False Memory Syndrome (FMS)
Posted in futurism
As Australia turns to nuclear power for its submarines, a UK prototype will test the use of autonomous green hydrogen submarines for freight transport.
A world-first green submarine project will soon get underway after a proposal to power an autonomous underwater vessel with green hydrogen won a share of a United Kingdom £23 million funding program.
Start-up company Oceanways is to build a prototype of a zero emission submarine initially designed to deliver cargo in a twenty-foot container between Glasgow and Belfast.
As the green submarines move underwater, they will also filter microplastics and microfibres out of the ocean, and collect information and data on ocean health and acidification via a number of onboard sensors.
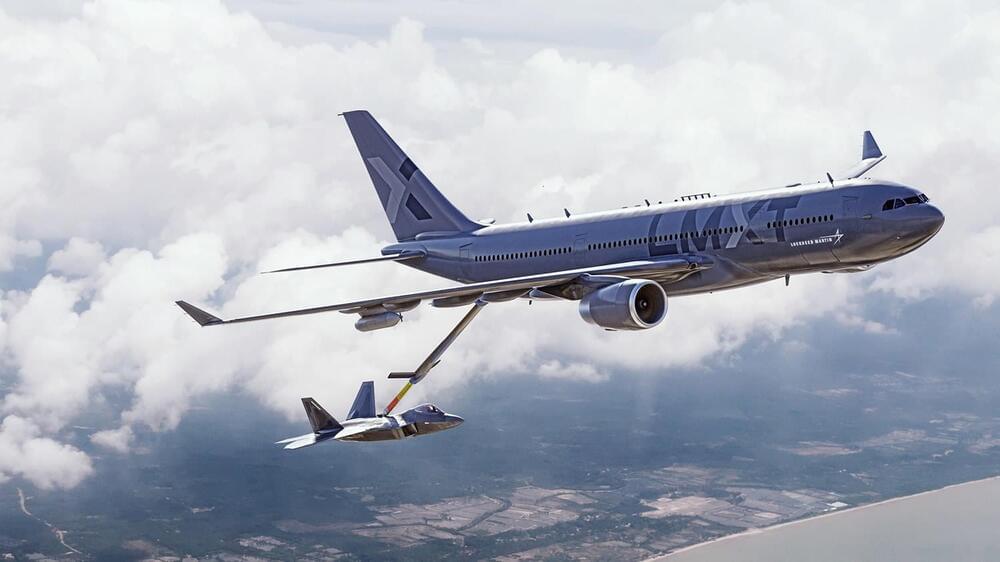
Some improvements of the new model include a significantly improved range, fuel offload capacity, operational and combat-proven advanced camera and vision system, and upgraded communications system. The tanker will have 271,700 pounds (123,241 kg) of fuel capacity – 12,000 kg more than the Airbus A330 MRTT and an almost 20-hour endurance.
“Lockheed Martin has a long and successful track record of producing aircraft for the US Air Force, and we understand the critical role tankers play in ensuring America’s total mission success,” said Greg Ulmer, executive vice president Lockheed Martin Aeronautics. “The LMXT combines proven performance and operator-specific capabilities to meet the Air Force’s refueling requirements in support of America’s National Defense Strategy.”
In addition to better range and increased payload, the LMXT tanker is equipped with a proven fly-by-wire boom currently certified and used by allies to refuel US Air Force receiver aircraft in operations around the world, the world’s first fully automatic boom/air-to-air refueling (A3R) system, and open system architecture JADC2 (Joint All-Domain Command and Control) systems.