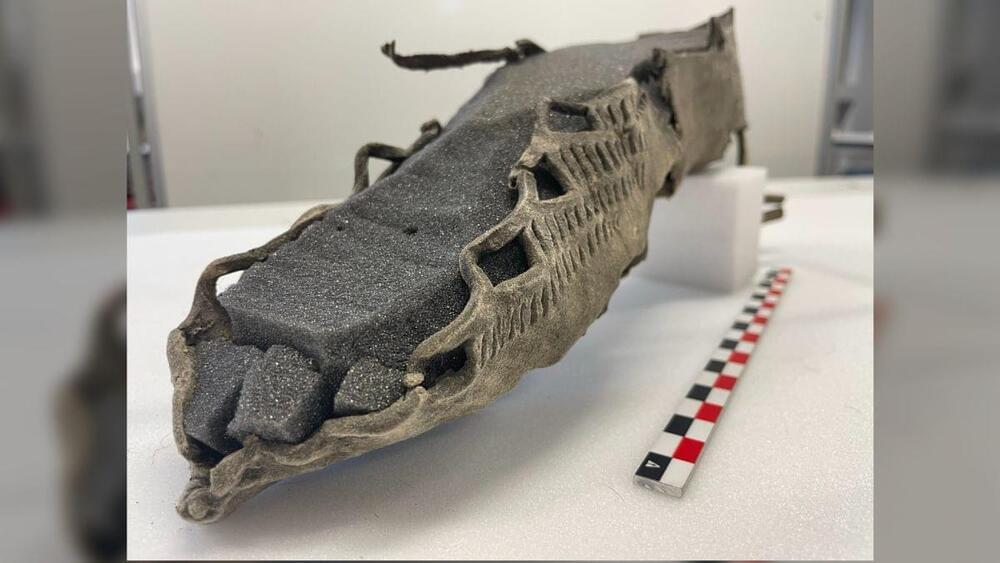
The sandal reveals that humans historically used the icy pass.




Our brains are awash with various unsung chemical heroes, making sure the electrical signals traveling all over the place don’t get out of control.
A new mouse study has now detailed the function of a pair of proteins vital to maintaining this balance – this could help us better understand a range of neurological disorders from epilepsy to schizophrenia.
The two proteins – Rab3-interacting molecule 1 (RIM1) and an enzyme called serine arginine protein kinase 2 (SRPK2) – work together to modify the transmission of information across the gaps between nerves called synapses.


NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 Mission to the Space Station
On April 18, the astronauts of our SpaceX Crew-4 mission arrived at our Kennedy Space Center to prepare for their launch to the International Space Station. NASA’s Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, along with Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) are excited about their scientific expedition to the station.
Stuart Russell warns about the dangers involved in the creation of artificial intelligence. Particularly, artificial general intelligence or AGI.
The idea of an artificial intelligence that might one day surpass human intelligence has been captivating and terrifying us for decades now. The possibility of what it would be like if we had the ability to create a machine that could think like a human, or even surpass us in cognitive abilities is something that many envision. But, as with many novel technologies, there are a few problems with building an AGI. But what if we succeed? What would happen should our quest to create artificial intelligence bear fruit? How do we retain power over entities that are more intelligent than us? The answer, of course, is that nobody knows for sure. But there are some logical conclusions we can draw from examining the nature of intelligence and what kind of entities might be capable of it.
Stuart Russell is a Professor of Computer Science at the University of California at Berkeley, holder of the Smith-Zadeh Chair in Engineering, and Director of the Center for Human-Compatible AI. He outlines the definition of AI, the risks and benefits it poses for the future. According to him, the idea of an AGI is the most important problem to intellectually to work on.
An AGI could be used for many good and evil purposes. Although there are huge benefits to creating an AGI, there are also downsides to doing so. If we create and deploy an AGI without understanding what risks it can cause for humans and other beings in our world, we could be contributing to great disasters.
Russel also postulates that we should focus on developing a machine that learns what each of the eight billion people on Earth would like the future to be like.
#AI #AGI #science.
SUBSCRIBE to our channel “Science Time”: https://www.youtube.com/sciencetime24
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Papers referenced in the video:
Dietary oxalate to calcium ratio and incident cardiovascular events: a 10-year follow-up among an Asian population.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35346210/
Predicting Age by Mining Electronic Medical Records with Deep Learning Characterizes Differences between Chronological and Physiological Age.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5716867/
Association between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular mortality in statin non-users: a prospective cohort study in 14.9 million Korean adults.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35218344/
Joint distribution of lipoprotein cholesterol classes. The Framingham study) AND abbott lipoproteins 1983
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6573877/
Incidental lymphopenia and mortality: a prospective cohort study.
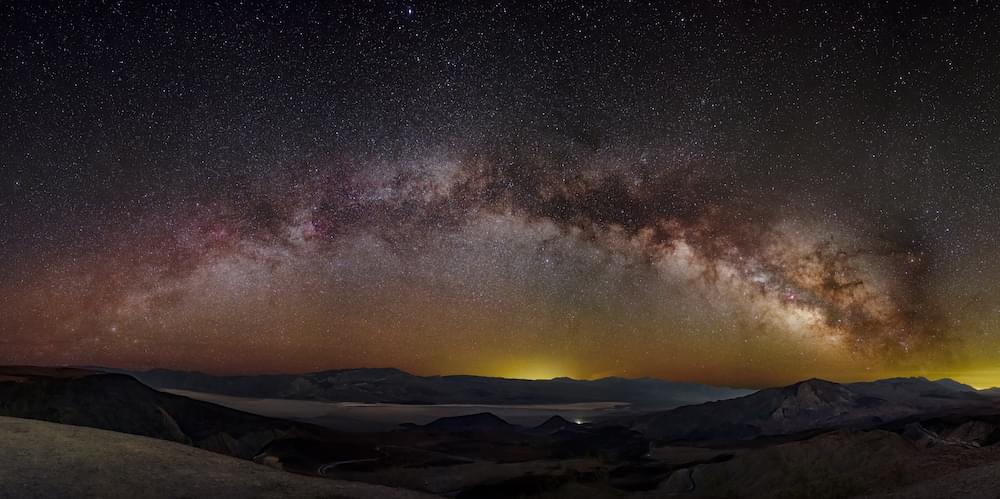

