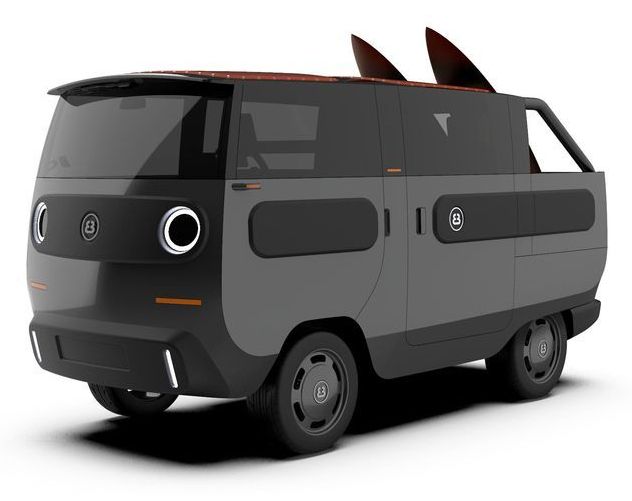
No offense to Volkswagen’s ID. Buzz, a successful design in its own right, but when we close our eyes and imagine an all-electric Volkswagen Type 2 for the 21st century, it’s the new eBussy that we see. That was true before we knew it existed, and it’s definitely true now that we’ve seen the actual design. Beyond timelessly simple styling, the new German-designed electric mini-bus also promises some of the most impressive modularity out there, switching between family van, cargo van, pickup truck, camper van, off-road adventure van and other configurations. And so far, it looks to be surprisingly affordable.
Volkswagen has given its own electric van concepts more of a futuristic identity, but Münster-based ElectricBrands keeps things more traditional. Its eBussy design looks very much like a T1/T2 Transporter, reinterpreted for modern times. It has the flat face, bright, round headlamps, softened-box body and partially covered rear wheels. Every time we stare it in the eyes, we see “T2 of the digital age” staring back at us.
Like those early VW Type 2’s, the eBussy isn’t a vehicle so much as the platform for an entire family of vehicles, ranging from flatbed and tipper trucks to delivery, family and camper vans. That modularity isn’t just a handy available feature, it’s THE feature that the eBussy design was based around, the idea being that owners can easily swap out individual modules to make one vehicle into any and every vehicle for all their passenger and cargo-hauling needs. ElectricBrands promises Lego-like simplicity in plugging and playing.