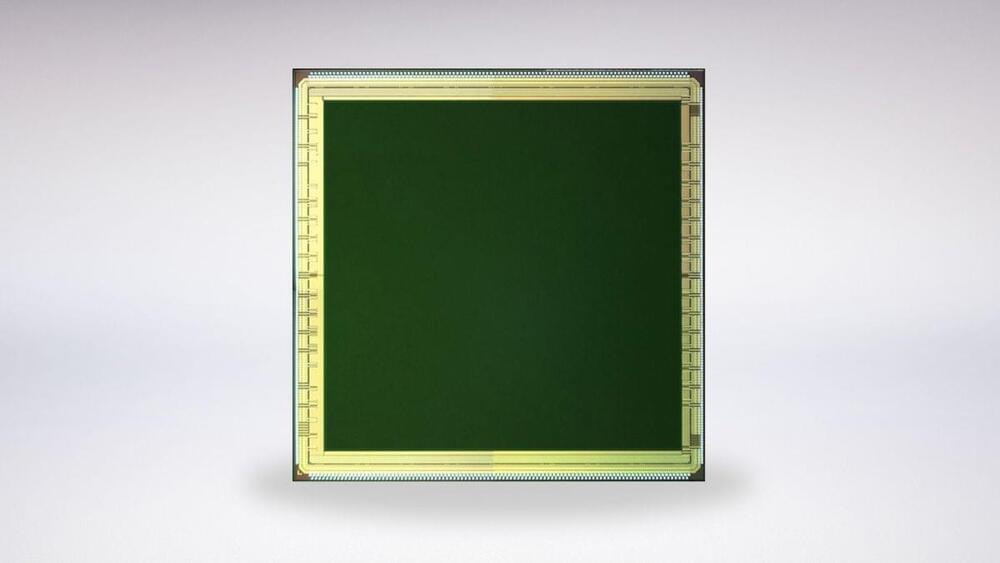
A bigger deal than computational photography?
Samsung and Canon have both announced new camera sensors that are both innovative in very different ways. But how exciting are they?
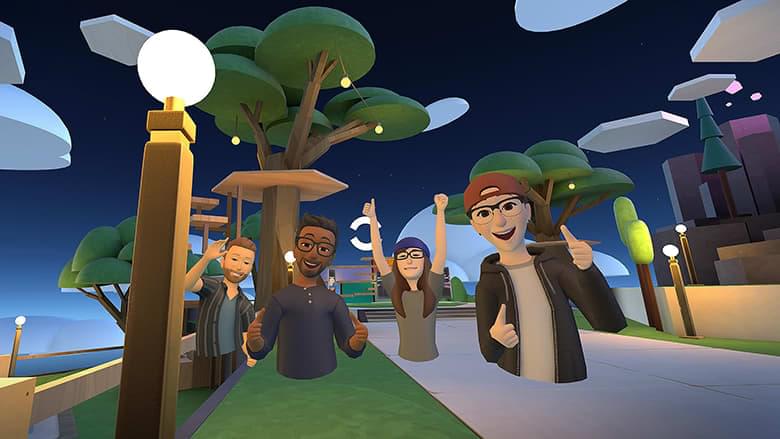

Facebook on Thursday announced that it is opening up Horizon Worlds, its virtual reality world of avatars, to anyone 18 and older in the U.S. and Canada.
Horizon Worlds launched in beta last year to select Oculus VR users, who answered invitations to join the virtual world. With the announcement on Thursday, users will no longer need to be invited.
The broader launch of Horizon Worlds is an important step for Facebook, which officially changed its name to Meta in October. The company adopted the new moniker, based on the sci-fi term metaverse, to describe its vision for working and playing in a virtual world.
😃
In a paper published today in the scientific journal Science, DeepMind demonstrates how neural networks can be used to describe electron interactions in chemical systems more accurately than existing methods.
