The successful all-private visit to the International Space Station paves the way for future flights.


What if we could use a hydrogen molecule as a quantum sensor in a terahertz laser-equipped scanning tunneling microscope? This would allow us to measure the chemical properties of materials at unprecedented time and spatial resolutions.
This new technique has now been developed by physicists at the University of California, Irvine, according to a statement released by the institution on Friday.
“This project represents an advance in both the measurement technique and the scientific question the approach allowed us to explore,” said in the press release co-author of the new study Wilson Ho, Donald Bren Professor of physics & astronomy and chemistry.
Meetups occur every day at 10 p.m. Central European Time. Users gather in Somnium Space’s city center, known as City Plaza, which is next to Somnium’s virtual headquarters. Events there include open-mic nights, concerts, and developer meetups.
Making money in Somnium Space
Somnium Space isn’t all socialization. Many players are making money by creating and selling NFT avatars.
There are competing notions of fairness — and sometimes they’re incompatible, as facial recognition and lending algorithms show.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX has signed its first ever deal with a major U.S. airline to provide wireless internet to passengers for free using the Starlink satellite network.
The deal with Hawaiian Airlines, which could be implemented as soon as next year, is expected to increase pressure on rival airlines to provide free Wi-Fi for passengers.
“Hawaiian doesn’t currently offer inflight Wi-Fi and has an extensive network of flights over the Pacific Ocean, serving the mainland U.S., Japan, Australia and New Zealand, among other destinations, from Hawaii,” CNBC reported. “It plans to offer Starlink connectivity on its flights out of its home state to cities throughout the mainland U.S. and to its international destinations.”
Do Charles Darwin’s ideas on sexual selection hold up today? The biologist was very much of his time, which meant it may have shaped his understanding of evolutionary biology.

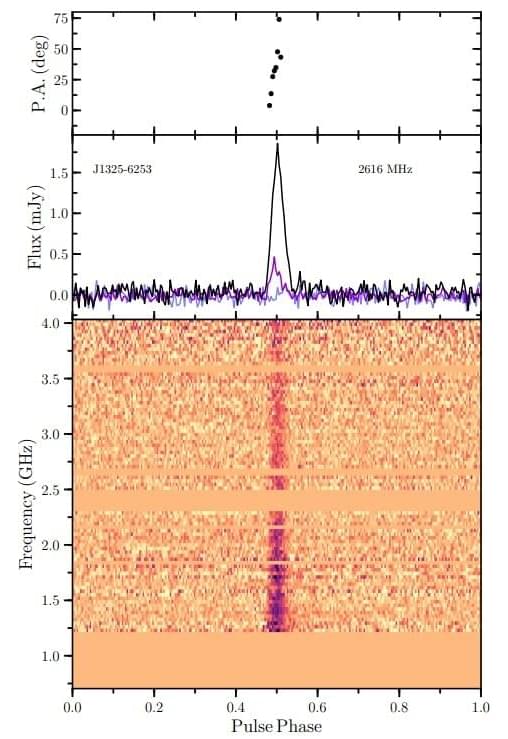
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a rare double neutron star millisecond pulsar. The newfound binary pulsar, designated PSR J1325−6253, consists of two neutron stars orbiting one another every 1.8 days. The finding is detailed in a paper published April 14 on arXiv.org.
The most rapidly rotating pulsars, those with rotation periods below 30 milliseconds, are known as millisecond pulsars (MSPs). It is assumed that they are formed in binary systems when the initially more massive component turns into a neutron star that is then spun-up due to accretion of matter from the secondary star.
Some pulsars consist of two neutron stars (dubbed double neutron star systems—DNS). They are one of the most important classes of objects used to test and understand numerous astrophysical and fundamental physics phenomena, including general relativity in the strong-field regime.

China plans to develop a system for monitoring asteroids that pose a threat to earth, highlighting the nation’s growing ambitions for its space program.
The country will also explore ways for taking out asteroids that endanger the planet, Wu Yanhua, deputy director of the China National Space Administration, said in a TV interview, according to the official Xinhua News Agency.
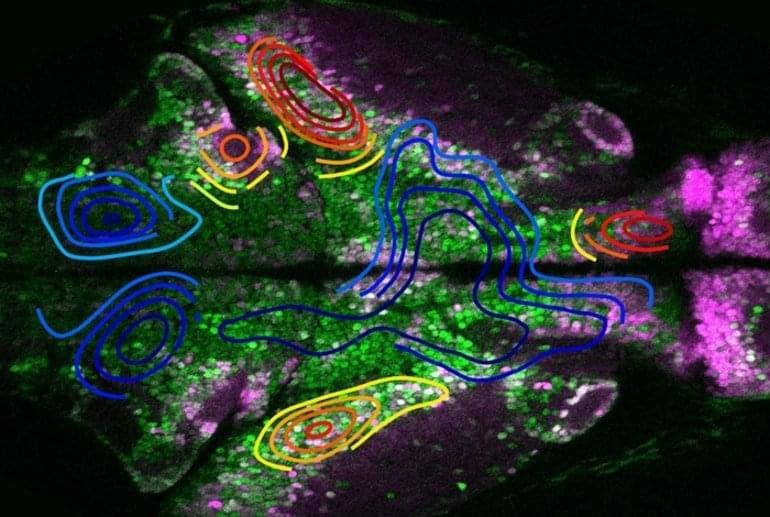
Summary: Seizures originate from an excess of excitatory over inhibitory neural activity in confined regions of the brain, and spread only when they overcome strong inhibitory activity in surrounding regions.
Source: Weill Cornell University.
New evidence from a zebrafish model of epilepsy may help resolve a debate into how seizures originate, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The findings may also be useful in the discovery and development of future epilepsy drugs.