Netflix’s fan-favorite Season 4 ‘Star Trek’-themed episode scores a direct sequel coming April 10.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Cyberpunk Realities: Blade Runner-Inspired Animation That Will Blow Your Mind
🌆 Step into a world of neon lights, towering skyscrapers, and rain-soaked streets in this stunning animated journey inspired by the iconic Blade Runner universe. Experience a cyberpunk dystopia brought to life through mesmerizing visuals and immersive animation. Whether you’re a fan of the original movie or just love futuristic worlds, this video will transport you straight into a world of high-tech chaos and mystery. Get ready to explore a world where the lines between humanity and technology blur. 🔮💻 #bladerunner #cyberpunk #animation #neonlights #dystopian #futureworld #animationart #aiart #fantasy #sciencefiction #cinematicai #cinema #midjourney #hailuoai #synthwave #darkwave #hailouai Wanna Try out Hailou? https://hailuoai.video?invite-code=13666198 Like what i do and want to show some love? https://buymeacoffee.com/feartube
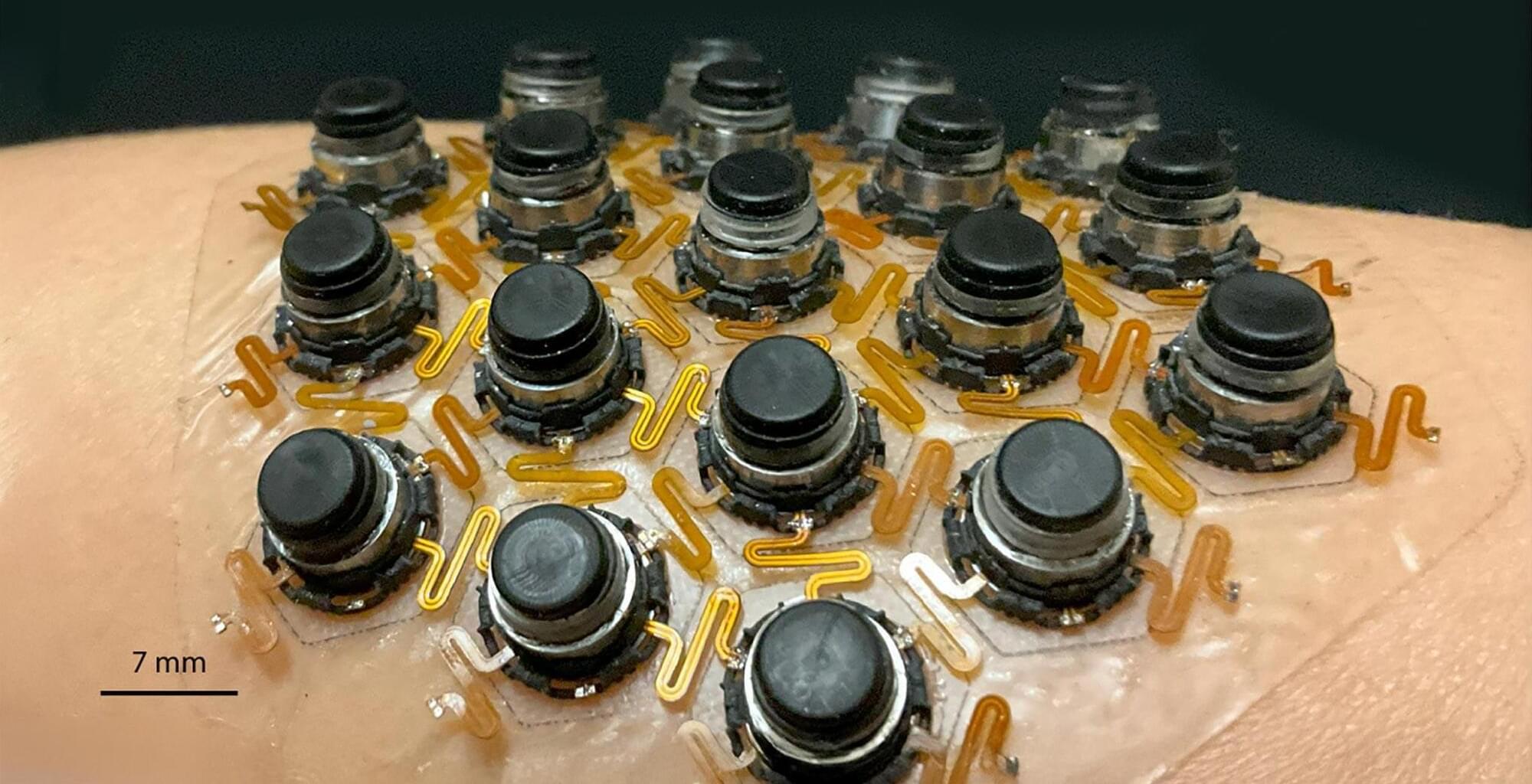

New Wearable Device Allows You To “Feel” Virtual Worlds
The device provides a range of sensations, such as vibrations, pressure, and twisting. A team of engineers led by Northwestern University has developed a new wearable device that stimulates the skin to deliver a range of complex sensations. This thin, flexible device gently adheres to the skin, offering more realistic and immersive sensory experiences. While it is well-suited for gaming and virtual reality (VR), the researchers also see potential applications in healthcare. For instance, the device could help individuals with visual impairments “feel” their surroundings or provide feedback to those with prosthetic limbs.