Density Functional Theory, established in the 1960s, describes the mapping between electron density and interaction energy. For more than 50 years, the exact nature of mapping between electron density and interaction energy—the so-called density functional—has remained unknown. In a significant advancement for the field, DeepMind has shown that neural networks can be used to build a more accurate map of the density and interaction between electrons than was previously attainable.
By expressing the functional as a neural network and incorporating exact properties into the training data, DeepMind was able to train the model to learn functionals free from two important systematic errors—the delocalisation error and spin symmetry breaking—resulting in a better description of a broad class of chemical reactions.
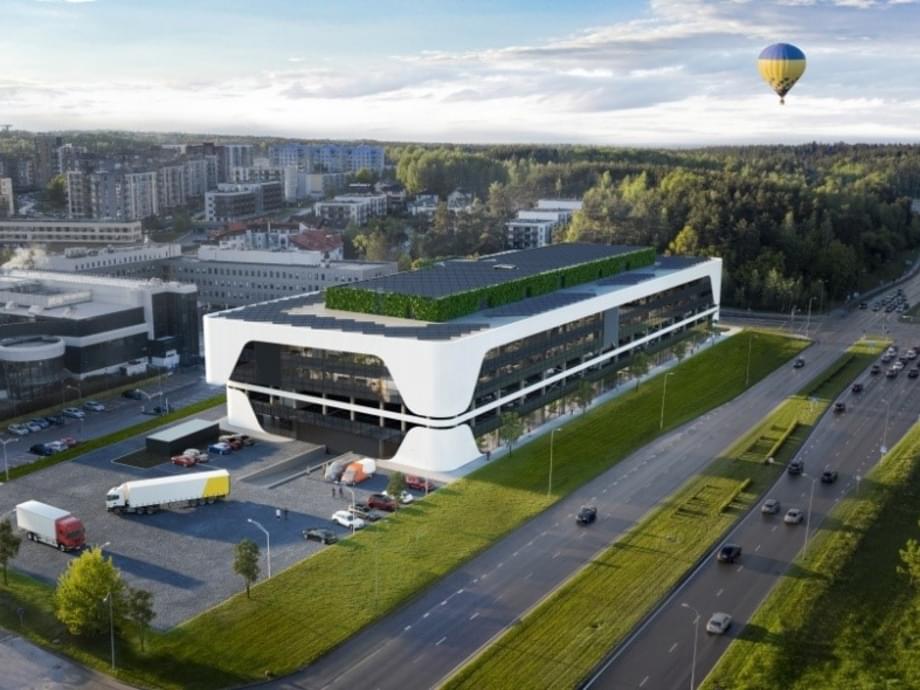
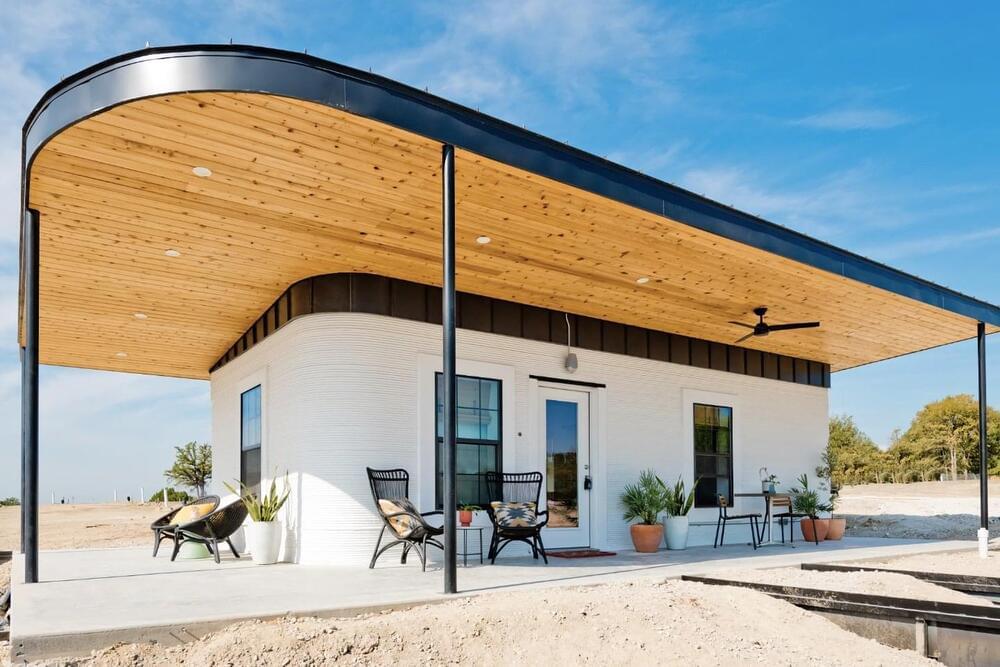



Nowadays almost everything is being 3D printed, so why should architecture be an exception? Many architectural firms are adopting 3D printing as their preferred technique to build structures. And 3D printed architecture is slowly but surely gaining a lot of popularity and momentum. This emerging trend is paving a path for itself in modern architecture. And I mean, no wonder, it has a ton of benefits! It’s a simple, efficient, and innovative technique that lowers the risks of errors, and also manages to save on time. 3D printing eradicates a lot of tedious steps during the construction process and simplifies it. It is being used to