmo robots at work because Skyline Robotics recently announced a new partnership with a company named Platinum, Inc. that currently has cleaning and maintenance contracts with 65% of the Class A buildings (a classification applied to the newest, most modern skyscrapers) in New York City. It’s the first time the Ozmo robots will be deployed in the US, so you can soon expect a sharp decrease in the number of ‘window washers dangling in peril’ stories on your local news.
For more info, join us on Patreon!
It’s been a long time coming, but NASA’s next moon rocket is just months from liftoff on its first uncrewed test flight. The Space Launch System (SLS) is a super heavy-lift vehicle capable of delivering 95 tons to Low Earth Orbit, but its primary purpose will be to deliver humans to lunar orbit and, eventually, to the lunar surface. SLS has been in development since 2,011 and it’s faced a series of delays, but launch day is finally within sight. Earlier this month, the rocket was fully stacked for the first time in the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center, and the Orion capsule (the spacecraft’s crew cabin) was attached to the top. The full stack stands an impressive 322 feet tall, just shy of the Saturn V’s 363 feet.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson (a former astronaut himself) told reporters that “with stacking and integration of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft complete, we’re getting closer and closer to embarking on a new era of human deep space exploration…Thanks to the team’s hard work designing, manufacturing, testing, and now completing assembly of NASA’s new rocket and spacecraft, we’re in the home stretch of preparations for the first launch on the Artemis I mission, paving the way to explore the Moon, Mars, and beyond for many years to come.”
With stacking complete, the next major task will be to roll the rocket out to the pad, where a full wet dress rehearsal will take place. The wet rehearsal involves loading propellant into the vehicle and performing a countdown, testing every aspect of the mission just shy of actually blasting off. The exact date for liftoff of Artemis 1 will be determined after the wet dress rehearsal ensures everything is in good working order.
Starbase, the city that never sleeps.
As the Federal Aviation Administration conducts research into SpaceX’s Texas project, a new video shows the company hard at work on its big rocket.