Q&A: Crystallizing time—physicists create a new phase of matter in the center of a diamond
In their ongoing efforts to push the boundaries of quantum possibilities, physicists in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis have created a new type of “time crystal,” a novel phase of matter that defies common perceptions of motion and time.
The WashU research team includes Kater Murch, the Charles M. Hohenberg Professor of Physics, Chong Zu, an assistant professor of physics, and Zu’s graduate students Guanghui He, Ruotian “Reginald” Gong, Changyu Yao, and Zhongyuan Liu. Bingtian Ye from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard University’s Norman Yao are also authors of the research, which has been published in the journal Physical Review X.
Zu, He, and Ye spoke about their achievement and the implications of catching time in a crystal.

New cancer therapy ‘disguises’ tumors as pork to trigger immune attack, 90% effective
In a groundbreaking moment for cancer, Chinese researchers turned the immune response provoked by organ transplants to fight the leading cause of death worldwide.
According to Columbia University’s Department of Surgery, 10–20% of patients who undergo transplant surgery will experience at least one rejection. However, researchers in China ingeniously turned that negative into a positive by directing that powerful impulse to attack cancer cells.
Called a “tumor-to-pork” strategy, a new study published in Cell earlier this year demonstrated immense success in engineering a virus that tricked the human body into believing that cancer cells were pig tissue, according to the South China Morning Post, thereby triggering a hyperacute inflammatory response. The virus began attacking the tumor with a staggering 90% success rate, to the point of curing a patient with advanced cervical cancer.
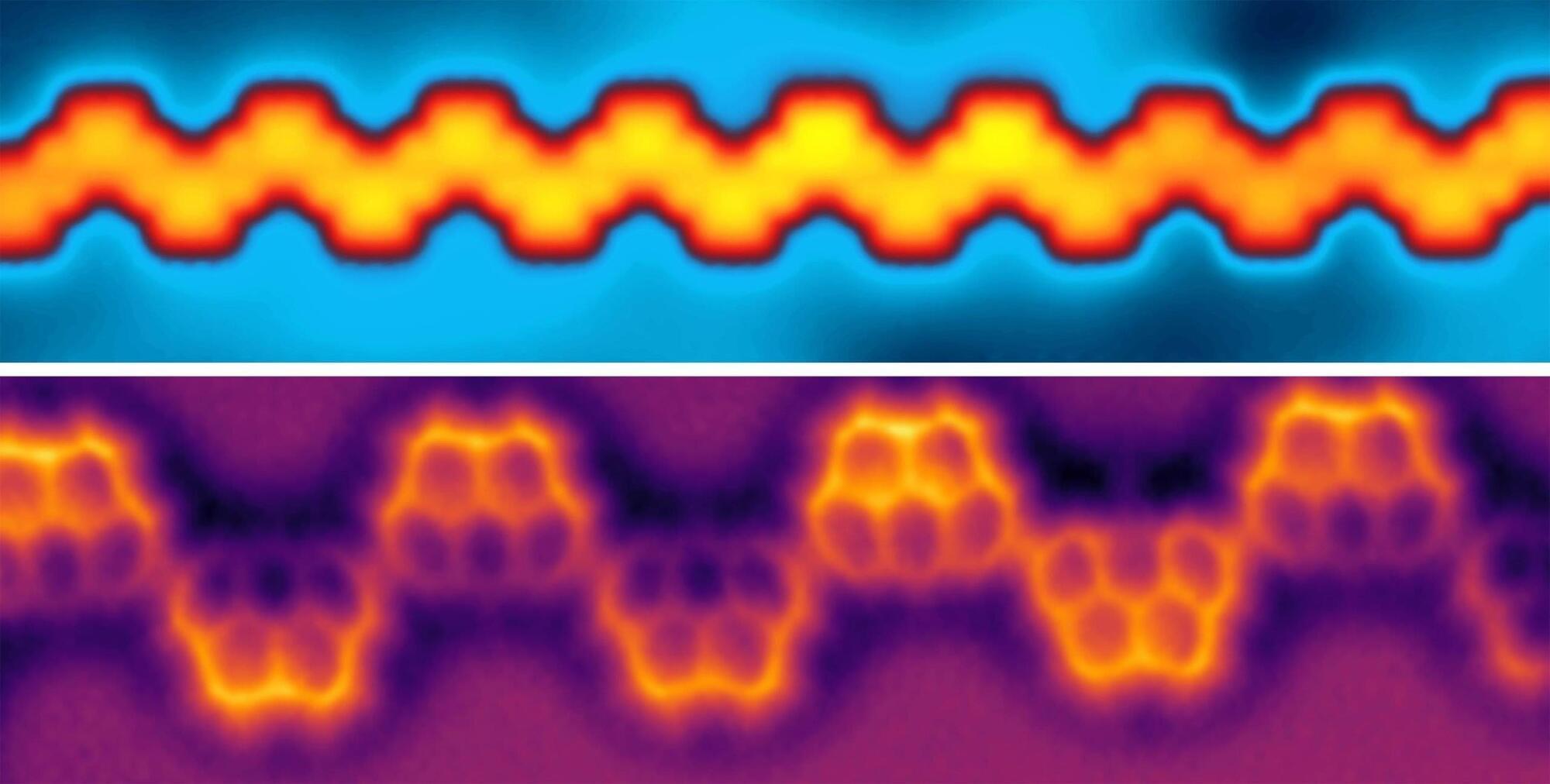
Physicists Just Made a Century-Old Quantum Theory a Reality
