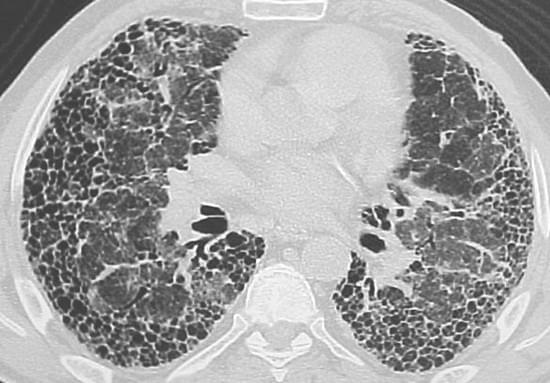
The content of Peter’s email blast has been edited by me (can’t help myself). But I believe I have captured its essence and hope you enjoy the retelling. As always your comments are welcomed.
What is Insilico Medicine?
Insilico Medicine is a pioneering drug company that is powered by a “drug discovery engine” that sifts through millions of data samples to determine the signature biological characteristics of specific diseases. It then identifies the most promising treatment targets and uses a new AI technique called generative adversarial networks (GANs) to create molecules perfectly suited against them.