SoftBank’s humanoid robot had big career plans, including a job at a bank and dancing with the elderly. Ask about Pepper these days, though, and the conversation gets awkward.
An engineer who helped develop a camera for Mars has built a tool to track the most fascinating car in the Solar System.
Europe’s largest battery storage project – and the first to reach 100 megawatts of capacity – has begun operations at Minety in Wiltshire, UK.
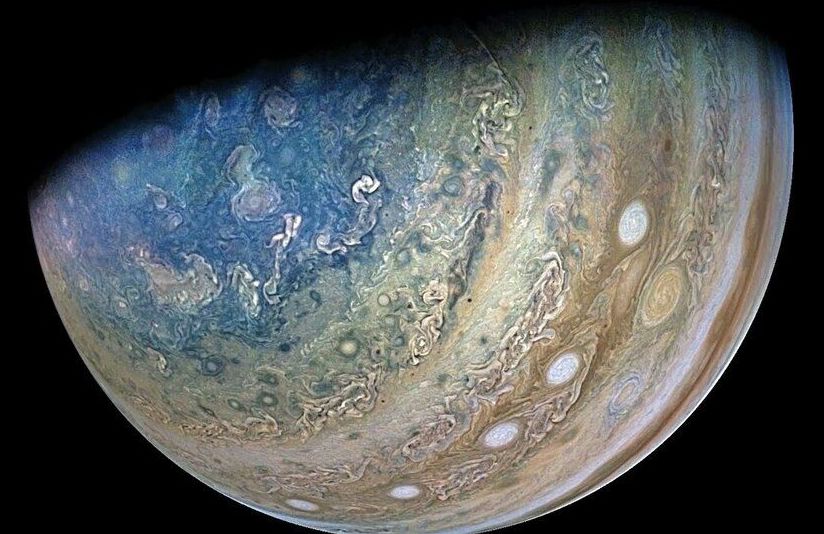
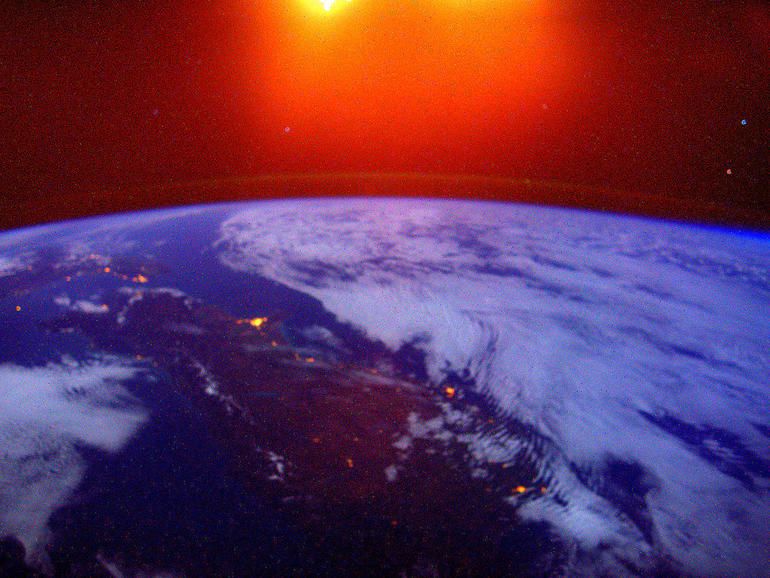
NASA’s Juno probe has flown closer to Jupiter and its largest moon, Ganymede, than any other spacecraft in more than two decades — and the images it beamed back of the gas giant and its icy orb are breathtaking.
Juno approached Ganymede on June 7, before making its 34th flyby of Jupiter the following day, traveling from pole to pole in under three hours.
On Thursday, NASA released an animated series of images captured by the spacecraft’s JunoCam imager, providing a “starship captain” point of view of each flyby. They mark the first close-up views of the largest moon in the solar system since the Galileo orbiter last flew past in 2000.
Researchers at UC San Francisco have successfully developed a “speech neuroprosthesis” that has enabled a man with severe paralysis to communicate in sentences, translating signals from his brain to the vocal tract directly into words that appear as text on a screen.
The achievement, which was developed in collaboration with the first participant of a clinical research trial, builds on more than a decade of effort by UCSF neurosurgeon Edward Chang, MD, to develop a technology that allows people with paralysis to communicate even if they are unable to speak on their own. The study appears July 15 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
😀
Microsoft is overhauling its emoji to make them 3D. The new design includes the return of Clippy to replace the paperclip emoji in Office and more.
The world’s largest contract chip maker said it expects the chip shortage that has hampered car makers to start easing in the next few months after it ramped up its production of auto chips.
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., the world’s largest contract chip maker, said it expects the chip shortage that has hampered car makers to start easing in the next few months after it ramped up its production of auto chips.
The company is on track to increase output of microcontrollers used in cars by about 60% this year compared with last, Chief Executive C.C. Wei said in an earnings call on Thursday. However, he said, the broader semiconductor shortage could persist until 2022.
A dearth of semiconductors, used in products including home appliances and smartphones, has stymied manufacturing activity, notably in the auto industry. That shortfall should be greatly reduced for TSMC customers in the current quarter, Mr. Wei said.
A breakthrough in quantum computing could expose every communications link. The same breakthrough could make everything secure again. What could change everything are all the events in-between.
Elon Musk confirmed that Tesla currently has a Powerwall backlog of 80000 orders, which is worth over $500 million, but it can’t ramp up production to meet that due to the global chip shortage.
Tesla has been production constrained with the Powerwall for a long time.
The demand has been strong in several markets, like the US and Australia, but production hasn’t been to catch up despite significant ramp-ups.