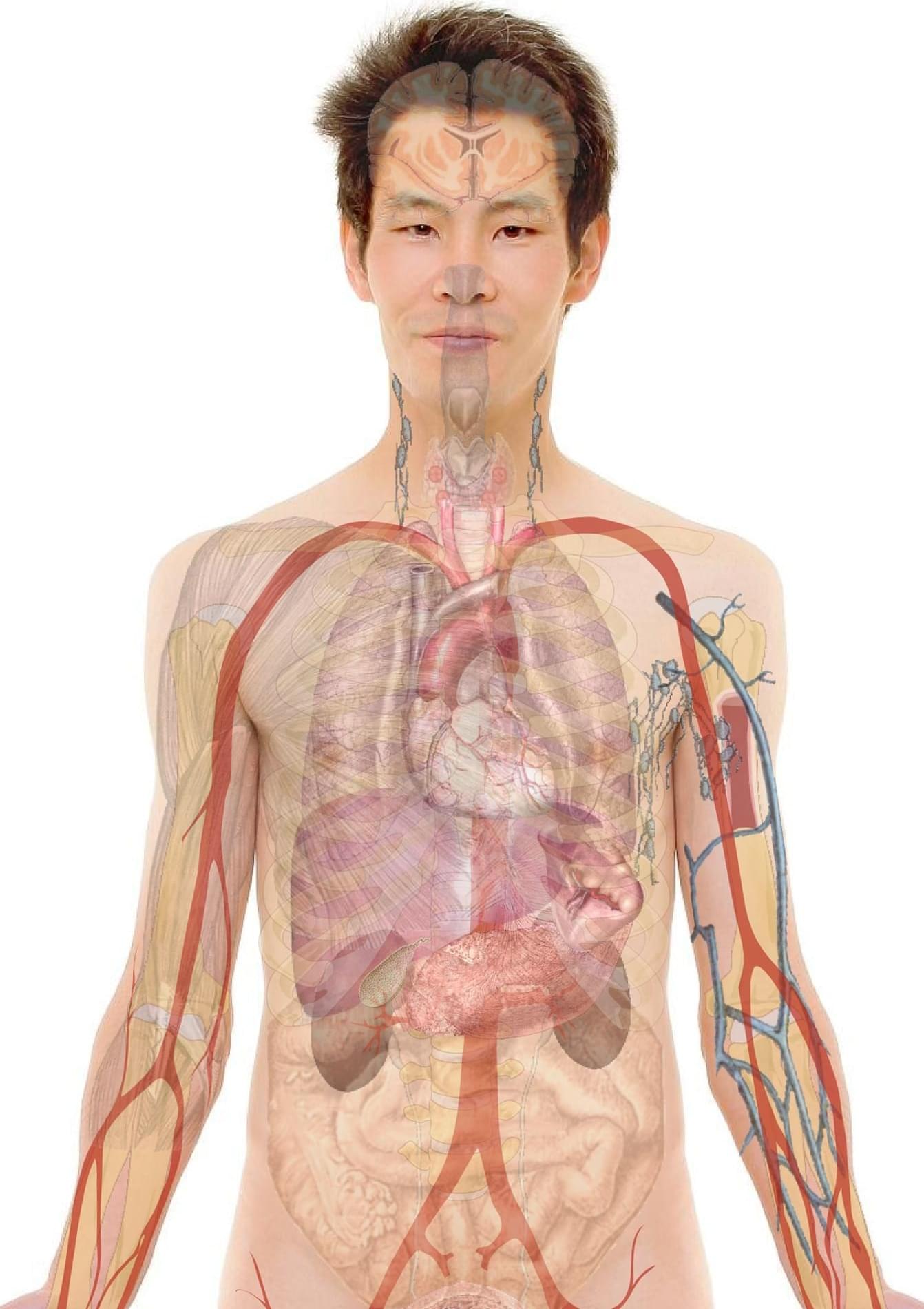
With rates of lung cancer climbing among non-smokers, new strategies are needed to detect lung cancer earlier. Drs. Sequist and Fintelmann at Mass General Brigham are discovering how AI can be used to address this growing concern.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
How cells respond to stress is more nuanced than previously believed
The body’s cells respond to stress—toxins, mutations, starvation or other assaults—by pausing normal functions to focus on conserving energy, repairing damaged components and boosting defenses.
If the stress is manageable, cells resume normal activity; if not, they self-destruct.
Scientists have believed for decades this response happens as a linear chain of events: sensors in the cell “sound an alarm” and modify a key protein, which then changes a second protein that slows or shuts down the cell’s normal function.
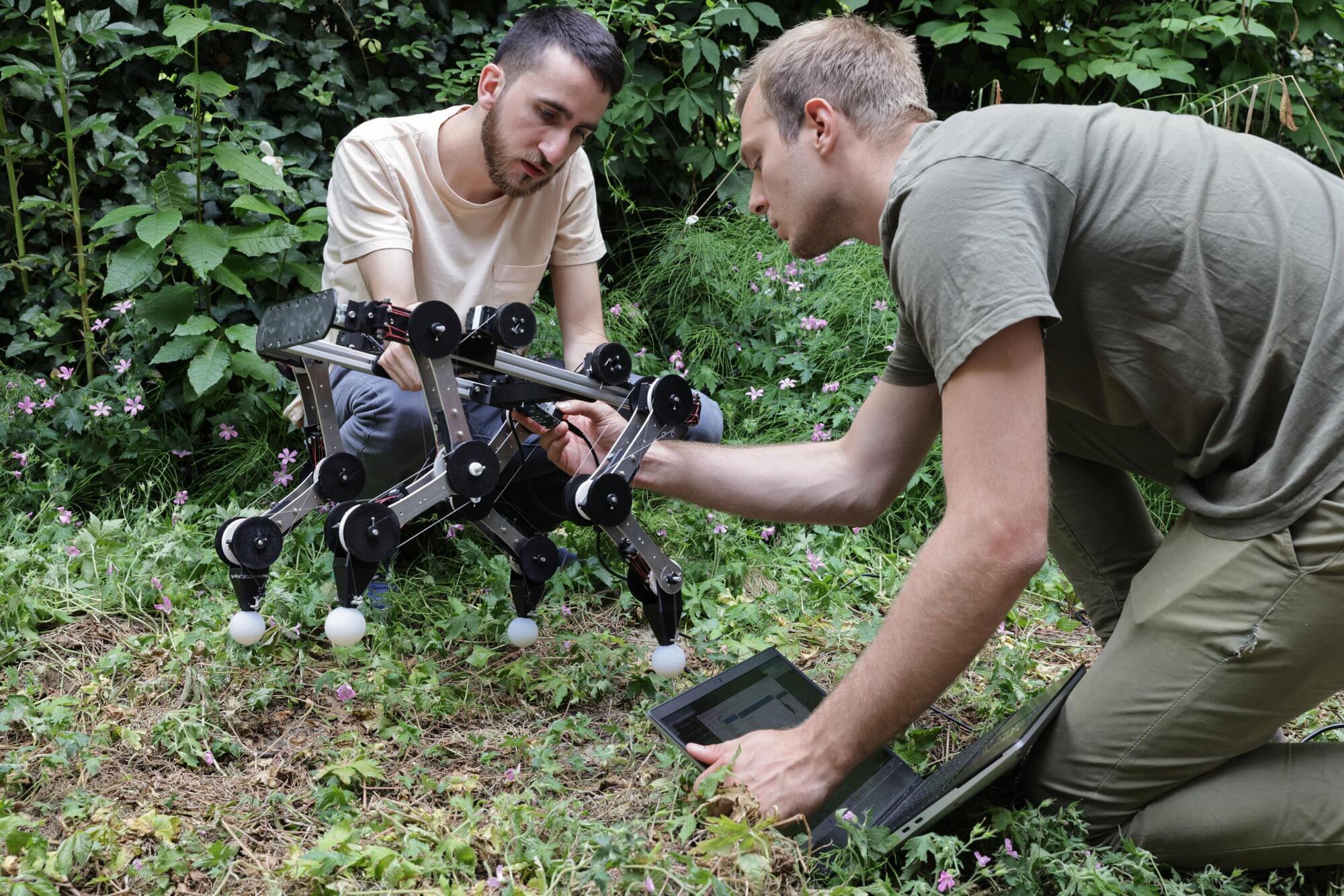

