For the first time, scientists have managed to restore central vision loss from an irreversible age-related eye condition via the help of a tiny retinal implant.



Volcanologists say the mountain isn’t erupting, yet it’s stirring. The air above the ridge is turning thorny and metallic, a caution flag for pilots and a puzzle for the scientists who listen to rocks. In a place where weather already rules the day, the sky just picked up a new voice.
The first hint wasn’t dramatic. It was a smell—faint, almost shy—like a match just struck and blown out on an icy ridge. A pilot crossing the Aleutians radioed a hazy strip hanging off a lonely summit, not smoke, not weather, something in between. Out on the gravel bar, a field tech rubbed a gloved thumb across a thin yellow smear on late spring snow and didn’t say a word. A satellite pass, then another, traced a ribbon of sulfur above open water. The mountain had gone from silence to a whisper. That whisper could carry.

Scientists have identified mutations in the CPD gene as a key cause of a rare congenital hearing loss, revealing how disruptions in arginine and nitric oxide signaling damage sensory cells in the ear. Using mouse and fruit fly models, the team showed that restoring arginine levels or using sildenafil improved cell survival and hearing function.

Adults with gum disease may be more likely to have signs of damage to the brain’s white matter, called white matter hyperintensities, than people without gum disease, according to a study published in Neurology Open Access.
White matter refers to nerve fibers that help different parts of the brain communicate. Damage to this tissue can affect memory, thinking, balance and coordination and has been linked to higher stroke risk.
White matter hyperintensities are bright spots that appear on brain scans that are thought to reflect damaged white matter tissue. While the study found an association, it does not prove that gum disease causes white matter damage.

Spinning crystals that twist, shatter, and rebuild themselves may hold the key to next-generation materials… Physicists have uncovered the fascinating world of “rotating crystals” — solids made of spinning particles that behave in strange, almost living ways. These odd materials can twist instead of stretch, shatter into fragments, and even reassemble themselves.

Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery of a colossal bridge of neutral hydrogen gas linking two dwarf galaxies. Scientists at The University of Western Australia’s node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) have made a remarkable discovery: a massive structure stretching about 185,000 light-years between two galaxies, NGC 4532 and DDO 137, located some 53 million light-years from Earth.
Multi-Modality Treg Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases — Dr. Fred Grossman, D.O., FAPA — President and Chief Medical Officer — Coya Therapeutics, Inc.
Dr. Fred Grossman, D.O., FAPA is President and Chief Medical Officer of Coya Therapeutics (https://coyatherapeutics.com/), a clinical-stage company focused on developing multi-modality, Regulatory T Cell (Treg) therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Coya has already developed strong proof of concept data in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s, and is also active in the autoimmune and metabolic disease domains.
Dr. Grossman brings over 20 years of drug development expertise having held senior executive leadership positions in large and small pharmaceutical companies, leading the development and FDA approval of numerous multi-billion dollar blockbuster drugs addressing significant unmet medical needs particularly across CNS disorders. He has close relationships with thought leaders worldwide and has negotiated directly with the FDA and Global Health Authorities for approval of many drugs across therapeutic areas.
Dr. Grossman held executive positions at Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Sunovion. He served as President and Chief Medical Officer at Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, a $1.5 Billion per annum global pharmaceutical company based in India, overseeing development of an entire pipeline including generics, complex generics including 505(b) candidates, and next-generation biologics (including bi-specific antibodies).
Dr. Grossman also previously served as Chief Medical Officer at Mesoblast, Inc., developing allogeneic cellular therapies for inflammatory diseases.
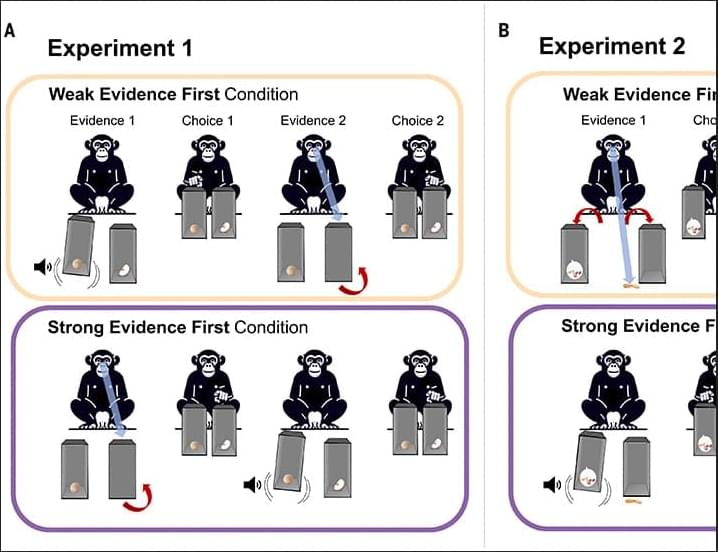
The study, titled “,” was conducted by a large research team that included UC Berkeley Psychology Postdoctoral Researcher Emily Sanford, UC Berkeley Psychology Professor Jan Engelmann and Utrecht University Psychology Professor Hanna Schleihauf. Their findings showed that chimpanzees — like humans — can change their minds based on the strength of available evidence, a key feature of rational thought.
Working at the Ngamba Island Chimpanzee Sanctuary in Uganda, the researchers presented chimps with two boxes, one containing food. Initially, the animals received a clue suggesting which box held the reward. Later, they were given stronger evidence pointing to the other box. The chimps frequently switched their choices in response to the new clues.
“Chimpanzees were able to revise their beliefs when better evidence became available,” said Sanford, who is a researcher in the UC Berkeley Social Origins Lab. “This kind of flexible reasoning is something we often associate with 4-year-old children. It was exciting to show that chimps can do this too.”
To ensure the findings reflected genuine reasoning rather than instinct, the team incorporated tightly controlled experiments and computational modeling. These analyses ruled out simpler explanations, such as the chimps favoring the latest signal (recency bias) or reacting to the most obvious cue. The models confirmed that the chimps’ decision-making aligned with rational strategies of belief revision.
“We recorded their first choice, then their second, and compared whether they revised their beliefs,” Sanford said. “We also used computational models to test how their choices matched up with various reasoning strategies.”
The study challenges the traditional view that rationality — the ability to form and revise beliefs based on evidence — is exclusive to humans.
“The difference between humans and chimpanzees isn’t a categorical leap. It’s more like a continuum,” Sanford said.
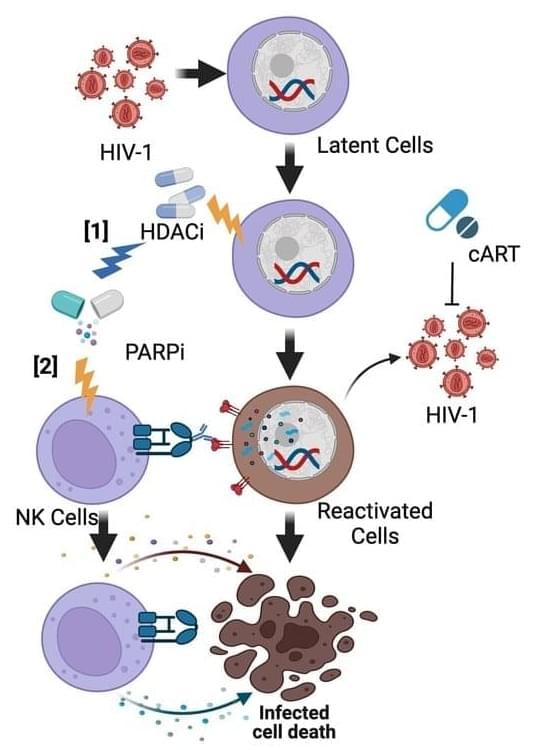
The “Kick and Kill” strategy, which aims to reactivate latent HIV reservoirs and facilitate the clearance of reactivated HIV-infected cells, has yet to achieve a functional cure due to the limited efficacy of current latency reversal agents. This study evaluates the combination efficacy of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor in latency reversal and immune-mediated clearance. Latently infected J-Lat cells and dual-fluorescent HIV-infected primary CD4 T cells were treated with the HDAC inhibitor (vorinostat) and one of four PARP inhibitors (olaparib, rucaparib, niraparib, or talazoparib). PARP inhibitors, when administered alone, showed no latency reversal activity. However, when combined with vorinostat, their efficacy increased threefold compared to vorinostat alone.
Flatworms can rebuild themselves from just a small fragment, and now scientists know why. Their stem cells ignore nearby instructions and respond to long-distance signals from other tissues. This discovery turns old stem cell theories upside down and could lead to new ways to repair or regrow human tissue. It also reveals a hidden complexity in one of nature’s simplest creatures.