Dopaminergic action prediction error signals are used by mice as a value-free teaching signal to reinforce stable sound–action associations in the tail of the striatum.





We live in extraordinary times.
I’ve been writing about this for the past decade, analysing AI and other exponential technologies and their impact on society. As you get started with Exponential View, I wanted to introduce you first to five charts — depicting key dynamics — to help you understand why the pace of change has increased.
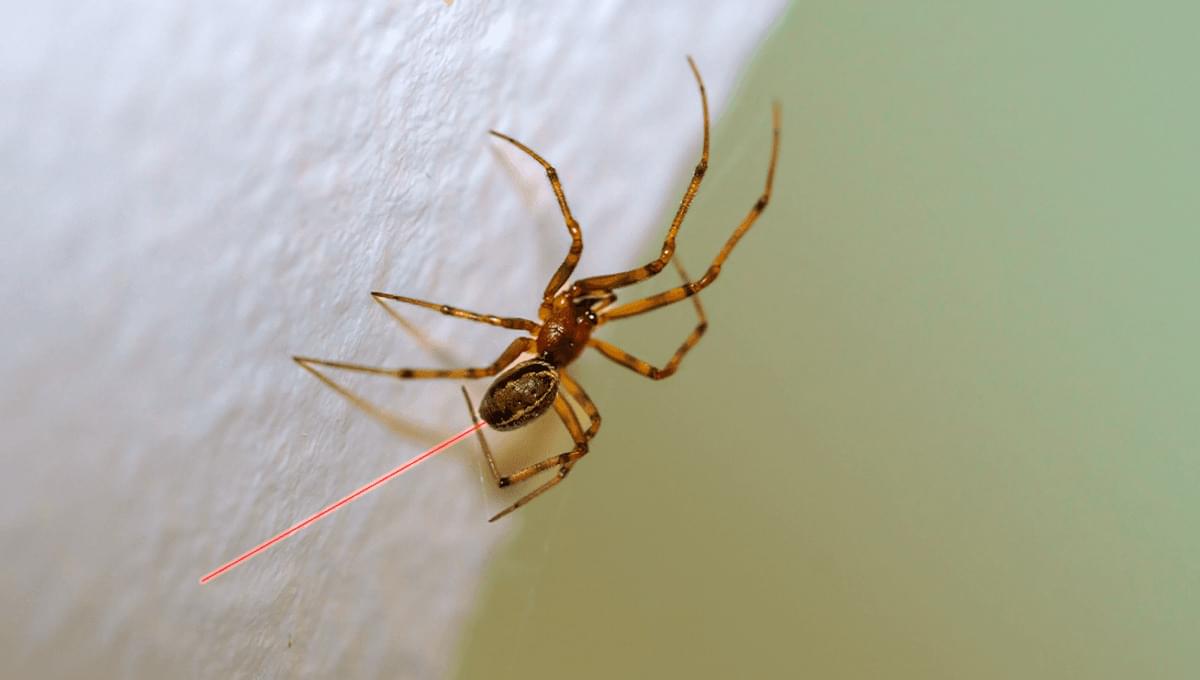


One of the reasons why this has never happened before is that spiders themselves are difficult organisms to work with within the laboratory. They are a diverse group, have a complex genome structure, and their cannibalistic nature means that they have to be reared individually, otherwise their cage neighbors would be gobbled up. Despite this, new developments in Parasteatoda tepidariorum have allowed this species to become a research model.
The research team looked into spider silk as the target. Spider silk is an incredibly strong and scientifically interesting substance, as it is five times stronger than a steel cable of the same weight, tear-resistant, while also being biodegradable, lightweight, and elastic.
To genetically modify this arachnophobe’s nightmare, the scientists developed an injection solution. This had a gene-editing system that also included a red fluorescent protein gene sequence. This solution was then injected into oocytes inside unfertilized female spiders, when these spiders mated with males, it resulted in the genetically modified offspring.

