Superconductivity and the end of resistance.
Superconductors will be a technology that we will greatly benefit from in the future. Innovative projects to solve our energy problems, such as fusion reactors, rely on their unique properties.

Cybercriminals have started using Static Web Apps, an Azure service, in their phishing attacks against Microsoft 365 (opens in new tab) users.
Researchers from MalwareHunterTeam noted Static Web Apps have two features that are being abused with ease — custom branding for web apps, and web hosting for static content such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or images.


West Virginia’s largest solar farm will sit on the site of the 5,800-acre Hobet Mine, one of the state’s largest former coal mines, which went bankrupt in 2015.
UnderstandSolar is a free service that links you to top-rated solar installers in your region for personalized solar estimates. Tesla now offers price matching, so it’s important to shop for the best quotes. Click here to learn more and get your quotes. — *ad.
The solar farm will be situated on 3,000 acres of the site, which straddles Boone and Lincoln counties in the southwestern part of the state, near Charleston. It will power an adjacent 2,800-acre site that will host industry, lodging, hospitality, and recreation, and the whole site will be known as SunPark. The solar farm is the first phase of the project.

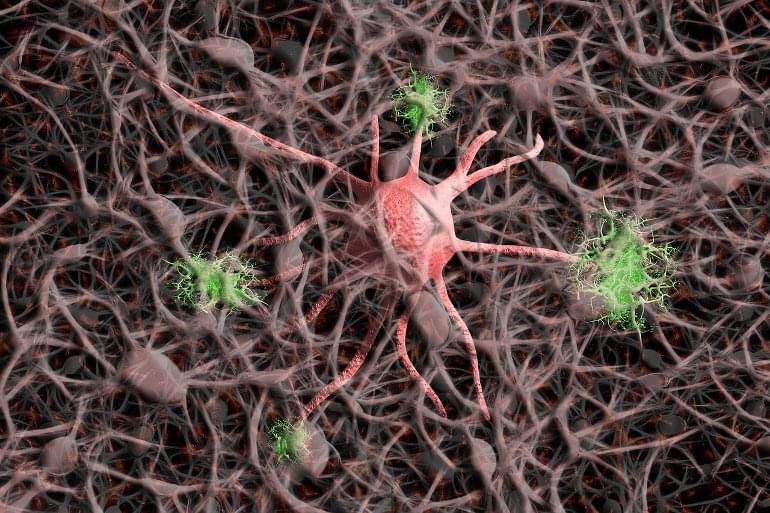
Summary: Researchers have released a whole-brain projectome consisting of over 6,000 single neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex.
Source: Chinese Academy of Science.
In a study published in Nature Neuroscience, scientists at the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with their collaborators, reported the first release of a whole-brain projectome comprising over 6,000 single neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex (PFC), making it the largest database of a whole-brain, single-neuron mouse projectome to date.

The dissemination of synthetic biology into materials science is creating an evolving class of functional, engineered living materials that can grow, sense and adapt similar to biological organisms.
Nature has long served as inspiration for the design of materials with improved properties and advanced functionalities. Nonetheless, thus far, no synthetic material has been able to fully recapitulate the complexity of living materials. Living organisms are unique due to their multifunctionality and ability to grow, self-repair, sense and adapt to the environment in an autonomous and sustainable manner. The field of engineered living materials capitalizes on these features to create biological materials with programmable functionalities using engineering tools borrowed from synthetic biology. In this focus issue we feature a Perspective and an Article to highlight how synergies between synthetic biology and biomaterial sciences are providing next-generation engineered living materials with tailored functionalities.
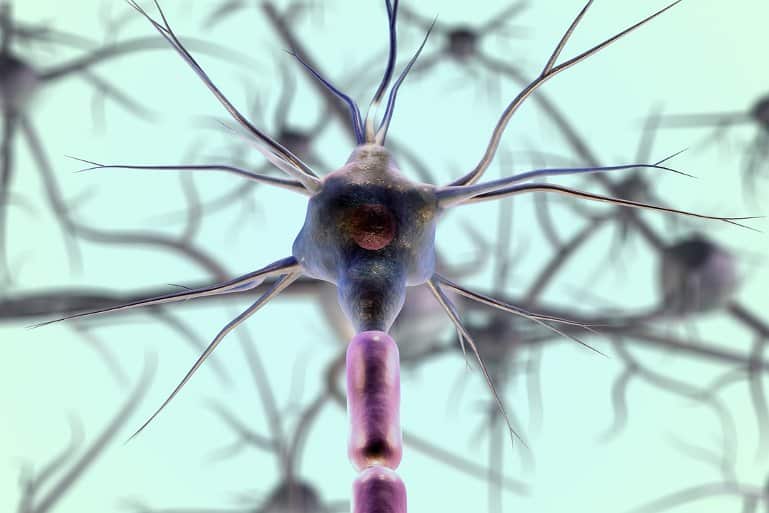
Summary: Using algebraic topography, researchers have created an algorithm that requires only a few examples to generate a large number of unique cells.
Source: EPFL
EPFL’s Blue Brain Project has found a way to use only mathematics to automatically draw neurons in 3D, meaning we are getting closer to being able to build digital twins of brains.


SpaceX’s first upgraded 33-engine Super Heavy booster appears to have passed a crucial test with surprising ease, boding well for a smooth qualification process.
Attempting that test so early on did not appear to be SpaceX’s initial plan. Instead, shortly before Super Heavy Booster 4’s third and likely final removal from Starbase’s ‘orbital launch mount’ (OLM) on March 24th, SpaceX transported a massive structural test stand from a Starbase storage yard to the orbital launch site (OLS), where technicians have focused on modifying nearby ground systems to support apparent structural testing of Super Heavy Booster 7. As of March 31st, all available evidence suggested that SpaceX was preparing that stand to verify Booster 7’s mechanical strength and simulate the major stresses it might experience before investing a significant amount of time and resources in qualification testing.
However, SpaceX appeared to change its plans at the last minute.