Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Secretive Giant TSMC’s $100 Billion Plan To Fix The Chip Shortage
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company makes 24% of all the world’s chips, and 92% of the most advanced ones found in today’s iPhones, fighter jets and supercomputers. Now TSMC is building America’s first 5-nanometer fabrication plant, hoping to reverse a decades-long trend of the U.S. losing chip manufacturing to Asia. CNBC got an exclusive tour of the $12 billion fab that will start production in 2024.
» Subscribe to CNBC: https://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBC
» Subscribe to CNBC TV: https://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBCtelevision.
» Subscribe to CNBC Classic: https://cnb.cx/SubscribeCNBCclassic.
About CNBC: From ‘Wall Street’ to ‘Main Street’ to award winning original documentaries and Reality TV series, CNBC has you covered. Experience special sneak peeks of your favorite shows, exclusive video and more.
Connect with CNBC News Online.
Get the latest news: https://www.cnbc.com/
Follow CNBC on LinkedIn: https://cnb.cx/LinkedInCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Facebook: https://cnb.cx/LikeCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Twitter: https://cnb.cx/FollowCNBC
Follow CNBC News on Instagram: https://cnb.cx/InstagramCNBC
#CNBC
Secretive Giant TSMC’s $100 Billion Plan To Fix The Chip Shortage.


Facebook is planning to rebrand the company with a new name
The tech giant wants to be known for more than social media’s ills.
Facebook is planning to change its company name next week to reflect its focus on building the metaverse, according to a source with direct knowledge of the matter.
The coming name change, which CEO Mark Zuckerberg plans to talk about at the company’s annual Connect conference on October 28th, but could unveil sooner, is meant to signal the tech giant’s ambition to be known for more than social media and all the ills that entail. The rebrand would likely position the blue Facebook app as one of many products under a parent company overseeing groups like Instagram, WhatsApp, Oculus, and more. A spokesperson for Facebook declined to comment for this story.
Facebook already has more than 10,000 employees building consumer hardware like AR glasses that Zuckerberg believes will eventually be as ubiquitous as smartphones. In July, he told The Verge that, over the next several years, “we will effectively transition from people seeing us as primarily being a social media company to being a metaverse company.”
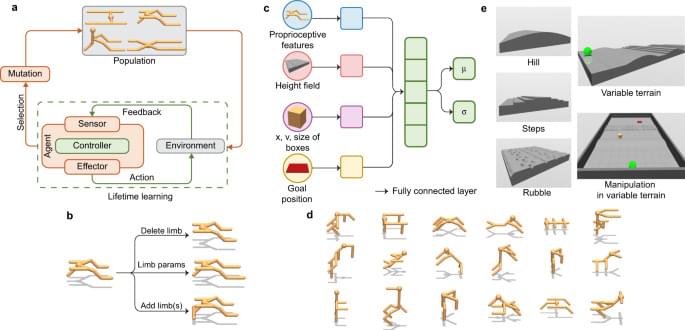
Embodied intelligence via learning and evolution
The authors present a high-resolution palaeomagnetic record for a Late Cretaceous limestone in Italy. They claim that their record robustly shows a ~12° true polar wander oscillation between 86 and 78 Ma, with the greatest excursion at 84–82 Ma.
The authors propose a new framework, deep evolutionary reinforcement learning, evolves agents with diverse morphologies to learn hard locomotion and manipulation tasks in complex environments, and reveals insights into relations between environmental physics, embodied intelligence, and the evolution of rapid learning.
SpaceX Crew-3 Dragon Falcon 9 Launch — Manned SpaceX Live Mission to The ISS!
We’re just 7 days away from the launch of Crew-3 to the ISS!
Mission livestream:
Discord: https://discord.gg/7Szs3Qma.
Become a member to my channel!
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCn8SmzG1xXx_inu-XADxcMg/join.
SpaceX and NASA are targeting Thursday, April 22 for Falcon 9’s launch of Dragon’s second six-month operational crew mission (Crew-2) to the International Space Station (ISS) from historic Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The instantaneous launch window opens at 2:21 a.m. EDT…
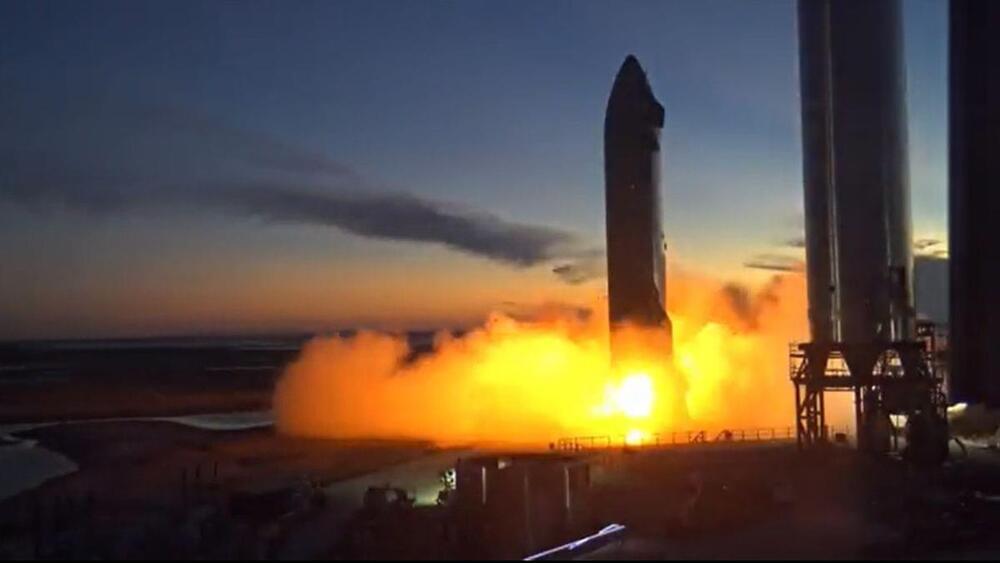

SpaceX shows off its ‘Gateway to Mars’ for Starship launches in video
SpaceX is hoping to launch its first orbital Starship test flight in the next few months from its Starbase facility in Texas and a new video captures the company’s work so far on the massive rocket.
The 90-second montage, which SpaceX showed off on Twitter, offers views of the company’s massive Starship spacecraft being wheeled to the launch pad, taking off, performing complex flips and then landing safely on the ground. You also catch a glimpse of Earth from up high.

NASA finds first ever planet outside our galaxy
A NASA telescope might have found the first ever planet outside of our own Milky Way galaxy.
If confirmed, the world would be thousands of times further away than the many exoplanets we have found in our own galaxy so far.
Scientists were able to do so using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, using techniques that could allow for the search for other worlds to dramatically the amount of space it is able to scan.