Type 5 diabetes has just been recognised as a distinct form of diabetes by the International Diabetes Federation. Despite the name, there are more than a dozen different types of diabetes. The classification isn’t quite as tidy as the numbering suggests.
Here’s a clear guide to the different types, including some that you may not have heard of, along with information about what causes them and how they are treated.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune reaction can occur at any age, from infancy through to old age.
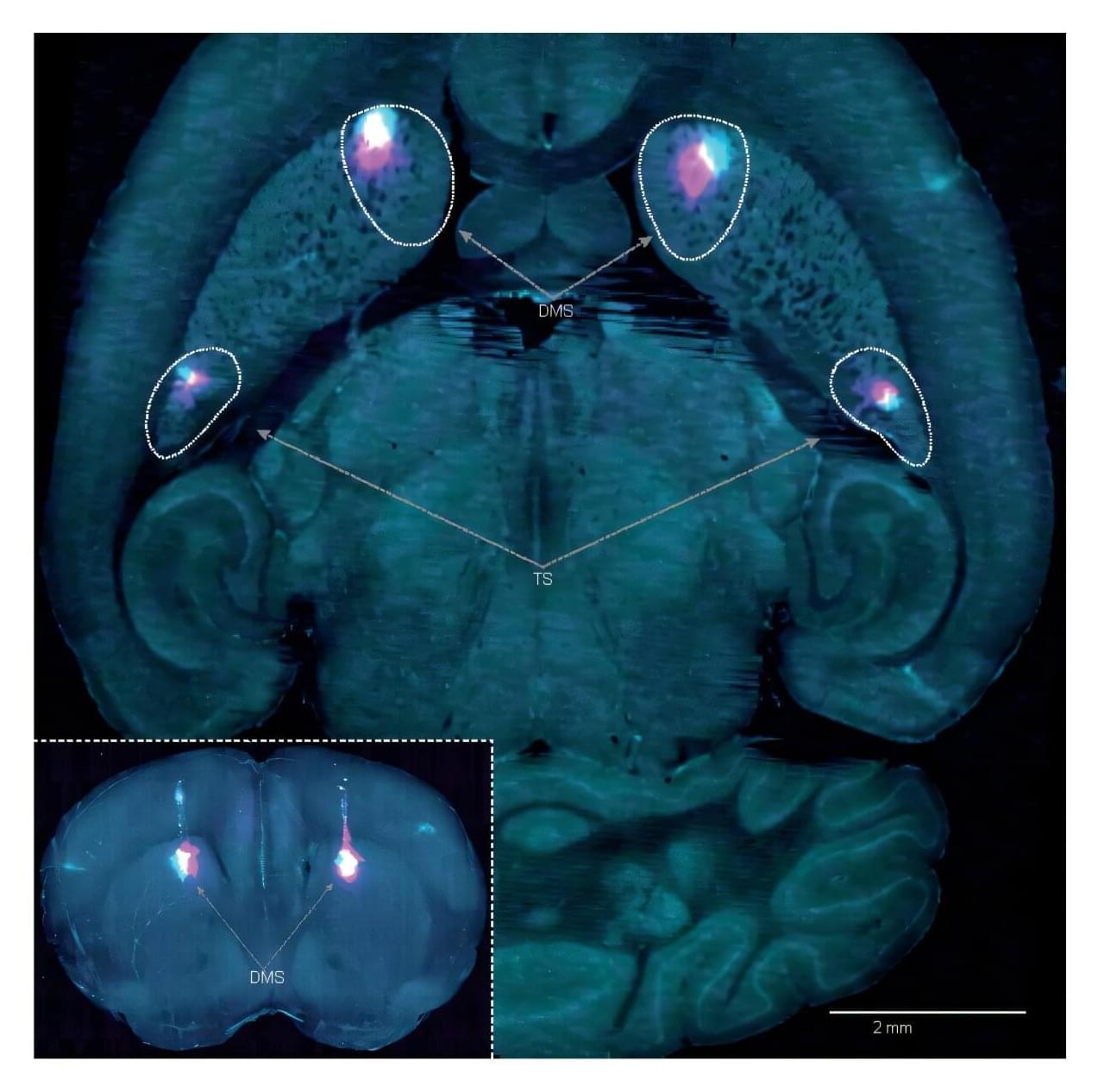
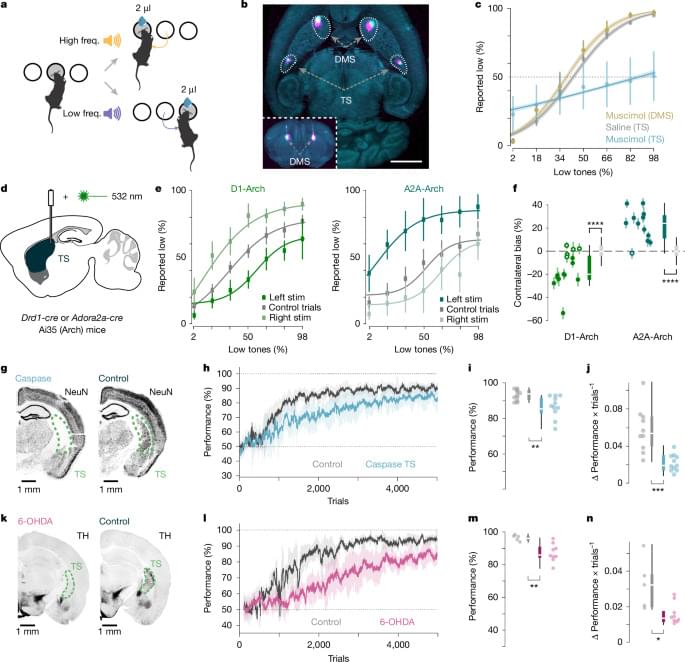
Neuroscientists at the Sainsbury Wellcome Center (SWC) at UCL have discovered that the brain uses a dual system for learning through trial and error. This is the first time a second learning system has been identified, which could help explain how habits are formed and provide a scientific basis for new strategies to address conditions related to habitual learning, such as addictions and compulsions.
Published in Nature, the study in mice could also have implications for developing therapeutics for Parkinson’s. The study is titled “Dopaminergic action prediction errors serve as a value-free teaching signal.”
“Essentially, we have found a mechanism that we think is responsible for habits. Once you have developed a preference for a certain action, then you can bypass your value-based system and just rely on your default policy of what you’ve done in the past. This might then allow you to free up cognitive resources to make value-based decisions about something else,” explained Dr. Marcus Stephenson-Jones, Group Leader at SWC and lead author of the study.