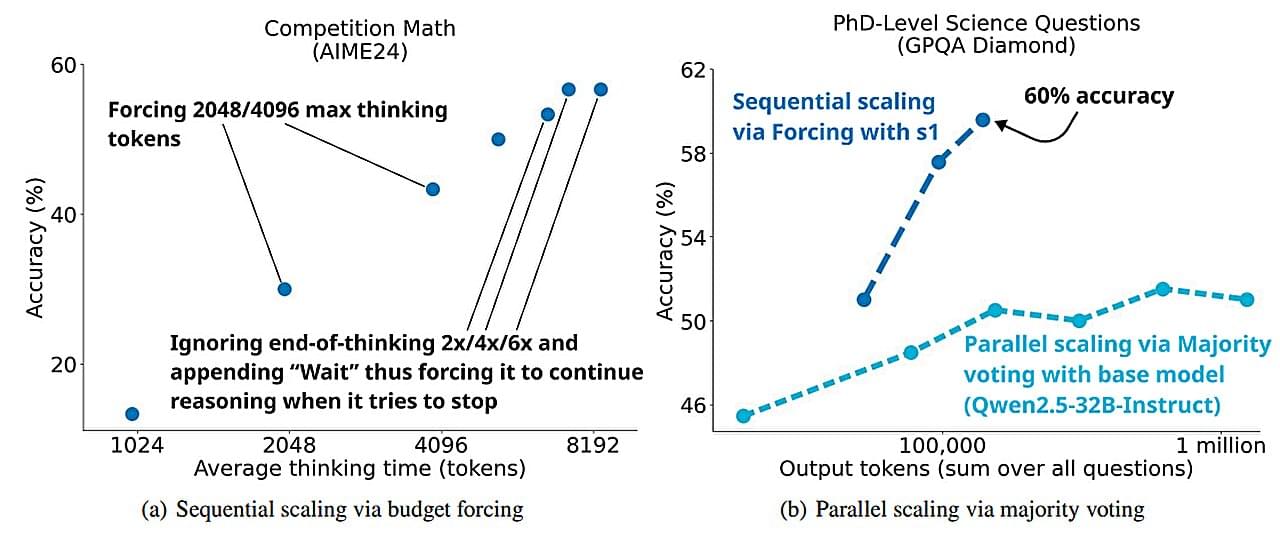
A small team of AI researchers from Stanford University and the University of Washington has found a way to train an AI reasoning model for a fraction of the price paid by big corporations that produce widely known products such as ChatGPT. The group has posted a paper on the arXiv preprint server describing their efforts to inexpensively train chatbots and other AI reasoning models.
Corporations such as Google and Microsoft have made clear their intentions to be leaders in the development of chatbots with ever-improving skills. These efforts are notoriously expensive and tend to involve the use of energy-intensive server farms.
More recently, a Chinese company called DeepSeek released an LLM equal in capabilities to those being produced by countries in the West developed at far lower cost. That announcement sent stock prices for many tech companies into a nosedive.