build homes, habitats on Mars, and even floating islands! The potential and possibilities of 3D printing in architecture are endless and mind-blowing. We’ve curated a collection of 3D-printed architectural structures that are our absolute favorites – from a 3D printed sustainable office pod to a 3D printed housing community for the homeless, every single one of these designs unleashes the magic and potential of 3D printing!


Moving CO2 from Air to Oceans May Be Necessary to Slow Warming.
Climbing concentrations of carbon dioxide make it likely that humans will have to move some gases from the atmosphere into the oceans to prevent crippling effects of climate change, the National Academies said in a major report released yesterday.
It came after months of deliberation among top U.S. scientists who concluded that global efforts to reduce emissions, even if successful, “may not be enough to stabilize the climate.” The report identified six ways to capture and store carbon dioxide in the oceans, a controversial idea that the report said “will likely be needed.”
Potential methods include stimulating more plant growth in and around the oceans and manipulating ocean currents to draw CO2 deep underwater.
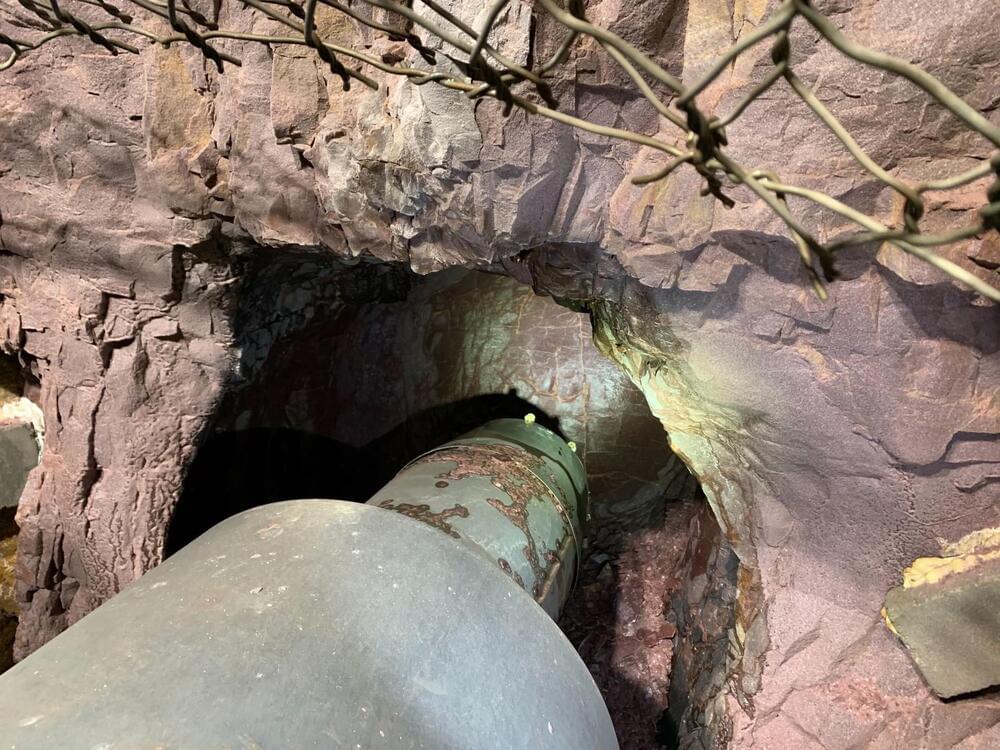

Petra emerged from stealth this week, announcing a $30 million Series A. The round, led by DCVC, brings the robotics company’s funding up to $33 million, with additional participation from ACME Capital Congruent Ventures, 8VC, Real Ventures, Elementum Ventures and Mac Venture Capital.
