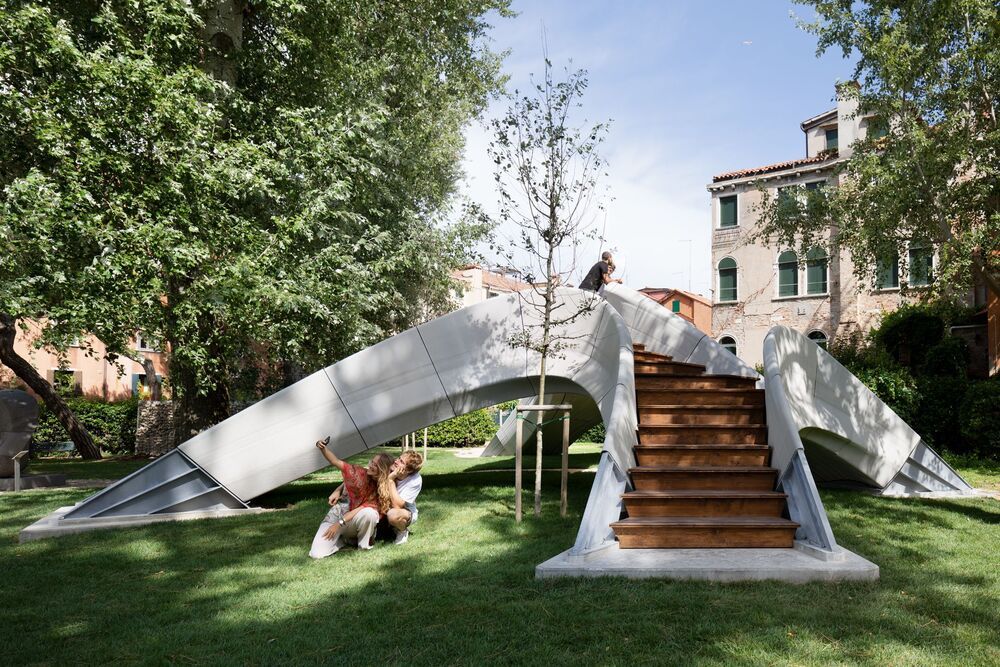
A first-of-its-kind 3D-printed concrete bridge has been unveiled in Venice, Italy. The bridge is a demonstration of a new 3D printing method resulting in a structure requiring no mortar or steel reinforcement.
The bridge was developed as part of a collaboration between ETH Zurich and Zaha Hadid Architects’ Computation and Design Group. The unreinforced structure was created by 3D-printing concrete blocks using a novel type of concrete ink produced by a company called Holcim.
“This precise method of 3D concrete printing allows us to combine the principles of traditional vaulted construction with digital concrete fabrication to use material only where it is structurally necessary without producing waste,” explains Philippe Block, a researcher from ETH Zurich.