To understand the nature of our galaxy, astronomers had to look to distant island universes.
Turn your eyes toward the night sky and you will see a bright, hazy band of light cutting across the sky.
For millennia, observers speculated about the Milky Way’s true nature. The Greeks said the streak of haze in the sky was milk spurting from the breast of the goddess, Hera, Egyptians thought it was cows’ milk, and some Aboriginal Australians thought it was a river flowing through the sky.
Today, we know that we are looking along the plane of our spiral galaxy, consisting of at least 100 billion stars. But understanding the shape of the Milky Way proved elusive up until the 20th century. The problem is we can’t get a bird’s eye view of our galaxy because our solar system is buried within the galaxy. But with the invention of the telescope, photography, spectroscopy, and radio astronomy, we have uncovered the shape and size of our home galaxy — and our place among the billions of stars that make up our island universe.
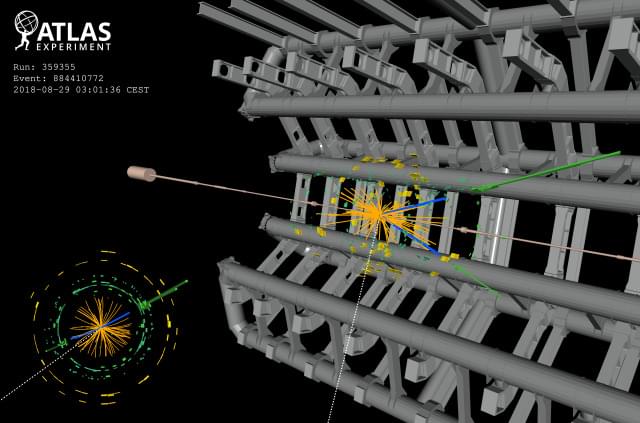
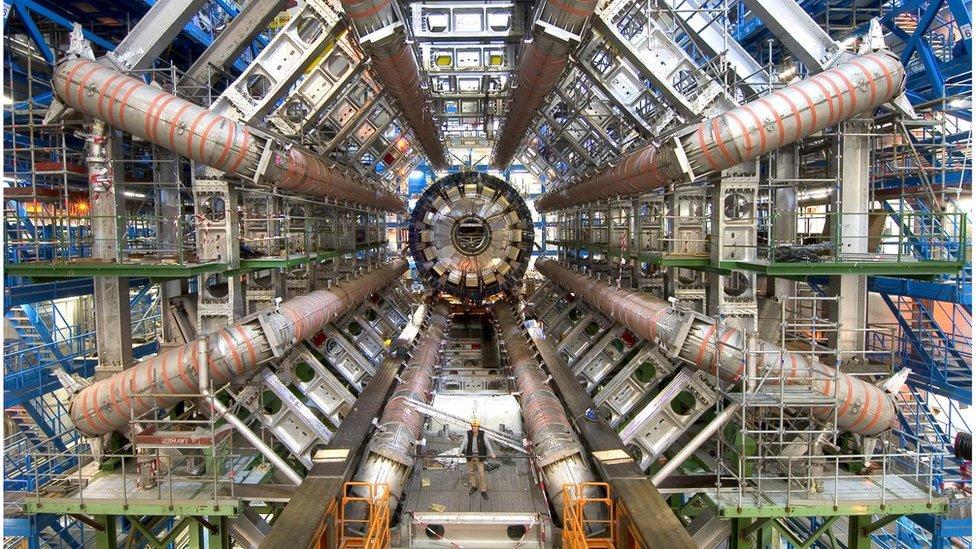
Where is all the new physics? In the decade since the Higgs boson’s discovery, there have been no statistically significant hints of new particles in data from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Could they be sneaking past the standard searches? At the recent Rencontres de Moriond conference, the ATLAS collaboration at the LHC presented several results of novel types of searches for particles predicted by supersymmetry.
Supersymmetry, or SUSY for short, is a promising theory that gives each elementary particle a “superpartner”, thus solving several problems in the current Standard Model of particle physics and even providing a possible candidate for dark matter. ATLAS’s new searches targeted charginos and neutralinos – the heavy superpartners of force-carrying particles in the Standard Model – and sleptons – the superpartners of Standard Model matter particles called leptons. If produced at the LHC, these particles would each transform, or “decay”, into Standard Model particles and the lightest neutralino, which does not further decay and is taken to be the dark-matter candidate.
ATLAS’s newest search for charginos and sleptons studied a particle-mass region previously unexplored due to a challenging background of Standard Model processes that mimics the signals from the sought-after particles. The ATLAS researchers designed dedicated searches for each of these SUSY particle types, using all the data recorded from Run 2 of the LHC and looking at the particles’ decays into two charged leptons (electrons or muons) and “missing energy” attributed to neutralinos. They used new methods to extract the putative signals from the background, including machine-learning techniques and “data-driven” approaches.