Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.



It contains a specially designed molecule that absorbs solar power
Take a closer look at the power of renewable energy: http://ow.ly/OGHF50IQ2Bb
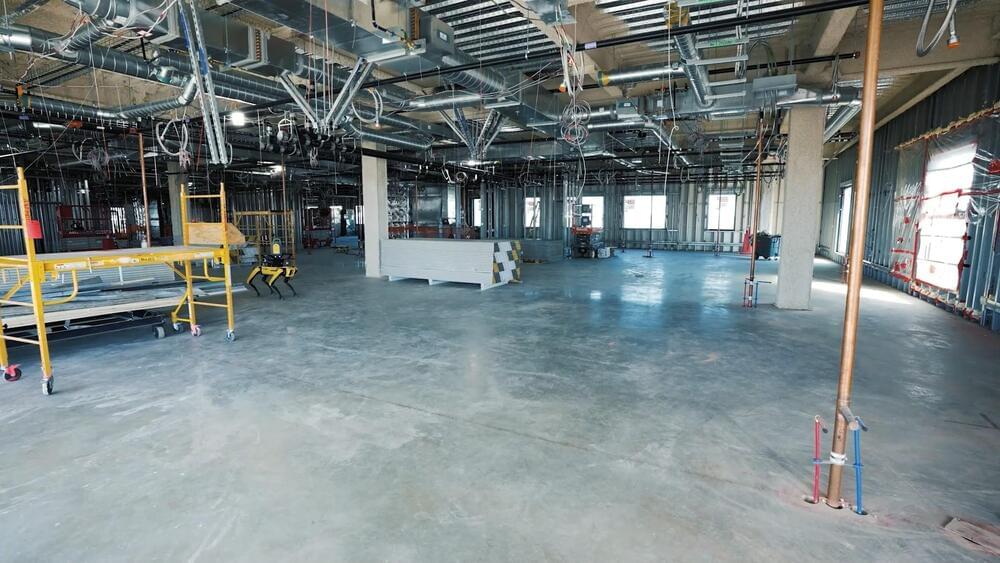





Understand what’s happening on your construction sites with effective reality capture data
See the robotic solution in action with Spot and Trimble Buildings!