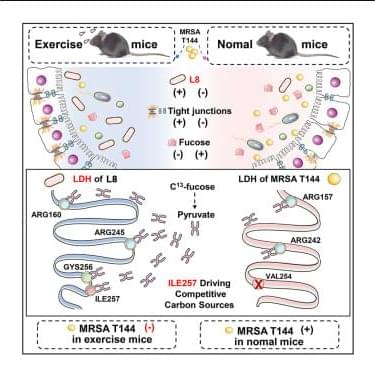

PAWS: Four-legged robot can reproduce animal movement with fewer actuators
Many of the robotic systems developed in the past decades are inspired by four-legged (i.e., quadruped) animals, such as dogs, cheetahs and horses. By replicating the agile movements of these animals, quadruped robots could move swiftly on the ground, crossing long distances on various terrains and rapidly completing missions.
Yet realistically and robustly replicating the fluid motions observed in animals using robotic systems can be very challenging. While some existing four-legged robots were found to be very agile and responsive to changes in their environment, these systems typically integrate advanced actuators and computational components that consume a lot of energy.
Researchers at EPFL’s CREATE Lab and Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) recently developed a new four-legged robot called PAWS (Passive Automata With Synergies), which could reproduce the fluid and adaptive movements of animals using fewer actuators. This robot, introduced in a paper in Nature Machine Intelligence, leverages so-called motor synergies, which are coordinated patterns of muscle activation that allow animals to perform agile motions consuming less energy.
55 Minutes Of Starship Troopers
Everyone needs to see “Starship Troopers.” It’s just a great movie – we’re doing our part! Whether you’ve seen it a million times or are just curious what the hype’s about, we’ve got everything you need to know about this satirical sci-fi classic.
#StarshipTroopers #SciFi #Movies.
Things You Only Notice In Starship Troopers As An Adult | 0:00
Deleted Starship Trooper Scenes That You Never Knew Existed | 9:30
The Most Pause-Worthy Moments In Starship Troopers | 15:27
The Starship Troopers scene that means more than you think | 25:38
The Biggest Differences Between Starship Troopers And The Book | 30:02
What Starship Troopers Looks Like Without Special Effects | 43:26.
Visit Official Looper Website.
https://www.looper.com

Autopsies can reveal intimate health details. Should they be kept private?
The very public sharing of Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa’s health details raises ethical questions over privacy.
Heart Rate Reduction Extends Lifespan
What’s Optimal For Biomarkers? https://www.patreon.com/posts/27-blood-whats-119239968Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount…