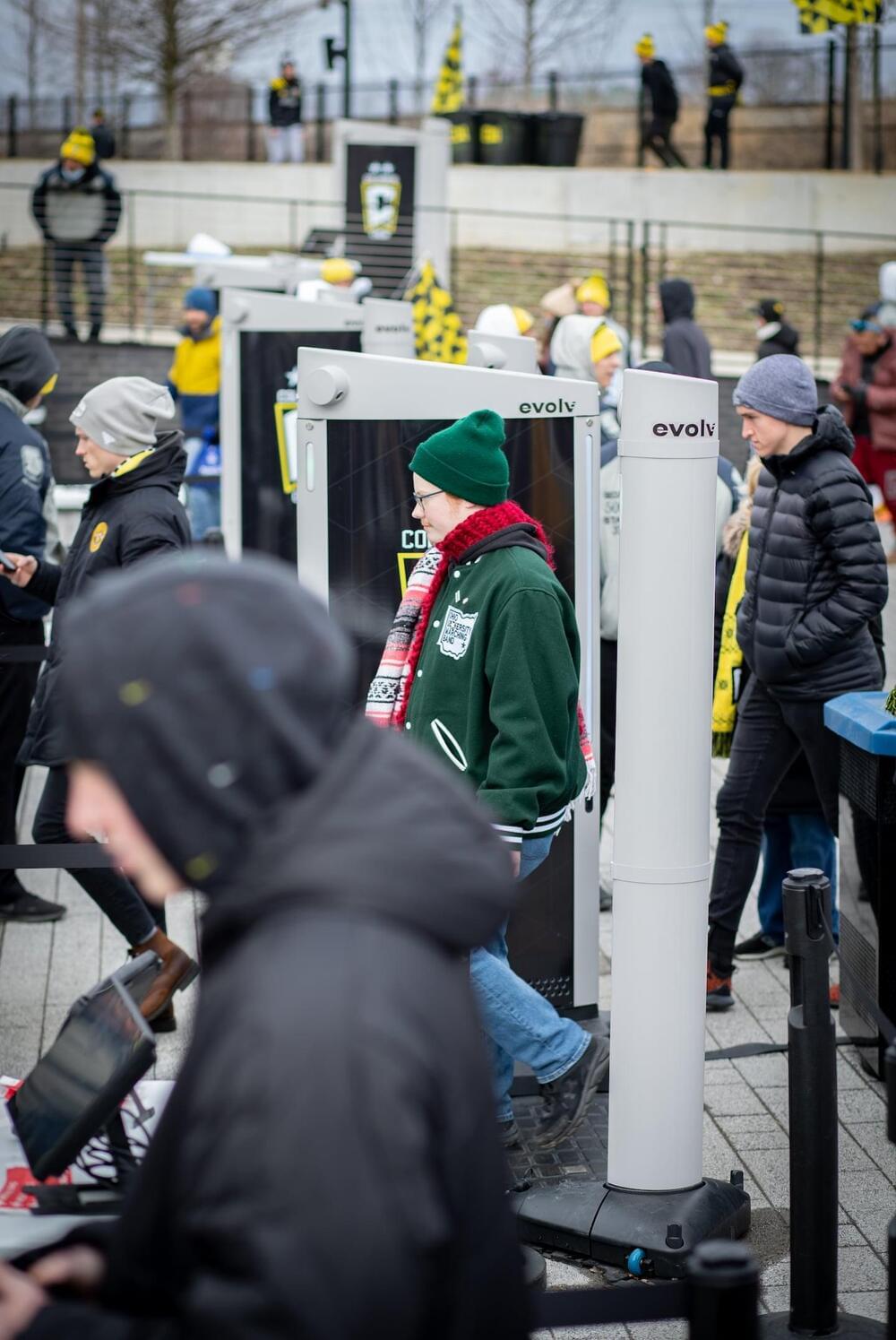
UK’s National Grid Electricity Transmission (NGET) is launching trials to fully automate the corrosion inspection of electricity transmission pylons with the help of autonomous drones.
NGET owns 21,900 steel lattice pylons that carry overhead transmission conductor wires in England and Wales. Transmission pylon steelwork conditions can deteriorate through corrosion, so periodic assessments are made to understand the health of the network. NGET inspects around 3,650 steel lattice pylons each year, capturing high definition still color images of steelwork using helicopters and manually-operated drones.