Quantum physics just took a leap from theory to reality! Empa researchers have, for the first time, successfully built a long-theorized one-dimensional alternating Heisenberg model using synthetic nanographenes.
By precisely shaping these tiny carbon structures, they’ve unlocked new ways to manipulate quantum states, confirming century-old predictions. This breakthrough could be a stepping stone toward real-world quantum technologies, from ultra-fast computing to unbreakable encryption.
Recreating a Century-Old Quantum Model.

Dark Matter May Be Annihilating Itself at the Heart of the Milky Way
A strange energy source at the center of the Milky WayThe Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System and is part of the Local Group of galaxies. It is a barred spiral galaxy that contains an estimated 100–400 billion stars and has a diameter between 150,000 and 200,000 light-years. The name “Milky Way” comes from the appearance of the galaxy from Earth as a faint band of light that stretches across the night sky, resembling spilled milk. tabindex=0 Milky Way may be a new type of dark matter.
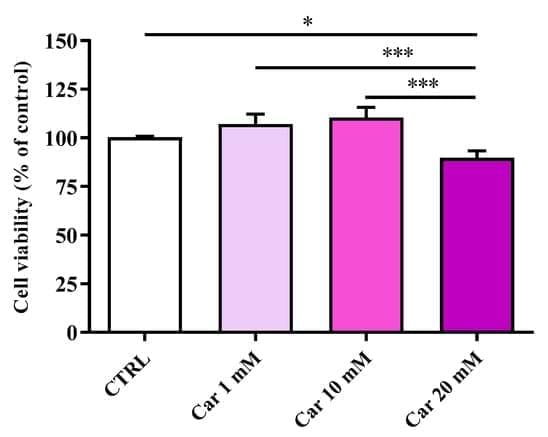
Characterization of Carnosine Effect on Human Microglial Cells under Basal Conditions
The activity of microglia is fundamental for the regulation of numerous physiological processes including brain development, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis, and its deviation from homeostasis can lead to pathological conditions, including numerous neurodegenerative disorders. Carnosine is a naturally occurring molecule with well-characterized antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, able to modulate the response and polarization of immune cells and ameliorate their cellular energy metabolism. The better understanding of microglia characteristics under basal physiological conditions, as well as the possible modulation of the mechanisms related to its response to environmental challenges and/or pro-inflammatory/pro-oxidant stimuli, are of utmost importance for the development of therapeutic strategies.