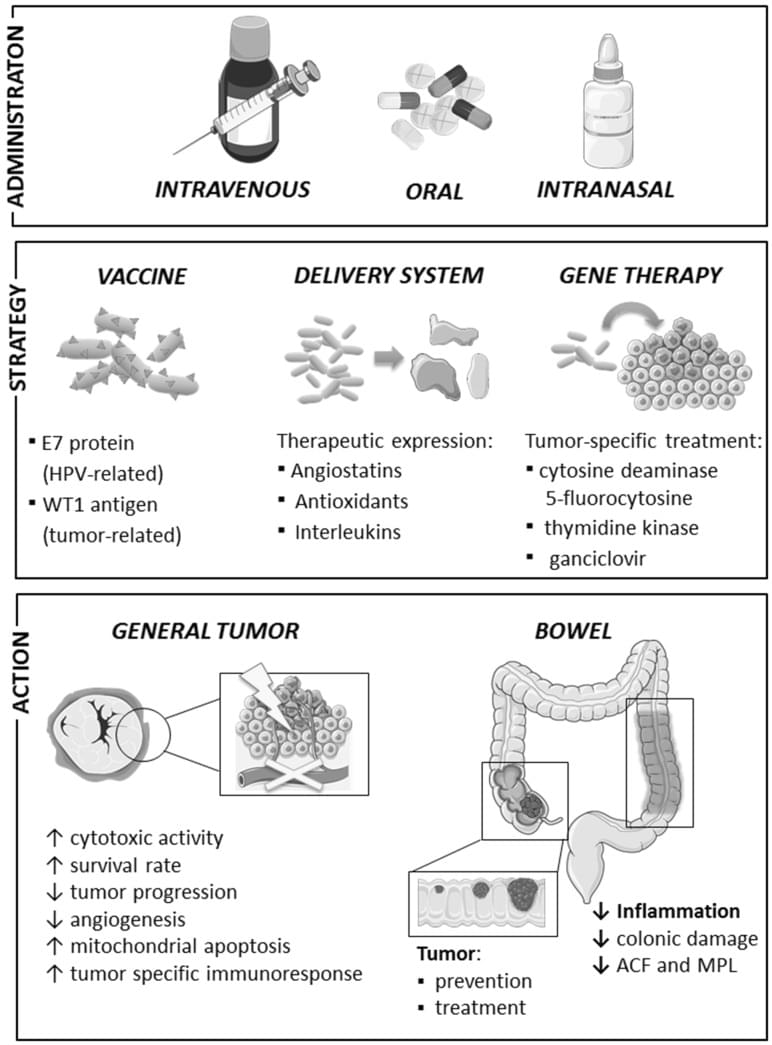
Probiotics show a new to battle cancer and other diseases keeping the host body healthy with its anti inflammation abilities.
Gut microbiota is widely considered to be one of the most important components to maintain balanced homeostasis. Looking forward, probiotic bacteria have been shown to play a significant role in immunomodulation and display antitumour properties. Bacterial strains could be responsible for detection and degradation of potential carcinogens and production of short-chain fatty acids, which affect cell death and proliferation and are known as signaling molecules in the immune system. Lactic acid bacteria present in the gut has been shown to have a role in regression of carcinogenesis due to their influence on immunomodulation, which can stand as a proof of interaction between bacterial metabolites and immune and epithelial cells. Probiotic bacteria have the ability to both increase and decrease the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines which play an important role in prevention of carcinogenesis. They are also capable of activating phagocytes in order to eliminate early-stage cancer cells. Application of heat-killed probiotic bacteria coupled with radiation had a positive influence on enhancing immunological recognition of cancer cells. In the absence of active microbiota, murine immunity to carcinogens has been decreased. There are numerous cohort studies showing the correlation between ingestion of dairy products and the risk of colon and colorectal cancer. An idea of using probiotic bacteria as vectors to administer drugs has emerged lately as several papers presenting successful results have been revealed. Within the next few years, probiotic bacteria as well as gut microbiota are likely to become an important component in cancer prevention and treatment.
Cancer is considered as one of the most significant causes of death. The treatment of tumors has received much attention in the last years; however, the number of people suffering neoplastic syndrome is still increasing. Thus, researchers are trying to face this process searching for innovative therapies and prophylaxis. Despite the fact that cancer risk indisputably depends on genetic factors, immunological condition of the organism plays a considerable role in it, that being closely associated with probiotic bacteria and commensal bacterial flora presented mainly in the digestive tract. Probiotic strains, inter alia Bifidobacterium, or Lactobacillus, widely present in commonly consumed fermented milk products, are known to have various beneficial effects on health. To date, there is a plethora of studies investigating the correlation between intestinal microbiota and carcinogenesis which have been evaluated in this article.