“We’ve invented a completely new way to excavate rock and this will have profound implications on the future of tunneling,” co-founder and CEO Kim Abrams said in release tied to the news. “By delivering a boring solution that affordably undergrounds utilities through high-grade rock, we can finally protect communities from exposure to wildfires and ensure the safety of critical infrastructure in disaster-prone areas, especially in places like the Sierra Nevada mountains, Rocky Mountains, and coastal regions.”
The news arrives as the company is announcing a successful pilot of its robot, Swifty. According to the firm, the robot successfully bored a 20-foot tunnel through Sioux Quartzite at a rate of one inch-per-minute. The metamorphic rock is notoriously hard, making it a popular choice for buildings in the upper Midwest region in which it is found. That strength, however, also makes it a formidable challenge from infrastructure and other projects that require tunneling.
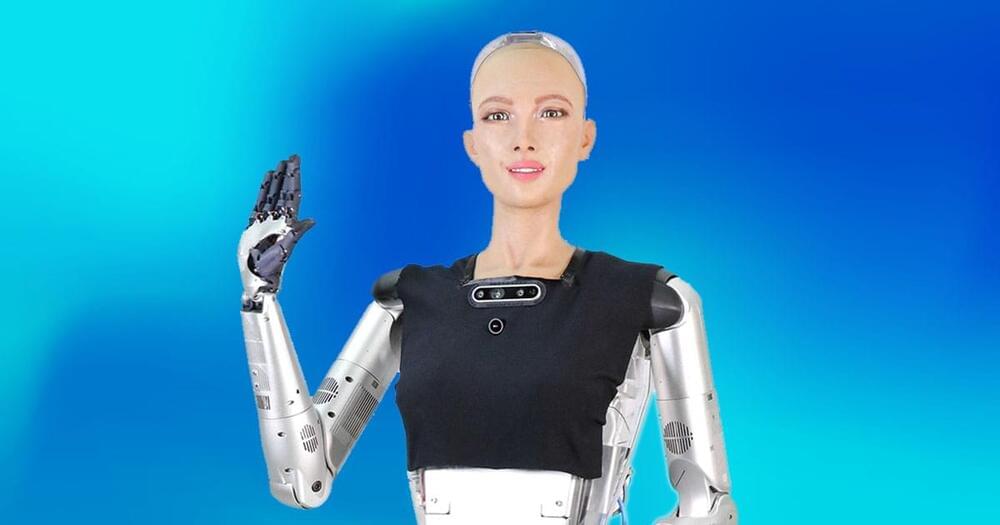

Since then, Sophia has spoken to audiences across the globe (in multiple languages), been interviewed on countless TV shows, and even earned a United Nations title (a first for a non-human).
Today, she’s arguably the most famous robot in the world, but she’s isn’t going to be unique for much longer. Her maker, Hanson Robotics, has announced plans to begin mass-producing Sophia the robot this year — so that she can help the world cope with the pandemic.