Data dashboards have been an important part of pandemic response and planning. What have their developers learnt about communicating science in a crisis?
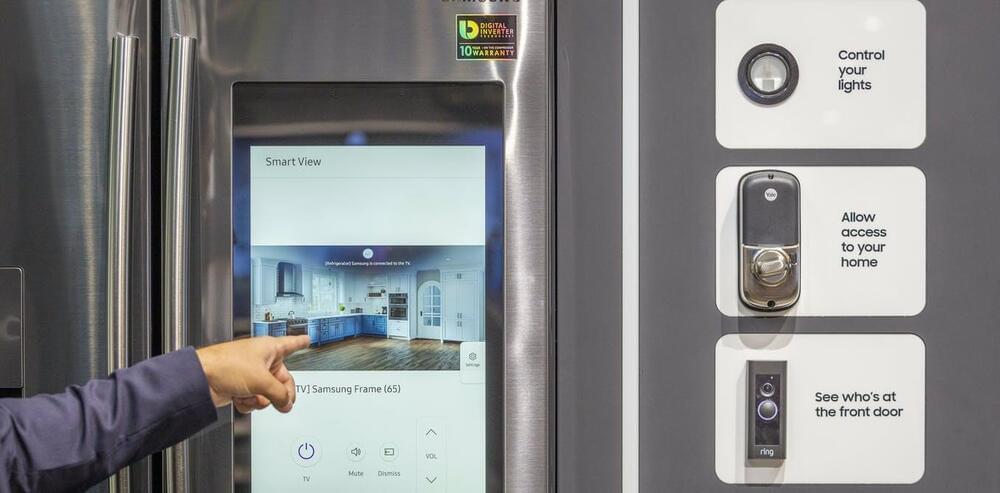



Your appliances, car and home are designed to make your life easier and automate tasks you perform daily: switch lights on and off when you enter and exit a room, remind you that your tomatoes are about to go bad, personalize the temperature of the house depending on the weather and preferences of each person in the household.
To do their magic, they need the internet to reach out for help and correlate data. Without internet access, your smart thermostat can collect data about you, but it doesn’t know what the weather forecast is, and it isn’t powerful enough to process all of the information to decide what to do.
But it’s not just the things in your home that are communicating over the internet. Workplaces, malls and cities are also becoming smarter, and the smart devices in those places have similar requirements. In fact, the Internet of Things (IoT) is already widely used in transport and logistics, agriculture and farming, and industry automation. There were around 22 billion internet-connected devices in use around the world in 2018, and the number is projected to grow to over 50 billion by 2030.


How to robotically build a human habitat in space…
Happening now.
Accelerate the accessibility and commercialization of cislunar space through cost-effective, habitable, scalable Infrastructure.
A talk with Sebastian Asprella CEO at ThinkOrbital: a commercial space-platform developer with a mission to accelerate the commercialization of cislunar space, focusing on On-orbit servicing, assembly and manufacturing technologies. Their flagship space-platform, the Orb2, is designed for a single-launch on-orbit assembly model, capable of delivering an internal spherical volume of up to 4000m3.
If you think you understand quantum mechanics, you don’t understand quantum mechanics
Richard Feynman
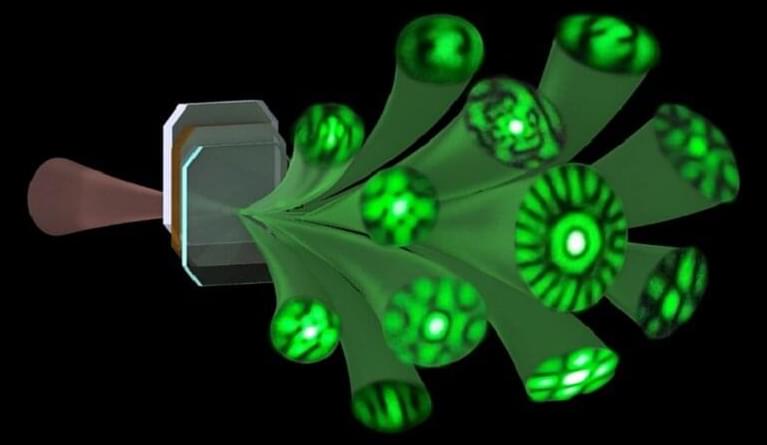


Extension of laser beam structures promises new laser applications. Exploration of how beam structures change during nonlinear frequency conversion processes has drawn increasing interest in recent years. Nonlinear conversion is an excellent route for structured beam generation and represents a growing, hybrid field for researchers in nonlinear optics and laser technology, as well as the emerging area of light-field regulation technology.
For structured beam generation and nonlinear frequency conversion, researchers have considered both intracavity oscillation and external cavity spatial modulation. To achieve flexible outputs, spatial light modulators can be used to obtain structured beams both inside and outside the laser cavity. But this is an indirect, inefficient method. Intracavity nonlinear frequency generation of structured beams offers a direct, efficient method that has only rarely been investigated, until recently.
Inside a laser cavity, an effect known as “transverse mode locking” (TML) enables the direct generation of the vortex beams or optical vortices from a laser cavity. It is known that both solid-state microchip lasers and VCSELs can produce quite similar outputs of TML beam patterns under large Fresnel number pumping conditions. The complex transverse patterns formed by the TML effect, commonly composed of different basic modes with different weight coefficients and different locking phases, make for abundant spatial information in fundamental frequency modes. Nonlinear frequency conversion of these directly generated TML beams is of great interest, but not yet well studied.

